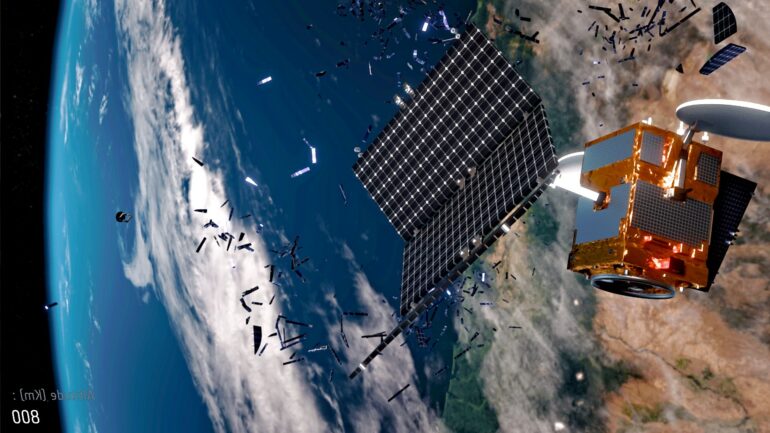
On Nov. 15, 2021, U.S. officials announced that they had detected a dangerous new debris field in orbit near Earth. Later in the day, it was confirmed that Russia had destroyed one of its old satellites in a test of an anti-satellite weapon. Wendy Whitman Cobb is a space security researcher. She explains what these weapons are and why the debris they create is a problem now – and in the future.
What do we know?
Russia launched an anti-satellite test that destroyed one of its older satellites. The satellite broke up and created thousands of pieces of debris in orbit, ranging in size from tiny specks up to pieces a few feet across. This space junk will linger in orbit for years, potentially colliding with other satellites as well as the International Space Station. The space station crew has already had to shelter in place as they passed near the debris cloud.

Many anti-satellite weapons are missiles launched from the ground, like this U.S. ASM-135 ASAT.
Lorax via WikimediaCommons, CC BY-SA
What’s an anti-satellite weapon?
Anti-satellite weapons, commonly referred to as ASATs, are any weapon that can temporarily impair or permanently destroy an orbiting satellite. The one that Russia just tested is known as a direct ascent kinetic anti-satellite weapon. These are usually launched from the ground or from the wings of an airplane and destroy satellites by running into them at high speeds.
A similar weapon type, called co-orbital anti-satellite weapons, are first launched into orbit and then change direction to collide with the targeted satellite from space.
A third type, non-kinetic anti-satellite weapons, use technology like lasers to disrupt satellites without physically colliding with them.
Space agencies have been developing and testing anti-satellite weapons since the 1960s. To date, the U.S., Russia, China and India have demonstrated the ability to attack satellites in orbit that support services like GPS, communications and weather forecasting.
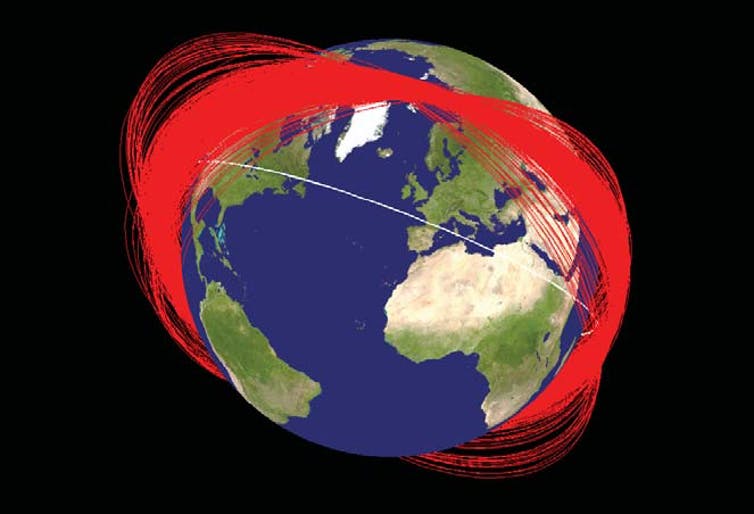
Debris from a single destroyed satellite can spread out rapidly, as seen in this image showing the orbits of debris from a Chinese satellite one month after it was destroyed in 2007.
NASA Orbital Debris Program Office via WikimediaCommons
Why is debris a problem?
Regardless of the cause, space debris is a serious problem.
Larger pieces are easier to track and avoid but it’s difficult to track pieces smaller than 4 inches (10 centimeters). Even small debris can still pose a major threat though. Space debris is often traveling faster than 17,000 mph around the Earth. At that speed, pieces of debris could destroy any spacecraft or satellite it collided with. In the 1980s, a Soviet satellite broke up as a result of a suspected debris strike.
More worrisome is the danger debris poses to crewed space missions. In July 2021, one of the International Space Station’s robotic arms was struck by a piece of…
