There is always something new and exciting happening in the field of black hole research.
Albert Einstein first published his book explaining the theory of general relativity – which postulated black holes – in 1922. One hundred years later, astronomers captured actual images of the black hole at the center of the Milky Way. In a recent paper, a team of astronomers describes another exciting new discovery: the first “dormant” black hole observed outside of the galaxy.
I am an astrophysicist who has studied black holes – the most dense objects in the universe – for nearly two decades. Dormant black holes are black holes that do not emit any detectable light. Thus, they are notoriously difficult to find. This new discovery is exciting because it provides insight into the formation and evolution of black holes. This information is vital for understanding gravitational waves as well as other astronomical events.
What exactly is VFTS 243?
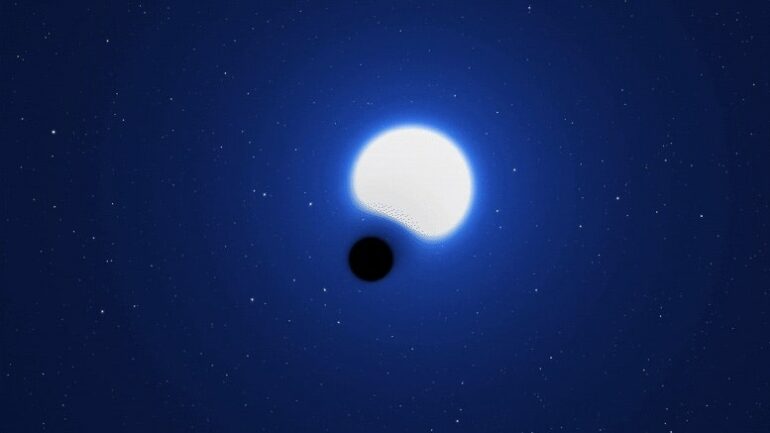
VFTS 243 is a binary system, meaning it is composed of two objects that orbit a common center of mass. The first object is a very hot, blue star with 25 times the mass of the Sun, and the second a black hole nine times more massive than the Sun. VFTS 243 is located in the Tarantula Nebula within the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way located about 163,000 light-years from Earth.
This video begins with a view of the Milky Way and zooms all the way to VFTS 243, which is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
The black hole in VFTS 243 is considered dormant because it is not emitting any detectable radiation. This is in stark contrast to other binary systems in which strong X-rays are detected from the black hole.
The black hole has a diameter of around 33 miles (54 kilometers) and is dwarfed by the energetic star, which is some 200,000 times larger. Both rapidly rotate around a common center of mass. Even with the most powerful telescopes, visually the system appears to be a single blue dot.
Finding dormant black holes
Astronomers suspect there are hundreds of such binary systems with black holes that do not emit X-rays hiding in the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Black holes are most easily visible when they are stripping matter from a companion star, a process known as “feeding”.
Feeding produces a disk of gas and dust that surrounds the black hole. When the material in the disk falls inward toward the black hole, friction heats the accretion disk to millions of degrees. These hot disks of matter emit a tremendous amount of X-rays. The first black hole to be detected in this manner is the famed Cygnus X-1 system.