Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier got its nickname the “Doomsday Glacier” for its potential to flood coastlines around the world if it collapsed. It is already contributing about 4% of annual sea-level rise as it loses ice, and one theory suggests the glacier could soon begin to collapse into the ocean like a row of dominoes.
But is that kind of rapid collapse really as likely as feared? A new study of Thwaites Glacier’s susceptibility to what’s known as marine ice cliff instability offers some hope. But the findings don’t mean Thwaites is stable.
Polar scientist Mathieu Morlighem, who led the study, explains the results.
Why is the Thwaites Glacier so important?
Thwaites Glacier drains a huge area of Antarctica’s ice sheet – about 74,000 square miles (192,000 square kilometers), an expanse bigger than Florida. If a snowflake falls within that drainage system, it will eventually end up as part of an iceberg in the ocean off Thwaites.
What we are seeing with Thwaites Glacier right now is a disaster in slow motion.
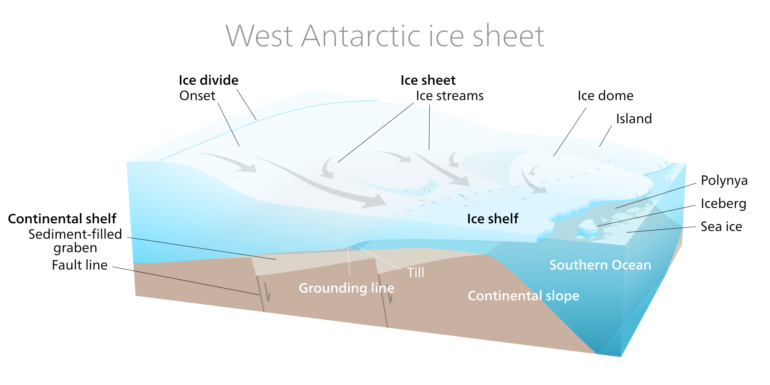
The bedrock under Thwaites Glacier sits below sea level and slopes downward going inland, so the glacier gets deeper toward the interior of the ice sheet. Once the glacier begins losing more ice than it gains from new snowfall and starts to retreat, it’s very hard to slow it down because of this slope. And Thwaites is already retreating at an accelerating rate as the climate warms.
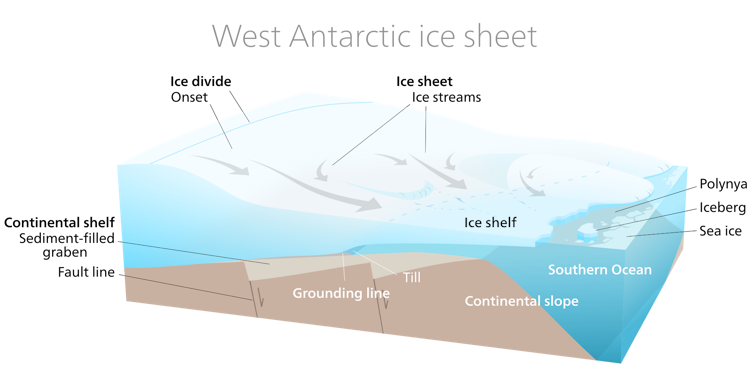
A cross-section showing an ice shelf and inward-sloping bedrock.
Kelvinsong via Wikimedia, CC BY-SA
Thwaites Glacier holds enough ice to raise global sea level by more than 2 feet (0.65 meters). Once Thwaites starts to destabilize, it also will destabilize neighboring glaciers. So, what happens to Thwaites affects all of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, and that affects sea-level rise along coastlines everywhere.
What is marine ice cliff instability?
Marine ice cliff instability is a relatively new concept proposed by scientists in the past decade.
Many of the glaciers around Antarctica have huge floating extensions called ice shelves that buttress the glacier and slow its ice flow into the ocean. With the climate warming, we have seen some of these floating extensions collapse, sometimes very rapidly, in the span of a few weeks or months.
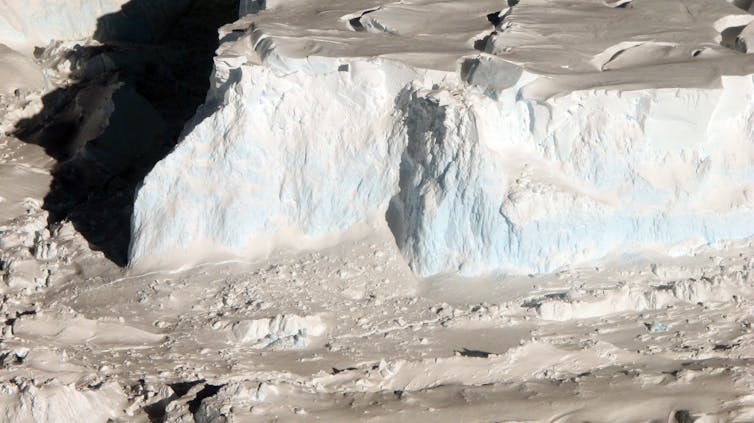

The front of Thwaites’ floating ice shelf is over 200 feet (60 meters) tall in places. It becomes higher closer to land.
James Yungel/NASA Icebridge 2012
If Thwaites’ ice shelf were to collapse, it would expose a very tall ice cliff facing the ocean along its 75-mile (120-kilometer) front. There is only so much force that ice can sustain, so if the cliff is too tall, it will collapse into the ocean.
Once that happens, a new ice cliff farther back would be exposed, and the new cliff would be even taller because it is farther inland. The theory of marine ice cliff instability suggests that if the cliffs collapse…