When I started my research on the Samuel George Morton Cranial Collection, a librarian leaned over my laptop one day to share some lore. “Legend has it,” she said, “John James Audubon really collected the skulls Morton claimed as his own.” Her voice was lowered so as not to disturb the other scholars in the hushed archive.
As my work progressed, I uncovered no evidence to substantiate her whispered claim. Audubon had collected human skulls, several of which he then passed on to Morton. But birds and ornithology remained Audubon’s passion.
Nevertheless, the librarian’s offhanded comment has proven useful – a touchstone of sorts that continues to remind me of the controversy and confusion long surrounding the Morton Collection.
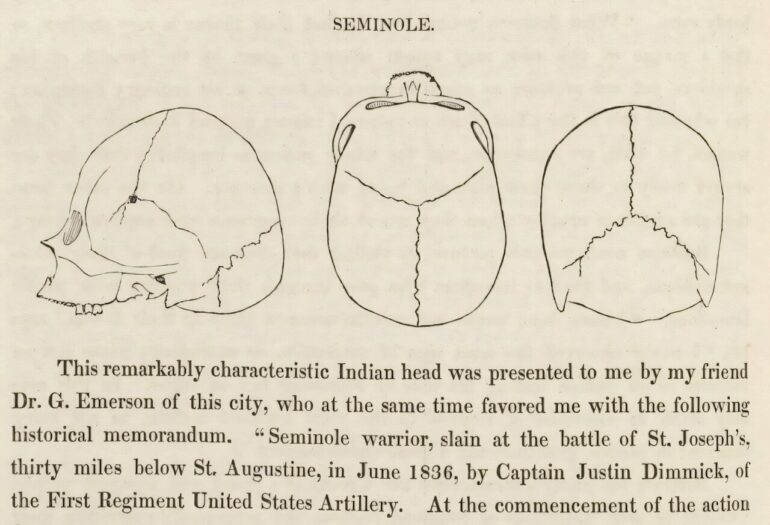
Morton was a physician and naturalist who lived in Philadelphia from 1799 until the end of his life in 1851. A lecture he delivered to aspiring doctors at the Philadelphia Association for Medical Instruction outlined the reasons for his cranial compulsion:
“I commenced the study of Ethnology in 1830; in which year, having occasion to deliver an introductory lecture on Anatomy, it occurred to me to illustrate the difference in the form of the skull as seen in the five great races of men … When I sought the materials for my proposed lecture, I found to my surprise that they could be neither bought nor borrowed.”
He would go on to acquire almost 1,000 human skulls.
Morton used these skulls to advance an understanding of racial differences as natural, easily categorizable and able to be ranked. Big-brained “Caucasians,” he argued in the 1839 publication “Crania Americana,” were far superior to small-skulled American Indians and even smaller-skulled Black Africans. Many subsequent scholars have since thoroughly debunked his ideas.
Certainly, condemnation of Morton as a scientific racist is warranted. But I find this take represents the man as a caricature, his conclusions as foregone. It provides little insight into his life and the complicated, interesting times in which he lived, as I detail in my book “Becoming Object: The Sociopolitics of the Samuel George Morton Cranial Collection.”
My research demonstrates that studies of skulls and diseases undertaken by Morton and his medical and scientific colleagues contributed to an understanding of U.S. citizenship that valued whiteness, Christianity and heroic masculinity defined by violence. It is an exclusionary idea of what it means to be American that persists today.
Yet, at the same time, the collection is an unintended testament to the diversity of the U.S. population during a tumultuous moment in the nation’s history.

Samuel Morton wasn’t a lone voice on the fringe of medicine.
‘Memoir of the life and scientific labors of Samuel George Morton’ by Henry S. Patterson, CC BY
Men of science and medicine
As a bioarchaeologist who has studied the Morton Collection for many years, I have…