A research group led by Professor Toshihiro Yamada from the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Hokkaido University, found an exceptionally well-preserved fossil of a Wataria parvipora forest which was almost exclusively accompanied by fossils of Byttneriophyllum leaves. Their findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Complete plant fossils are seldom found as a single piece, as wood, leaves, flowers, fruits, seeds, or pollen detach easily from plants. This results in leaves and trunks having separate scientific names. Putting together the different parts to reveal the complete plant is like putting together a jigsaw puzzle. Connecting these dots and reconstructing plants is important to establish their taxonomic identity.
In 1994, Kiso River (in Minokamo City, Gifu Prefecture) underwent a historic drought, in the process of which 400 in situ fossilized tree stumps surfaced. While most of the stumps have since been submerged, the team examined 137 stumps, of which 130 were identified as Wataria parvipora.
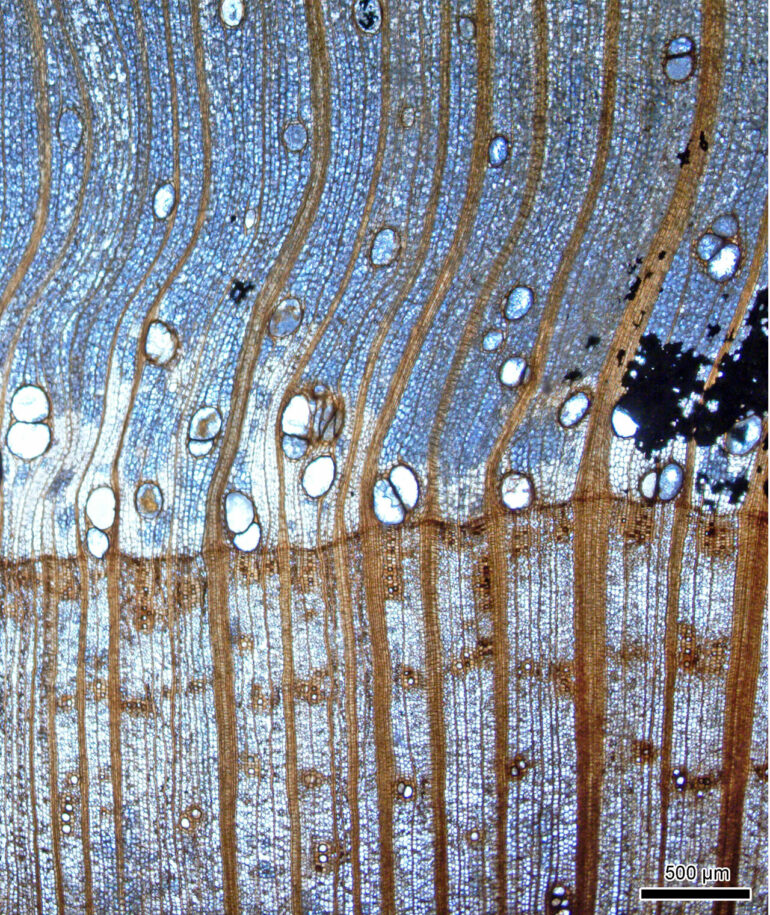
“Wataria is a wood-fossil, recognized by its distinctive growth rings, abundant parenchyma rays and lack of resin canals. In the 2,000 m2fossil site, these stumps accounted for 95% of the tree remains, indicating that we discovered a forest predominantly of this species,” says Yamada.
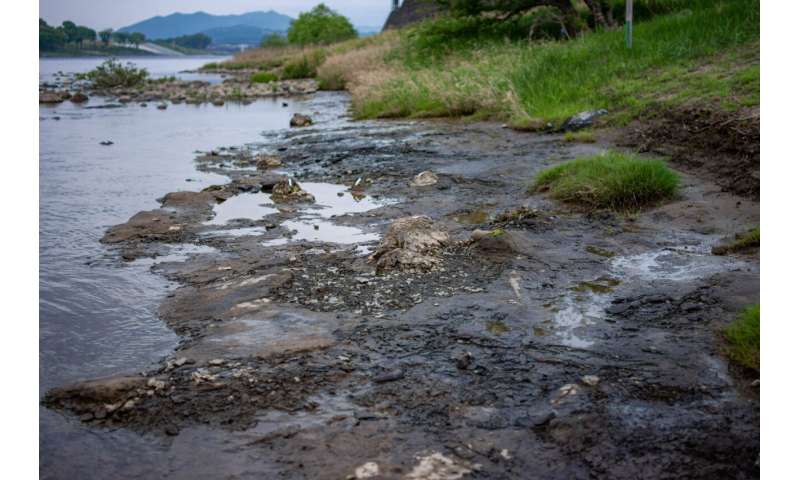

Exposed riverbed from where the fossils were found. © Toshihiro Yamada
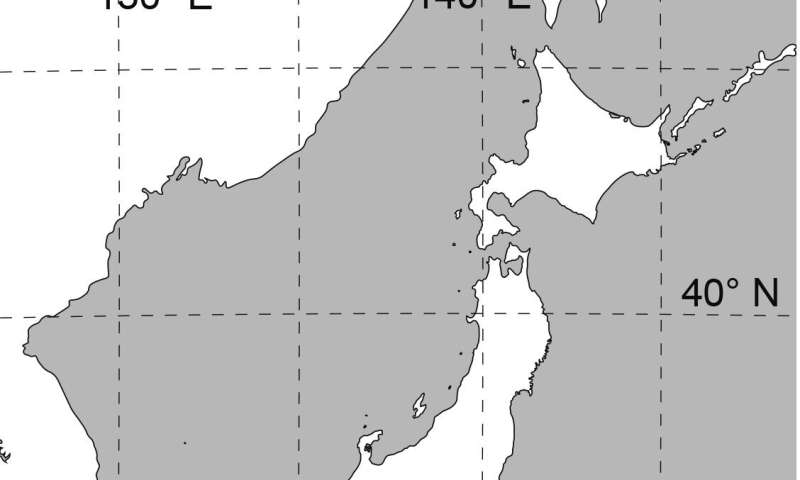
A fossil forest of Wataria was found in the Gifu Prefecture, on the bed of the Kiso River. Location of study site in Japan. © Nishino et al., Scientific Reports, June 22, 2023
The team also found that the stumps were exclusively covered by a bed of one specific kind of leaf. Byttneriophyllum tiliifolium is a leaf-fossil species belonging to the mallow family (which includes cotton, cacao and durian). Fossils of this leaf were widely distributed throughout Eurasia during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs and the discovery of the Wataria fossil forest indicates that Byttneriophyllum tiliifolium are the leaves of Wataria.
