Scientists from the University of Sheffield have discovered a new sensory capability in bacteria which could transform treatments for bacterial infections.
It was previously thought that bacteria are too small to directly sense differences in chemical concentration. However, contrary to decades of established scientific belief, a new study has shown bacteria can in fact directly sense their chemical environment across the length of their cell bodies with an unprecedented degree of precision.
The research, published today in Nature Microbiology, is a key step towards the development of innovative treatments that manipulate bacterial motility to enhance antibiotic efficacy.
The study focused on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which has been listed as a priority pathogen by the World Health Organization due to its ability to cause highly antibiotic resistant infections in humans.
Senior author of the study, Dr. William Durham, Senior Lecturer in Biological Physics at the University of Sheffield’s Department of Physics and Astronomy, said, “In principle, cells can figure out whether they are moving towards or away from a nutrient source in two different ways.
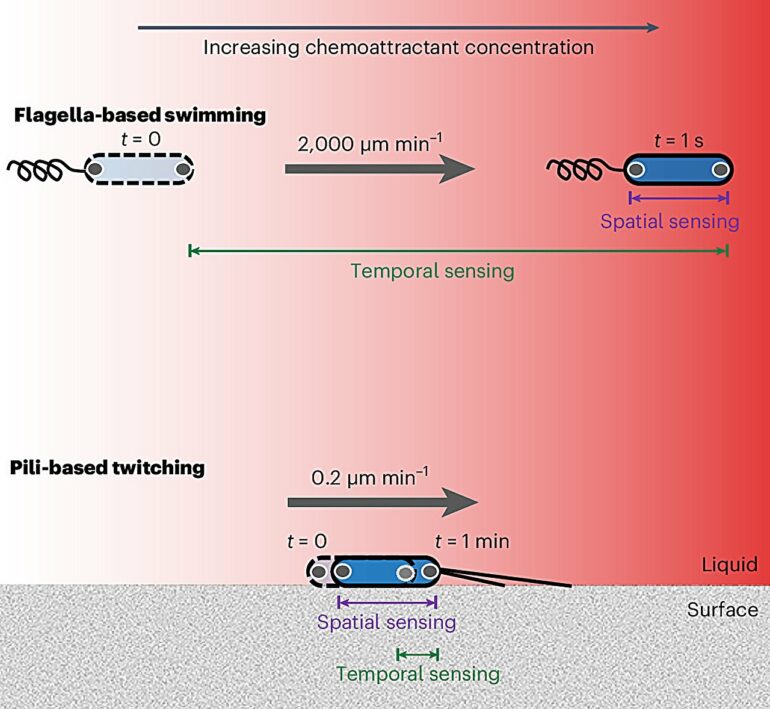
“First, they can wander randomly and measure if the concentration increases or decreases over time. Alternatively, cells can measure changes in concentration over the length of their bodies, allowing them to directly move towards the source. Our research demonstrates that bacteria can do the latter, which was previously thought beyond their capabilities due to their tiny size.
“Bacteria then use this information to navigate across surfaces toward chemical sources using tiny grappling hooks called pili.”
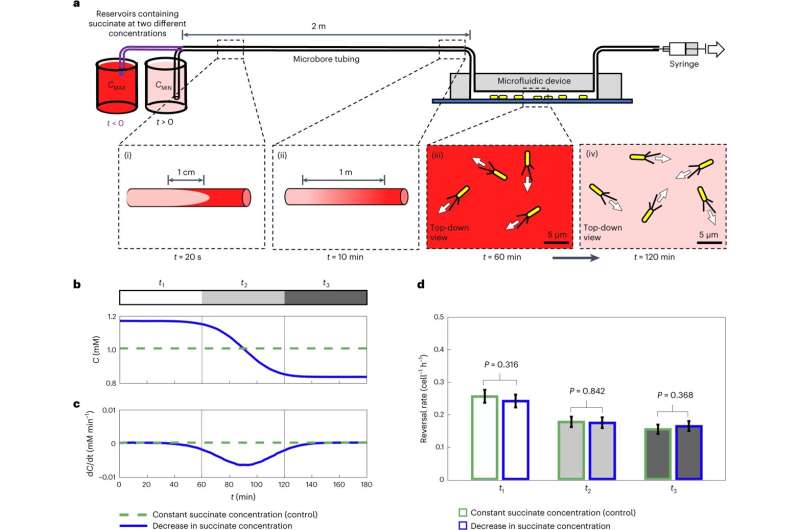
Temporal changes in concentration do not induce a chemotactic response in surface-attached P. aeruginosa. © Nature Microbiology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41564-024-01729-3, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01729-3
By developing a combination of innovative microfluidic experiments and novel P. aeruginosa strains whose motility systems were engineered so they could be directly visualized using powerful microscopes, the researchers mapped out how individual cells responded to precise changes in nutrient concentrations. They uncovered that these cells can compare nutrient concentrations along the length of their cell bodies—a phenomenon termed “spatial sensing.”
Dr. Jamie Wheeler, a postdoctoral researcher in the University of Sheffield’s Department of Physics and Astronomy, and lead author of the study, said, “This work overturns our understanding of how bacteria navigate and sense their environment. As such, it sheds new light on how bacteria could direct their motility during human infection and potentially how it could be manipulated by different clinical treatments.”
The discovery means that bacteria do not necessarily have to move to sense changes in their chemical environment, suggesting that the densely packed bacteria within localized infections can use this information to guide their behavior. This ability raises new questions about the mechanisms that bacteria use to perform these microscopic measurements and how they could be manipulated by antimicrobial treatments.
Dr. Wheeler continued, “As is often the case, answering one question has raised a whole new set of unknowns. Exciting new experiments are already planned to continue writing this new chapter in our understanding of how bacteria navigate through their environment.”
More information:
Wheeler, J. H. R. et al. Individual bacterial cells can use spatial sensing of chemical gradients to direct chemotaxis on surfaces, Nature Microbiology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41564-024-01729-3. www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01729-3
Provided by
University of Sheffield
Citation:
New discovery of how bacteria navigate their environment could change how we treat infection (2024, September 2)