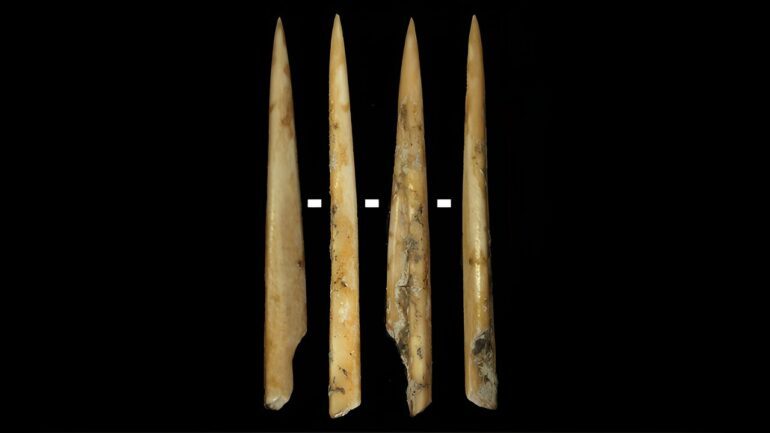
A study led by researchers from the UAB and the CSIC has revealed that the earliest Neolithic groups to settle some 7,000 years ago in the Pyrenean site of Coro Trasito (Tella, Huesca) used species selection strategies to manufacture their tools made out of bone and chose deer for the projectile tips.
The study, published in the journal PLoS ONE, applied for the first time in a Neolithic site an innovative combination of methods to obtain these results.
The study was coordinated by the research group EarlyFoods from the Department of Prehistory of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) and ICTA-UAB, under the framework of the European project ChemArch. Also involved in the study were researchers from the High Mountain Archaeology Research Group (GAAM, UAB and IMF-CSIC), the General Council of Aragón, and the University of Copenhagen.
The research delved deeper into the relationship between the species selected for the manufacturing of artifacts and their function by applying archaezoological, use-wear and paleoproteomic analyses to some 20 ancient Neolithic bone artifacts found at Coro Trasito, a site in the Central Pyrenees located 1,548 meters above sea level.
The study is one of the few so far to combine use-wear, archaeozoology and paleoproteomics in archaeological material and the first to do so in bone artifacts from the ancient Neolithic.
“This combination has made it possible to discover nuances that would otherwise go unnoticed and to add new layers of knowledge by evaluating the same data from multiple perspectives,” explains Maria Saña, UAB researcher and coordinator of the study.
The analyses showed that the groups that inhabited the site 7,000 years ago chose sheep and goat bones for the production of bone tips to handle vegetables, but also used cervid bones (deer and roe deer) for a wider variety of artifacts. For the projectile tips identified, they chose deer bones.
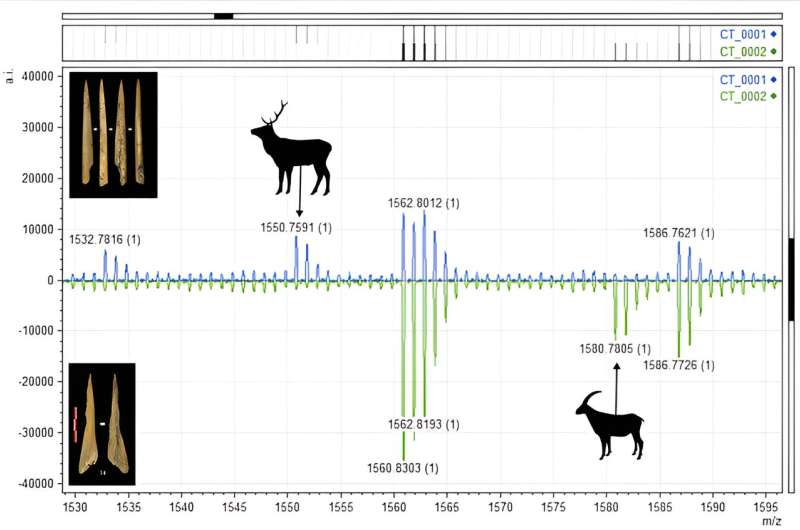
Illustration of the mass spectrometry analysis graph that has allowed the taxonomic identification of the species (cervids or goats) of the tools analysed. © PLOS ONE (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306448
In contrast to other studies based on the morphological study of artifacts, which suggest that sheep and goats were the species most commonly used in the production of bone tools, the study found that deer as well as sheep and goats were more equally selected for tool manufacturing.
This greater species balance observed at Coro Trasito and the use of only deer bones for projectile tips leads the researchers to consider that this animal may have played a prominent role in ancient Neolithic society.
“Obtaining long bones from deer, probably through hunting, requires more effort than using long bones from domesticated animals,” says Jakob Hansen, first author of the study and predoctoral researcher in the Department of Prehistory at the UAB.
“This is particularly interesting because of the large number of cervid bone tools identified compared to the number of cervid observed in the untouched bone deposits. This selection could be due, in part, to the properties of the bone, but also to the beliefs and values associated with this animal species.
“In any case, further research at other sites with the same combination of methods that we have applied here is required to explore this hypothesis,” he adds.
Methodological strength
The researchers highlight the methodological strength of the study. Previously, based on the study of morphological characteristics, deer bone artifacts had been detected in other Neolithic sites of the Iberian Peninsula, but this is the first time that the species were taxonomically identified and a strategy in the selection of the animals was directly evidenced.
In addition to the classical approach of archaeozoology, use-wear analysis was added to identify the specific uses of the tools and the materials with which they were produced by high-resolution microscopy, and taxonomic identification, carried out by mass spectrometry (ZooMS) through the evaluation of peptide biomarkers.
“Future research could benefit from the integration of these three approaches for a better understanding of the relationship between artifact types and the species selected for their production. This study is only the tip of the iceberg,” concludes Ignacio Clemente, researcher at GAAM and at the Milà i Fontanals Institution for Research in the Humanities (IMF-CSIC) who also coordinated the study.
More information:
Jakob Hansen et al, Combining traceological analysis and ZooMS on Early Neolithic bone artefacts from the cave of Coro Trasito, NE Iberian Peninsula: Cervidae used equally to Caprinae, PLOS ONE (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306448
Provided by
Autonomous University of Barcelona
Citation:
Early Pyrenean Neolithic groups applied species selection strategies to produce bone artifacts, reveals study (2024, July 11)



