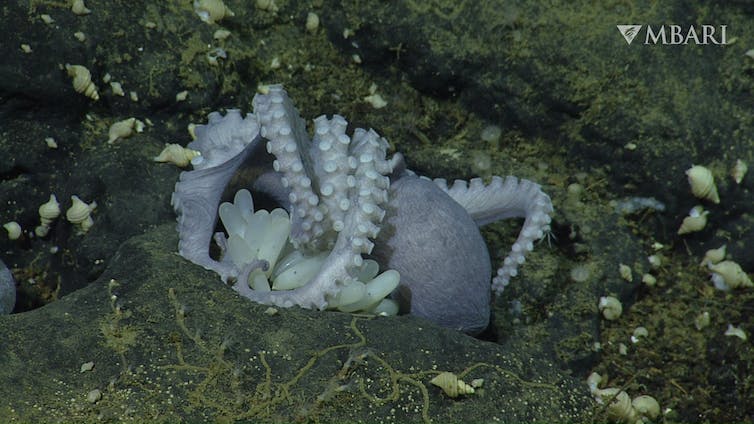
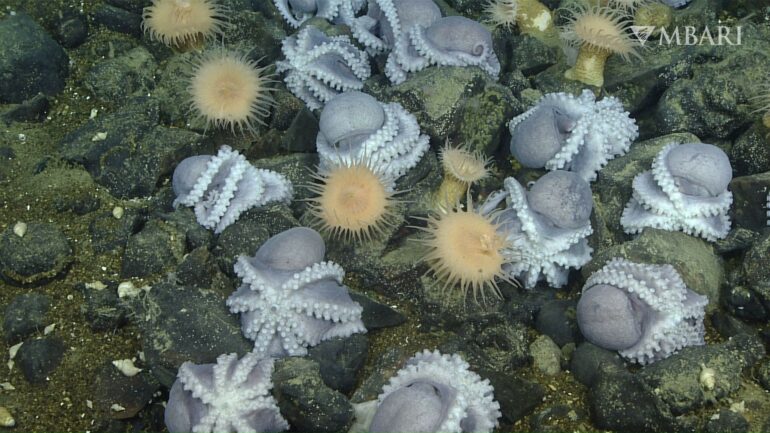
Two miles below the ocean surface off Monterey, California, warm water percolates from the seafloor at the base of an underwater mountain. It’s a magical place, especially if you’re an octopus.
In 2018, one of us, Amanda Kahn, was aboard the research vessel E/V Nautilus when scientists discovered the “Octopus Garden.” Thousands of pearl octopuses (Muusoctopus robustus) were curled up into individual balls in lines and clumps. As Nautilus Live streamed the expedition online, the world got to share the excitement of the discovery.
We now know why these amazing creatures gather at this and other underwater warm springs.
Scientists with the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute take viewers on a journey to Davidson Seamount in a video narrated by Jim Barry, an author of this article. MBARI.
In a new study involving scientists from several fields, we explain why octopuses migrate to the Octopus Garden. It’s both a mating site and a nursery where newborn octopuses develop faster than expected, giving them the best shot at survival in the deep, cold sea.
Life in the Octopus Garden
Female octopuses seek out rocky cracks and crevices where warm water seeps from the rocks. There, they vigilantly guard their broods. Subsisting off their energy reserves alone, these mothers will never eat again. Like most cephalopods, they make the ultimate sacrifice for their offspring and die after their eggs hatch.
The Octopus Garden, at the base of Davidson Seamount about 80 miles (130 kilometers) southwest of Monterey, California, is the largest of a handful of octopus nurseries recently discovered in the Eastern Pacific. Many have been found near hydrothermal springs where warm water seeps from the seafloor.
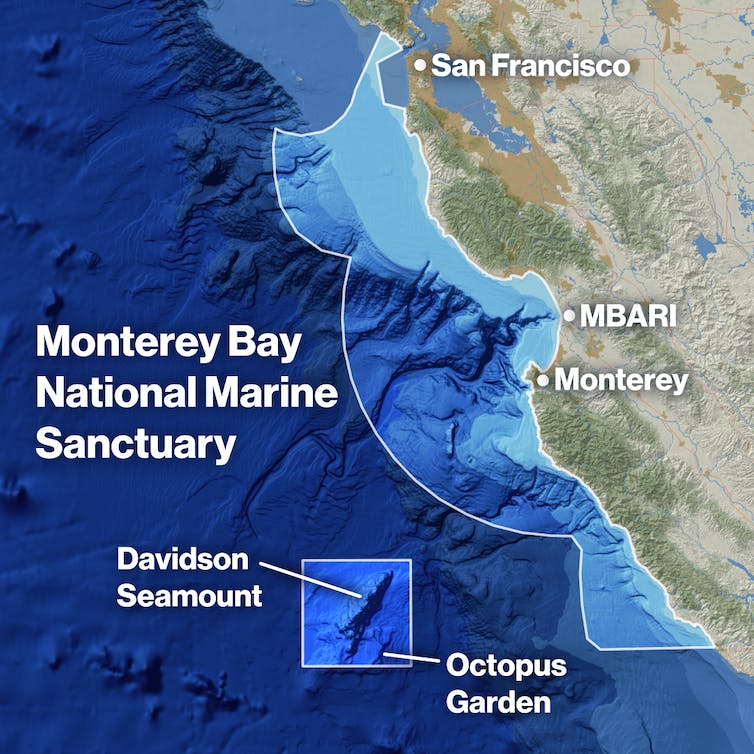
The Octopus Garden is about 2 miles deep near Davidson Seamount, an inactive volcano off the Central California coast. It is inside the Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary.
Illustration by Madeline Go/MBARI, basemap created via ArcGIS Online, sources: Esri, USGS | Esri, GEBCO, DeLorme, NaturalVue | California State Parks, Esri, HERE, Garmin, SafeGraph, FAO, METI/NASA, USGS, Bureau of Land Management, EPA, NPS
We wanted to know what makes these environments so appealing for nesting octopuses.
To solve this mystery, we assembled geologists, biologists and engineers. Using Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute’s deep-sea robots and sensors, we studied and mapped the Octopus Garden during several visits over three years to examine the links between thermal springs and breeding success for pearl octopuses. We found nearly 6,000 nests in a 6-acre (2.5-hectare) area, suggesting more than 20,000 octopuses occupy this site.
A time-lapse camera that kept watch over a group of nesting mothers for six months opened a window into the dynamic life in the Octopus Garden.

