In 2024, space exploration dazzled the world.
NASA’s Europa Clipper began its journey to study Jupiter’s moon Europa. SpaceX’s Starship achieved its first successful landing, a critical milestone for future deep space missions. China made headlines with the Chang’e 6 mission, which successfully returned samples from the far side of the Moon. Meanwhile, the International Space Station continued to host international crews, including private missions like Axiom Mission 3.
As an aerospace engineer, I’m excited for 2025, when space agencies worldwide are gearing up for even more ambitious goals. Here’s a look at the most exciting missions planned for the coming year, which will expand humanity’s horizons even further, from the Moon and Mars to asteroids and beyond:
Scouting the lunar surface with CLPS
NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services, or CLPS, initiative aims to deliver science and technology payloads to the Moon using commercial landers. CLPS is what brought Intuitive Machines’ Odysseus lander to the Moon in February 2024, marking the first U.S. Moon landing since Apollo.
In 2025, NASA has several CLPS missions planned, including deliveries by companies Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and Firefly Aerospace.
These missions will carry a variety of scientific instruments and technology demonstrations to different lunar locations. The payloads will include experiments to study lunar geology, test new technologies for future human missions and gather data on the Moon’s environment.
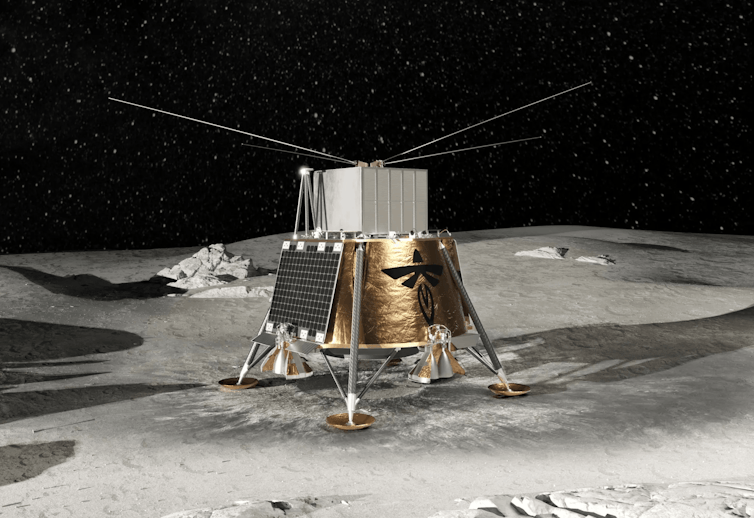
An illustration of Firefly’s Blue Ghost Lander, which will bring scientific instruments to the lunar surface.
NASA/Firefly Aerospace
Surveying the sky with SPHEREx
In February 2025, NASA plans to launch the Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, or SPHEREx, observatory. This mission will survey the sky in near-infrared light, which is a type of light that is invisible to the naked eye but that special instruments can detect. Near-infrared light is useful for observing objects that are too cool or too distant to be seen in visible light.
SPHEREx will create a comprehensive map of the universe by surveying and collecting data on more than 450 million galaxies along with over 100 million stars in the Milky Way. Astronomers will use this data to answer big questions about the origins of galaxies and the distribution of water and organic molecules in stellar nurseries – where stars are born from gas and dust.
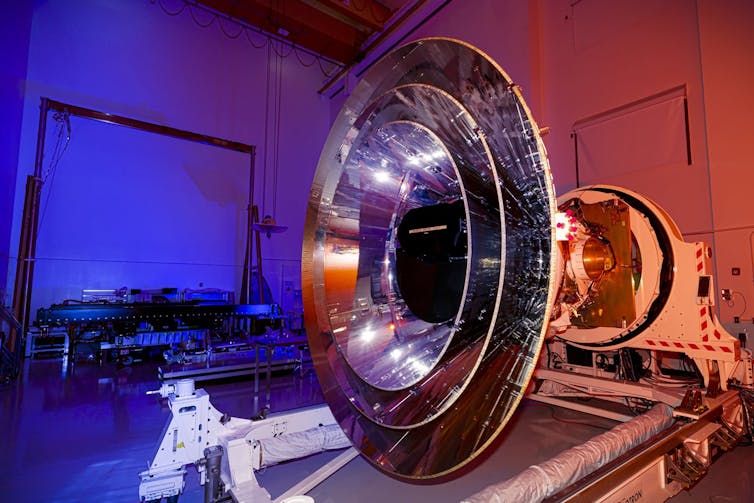
NASA’s SPHEREx observatory will make the most colorful cosmic map.
NASA/BAE Systems
Studying low Earth orbit with Space Rider
The European Space Agency, or ESA, plans to conduct an orbital test flight of its Space Rider uncrewed spaceplane in the third quarter of 2025. Space Rider is a reusable spacecraft designed to carry out various scientific experiments in low Earth orbit.
These…



