Each day, you leave digital traces of what you did, where you went, who you communicated with, what you bought, what you’re thinking of buying, and much more. This mass of data serves as a library of clues for personalized ads, which are sent to you by a sophisticated network – an automated marketplace of advertisers, publishers and ad brokers that operates at lightning speed.
The ad networks are designed to shield your identity, but companies and governments are able to combine that information with other data, particularly phone location, to identify you and track your movements and online activity. More invasive yet is spyware – malicious software that a government agent, private investigator or criminal installs on someone’s phone or computer without their knowledge or consent. Spyware lets the user see the contents of the target’s device, including calls, texts, email and voicemail. Some forms of spyware can take control of a phone, including turning on its microphone and camera.
Now, according to an investigative report by the Israeli newspaper Haaretz, an Israeli technology company called Insanet has developed the means of delivering spyware via online ad networks, turning some targeted ads into Trojan horses. According to the report, there’s no defense against the spyware, and the Israeli government has given Insanet approval to sell the technology.
Sneaking in unseen
Insanet’s spyware, Sherlock, is not the first spyware that can be installed on a phone without the need to trick the phone’s owner into clicking on a malicious link or downloading a malicious file. NSO’s iPhone-hacking Pegasus, for instance, is one of the most controversial spyware tools to emerge in the past five years.
Pegasus relies on vulnerabilities in Apple’s iOS, the iPhone operating system, to infiltrate a phone undetected. Apple issued a security update for the latest vulnerability on Sept. 7, 2023.
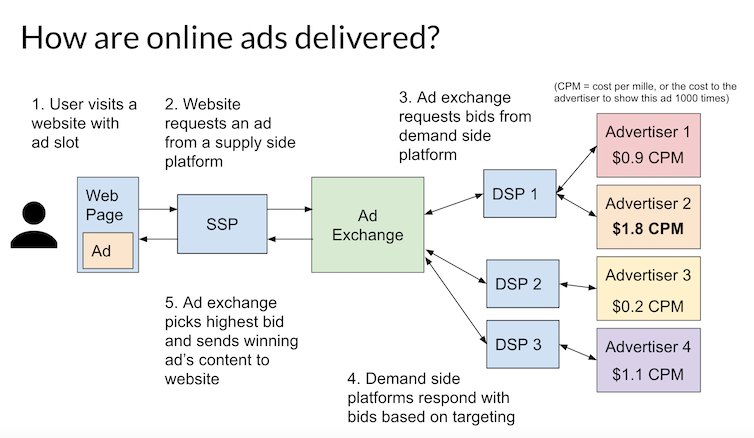
When you see an ad on a web page, behind the scenes an ad network has just automatically conducted an auction to decide which advertiser won the right to present their ad to you.
Eric Zeng, CC BY-ND
What sets Insanet’s Sherlock apart from Pegasus is its exploitation of ad networks rather than vulnerabilities in phones. A Sherlock user creates an ad campaign that narrowly focuses on the target’s demographic and location, and places a spyware-laden ad with an ad exchange. Once the ad is served to a web page that the target views, the spyware is secretly installed on the target’s phone or computer.
Although it’s too early to determine the full extent of Sherlock’s capabilities and limitations, the Haaretz report found that it can infect Windows-based computers and Android phones as well as iPhones.
Spyware vs. malware
Ad networks have been used to deliver malicious software for years, a practice dubbed malvertising. In most cases, the malware is aimed at computers rather than phones, is…