“We found that 98% of the fossil-leaves found at the site belonged to Byttneriophyllum, strongly indicating that they were shed from the parent trees. We could see that the leaves were deposited para-autochthonously on the forest floor—they got fossilized where they fell,” Yamada elaborated.
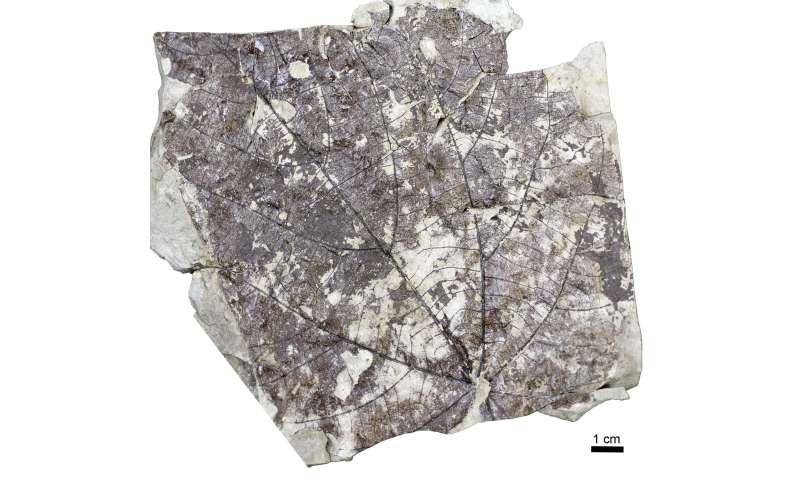

Surface view of the fossil leaf Byttneriophyllum tiliifolium which was found abundantly in the fossil forest, indicating a strong link to Wataria parvipora. © Nishino et al., Scientific Reports, June 22, 2023
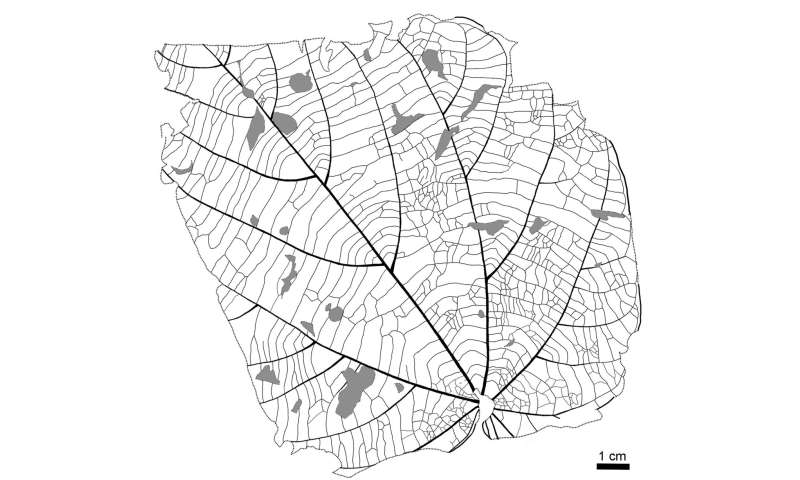
Line drawing of one of the Byttneriophyllum tiliifolium leaves found abundantly in the fossil forest. © Nishino et al., Scientific Reports, June 22, 2023
Research by other groups has shown that the fossil fruit Banisteriaecarpum giganteum is related to Byttneriophyllum tiliifolium. Future research will focus on searching for Banisteriaecarpum giganteum in Japan, as this discovery would provide strong evidence that all three are part of the same species.
More information:
Megumi Nishino et al, An exceptionally well-preserved monodominant fossil forest of Wataria from the lower Miocene of Japan, Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-37211-z
Provided by
Hokkaido University
Citation:
Exquisitely preserved fossil forest from Japan helps reconstruct a whole Eurasia plant from the late Miocene (2023, July 21)