Human beings have a conflicted relationship with the sun. People love sunshine, but then get hot. Sweat gets in your eyes. Then there are all the protective rituals: the sunscreen, the hats, the sunglasses. If you stay out too long or haven’t taken sufficient precautions, your skin lets us you know with an angry sunburn. First the heat, then the pain, then the remorse.
Were people always this obsessed with what the sun would do to their bodies? As a biological anthropologist who has studied primates’ adaptations to the environment, I can tell you the short answer is “no,” and they didn’t need to be. For eons, skin stood up to the sun.
Skin, between you and the world
Human beings evolved under the sun. Sunlight was a constant in people’s lives, warming and guiding them through the days and seasons. Homo sapiens spent the bulk of our prehistory and history outside, mostly naked. Skin was the primary interface between our ancestors’ bodies and the world.
Human skin was adapted to whatever conditions it found itself in. People took shelter, when they could find it, in caves and rock shelters, and got pretty good at making portable shelters from wood, animal skins and other gathered materials. At night, they huddled together and probably covered themselves with fur “blankets.” But during the active daylight hours, people were outdoors and their mostly bare skin was what they had.
During a person’s lifetime, skin responds to routine exposure to the sun in many ways. The surface layer of the skin – the epidermis – becomes thicker by adding more layers of cells. For most people, the skin becomes gradually darker as specialized cells kick into action to produce a protective pigment called eumelanin.
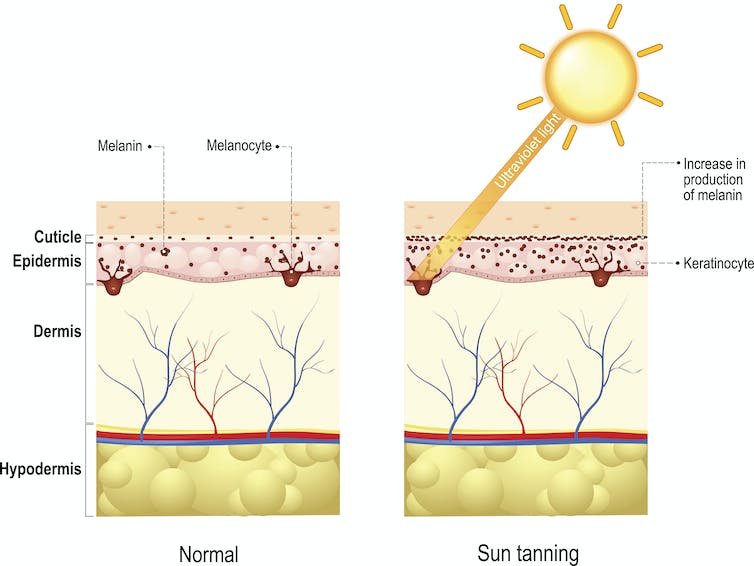
Exposure to the sun’s rays triggers production of more protective eumelanin, which also darkens the skin’s appearance.
ttsz/iStock via Getty Images Plus
This remarkable molecule absorbs most visible light, causing it to look very dark brown, almost black. Eumelanin also absorbs damaging ultraviolet radiation. Depending on their genetics, people produce different amounts of eumelanin. Some have a lot and are able to produce a lot more when their skin is exposed to sun; others have less to start out with and produce less when their skin is exposed.
My research on the evolution of human skin pigmentation has shown that the skin color of people in prehistory was tuned to local environmental conditions, primarily to local levels of ultraviolet light. People who lived under strong UV light – like you’d find near the equator – year in and year out had darkly pigmented and highly tannable skin capable of making a lot of eumelanin. People who lived under weaker and more seasonal UV levels – like you’d find in much of northern Europe and northern Asia – had lighter skin that had only limited abilities to produce protective pigment.
With only their feet to carry them, our…
