Imagine inhaling just a few drops of liquid or mist to get protected from COVID-19. That is the idea behind nasal COVID-19 vaccines, and they have been getting a lot of attention recently as a spray or liquid. These nasal vaccines would be based on the same technology as normal vaccines given by injection. But as Mayuresh Abhyankar, a University of Virginia researcher who studies infectious diseases and works on nasal vaccines, explains, vaccinating someone right where the coronavirus is likely to start its attack comes with many immunological benefits.
1. What are nasal vaccines?
Nasal vaccines are administered, as the name suggests, through the nose. More accurately called intranasal vaccines, these vaccines are liquids that can be given as a spray or through a dropper or syringe. The most common nasal vaccine is FluMist, a nasal spray that uses inactivated flu virus to protect against influenza. An intranasal vaccine could be a weakened live virus similar to FluMist, a nucleic acid vaccine like mRNA coronavirus vaccines or a protein vaccine like Hepatitis B vaccines or the CorbeVax coronavirus vaccine.
Intranasal vaccines are best suited to protect against pathogens that enter through the nose, like the flu or the coronavirus. By mimicking the first step of natural exposure to an airborne pathogen, these vaccines help train a person’s immune system at the potential place of infection. Scientists have shown that the first immune response in the respiratory tract after a person is exposed to an airborne virus can influence how sick a person gets. So in theory, intranasal vaccines could provide better protection than vaccines given through a shot in the arm.
2. How does the coronavirus infect people?
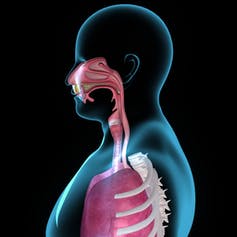
Nasal vaccines differ from intramuscular vaccines because they mimic the mechanism of infection and trigger a stronger immune response in the throat and nose specifically.
7activestudio/iStock via Getty Images
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, usually enters the body through the nose and lands on the mucus membrane at the back of the nasal passage and in the throat. The virus then enters the cells it touches, replicates and spreads.
Just underneath these cells of the mucus membrane are many types of immune cells that form what is called the mucosal immune system. Cells of the mucosal immune system are the first to identify invading coronavirus particles and start mounting a protective response.
In an unvaccinated individual, it takes about two weeks for these immune cells to build up a protective response after encountering the coronavirus. By that time, the virus can easily have infected other body parts, like the lungs, which can lead to severe disease.
Nasal vaccines follow a lot of the same steps. When you inhale a nasal vaccine, the particles land on the mucus membrane in your nasal cavity or the back of your throat, enter the cells in those places and trigger an immune…