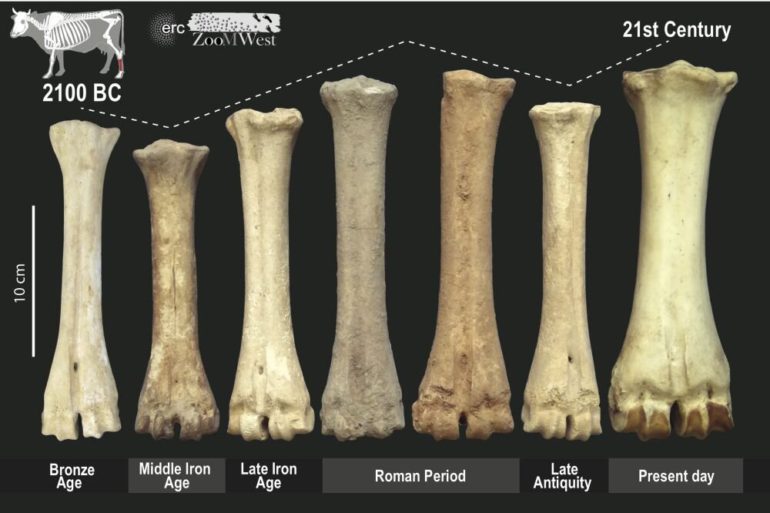
In ancient European settlements, livestock use was likely primarily determined by political structure and market demands, according to a study published February 17, 2021 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ariadna Nieto-Espinet and colleagues of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Barcelona.
Zooarchaeology—the study of animal remains from archaeological sites—has great potential to provide information on past human communities. Livestock preferences are known to have changed over time in Europe, but little is known about how much these changes are influenced by environmental, economic, or political conditions of ancient settlements.
In this study, Nieto-Espinet and colleagues gathered data from 101 archaeological sites across the northeastern Iberian Peninsula, ranging from the Late Bronze Age to Late Antiquity, a span of around 1700 years during which European cultural and agricultural practices underwent significant changes. At each site, they compared livestock remains with data on the local environment (including plant and climate data) and the economic and political conditions of the settlement.
These data show that political and economic factors were most important in determining the species distribution and body size of ancient livestock. During the Late Bronze Age and Late Antiquity, when political systems were more fragmented and food production was focused more on local markets, livestock choice was more dependent upon local environmental conditions. But during the later Iron Age and the time of the Roman Empire, the demands of a pan-Mediterranean market economy favored more changes in livestock use independent of environmental factors. Zooarchaeology is thus a vital source of information for understanding political and economic changes through time.
The authors add: “Archaeology reveals the influence of political systems on livestock practices over time.”
Archaeologists reveal human resilience in the face of climate change in ancient Turkey
More information:
Nieto Espinet A, Huet T, Trentacoste A, Guimarães S, Orengo H, Valenzuela-Lamas S (2021) Resilience and livestock adaptations to demographic growth and technological change: A diachronic perspective from the Late Bronze Age to Late Antiquity in NE Iberia. PLoS ONE 16(2): e0246201. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0246201
Provided by
Public Library of Science
Citation:
Changing livestock in ancient Europe reflect political shifts (2021, February 17)
retrieved 17 February 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-02-livestock-ancient-europe-political-shifts.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.