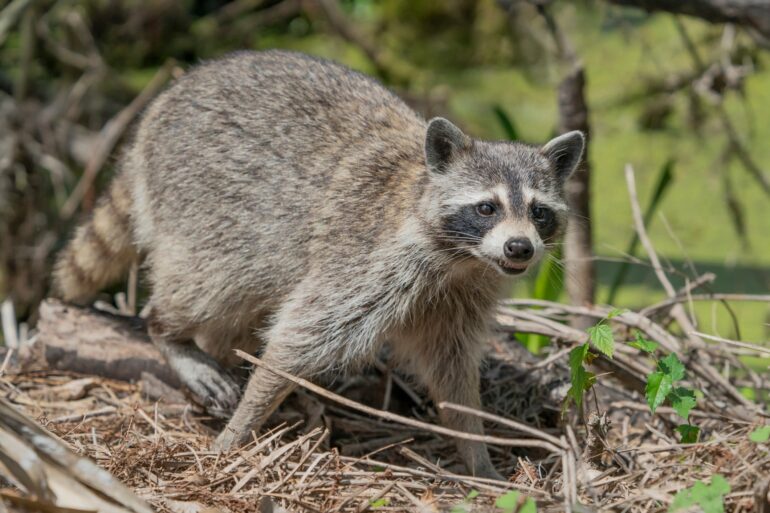
When a curious raccoon broke into an Ashland, Virginia, liquor store in December 2025, sampled the stock and passed out on the bathroom floor, the story went viral within minutes. The local animal shelter’s Facebook post was picked up by national and international outlets and quickly inspired raccoon-themed cocktails, “trashed panda” merchandise and even a cameo on “Saturday Night Live.”
For me, the story hit close to home. The store that hosted this inebriated bandit sits just blocks from the small behavioral neuroscience laboratory where I began investigating raccoon brains about 15 years ago. Although the so-called drunken raccoon made questionable decisions after breaking into the liquor store, the species – Procyon lotor – is known for its impressive intelligence, curiosity and problem-solving skills.
Despite being one of the most intriguing mammals living alongside humans, raccoons have avoided the scientific spotlight. Why aren’t more neuroscientists and psychologists studying raccoons? What have researchers missed about the mammalian brain by focusing on rodents instead?
Someone had a good time.
Why raccoons aren’t lab staples
In the U.S., it is estimated that laboratories use more than 100 million rodents, including mice and rats, each year. Rodents are ideal for research because they reproduce easily and adapt well to confinement. Scientists have tailored extensive research tools to study them. Long before rats dominated psychology labs, raccoons were actually a leading candidate for animal models of problem-solving and intelligence.
That ended when scientists realized they’d met their cognitive match. In one study, researchers reported that all raccoon participants escaped through the laboratory ventilation system.
Unsurprisingly, scientists promptly shifted to rodents. Practicality – not scientific suitability – ultimately crowned the rat as king of the laboratory. I have studied rats for decades, and I can confirm that none have ever disappeared into the ceiling.
Neither pet nor pest
Humans have an ambivalent relationship with raccoons. They appear too wild to be domesticated, too endearing to be treated purely as pests and too ubiquitous to be considered exotic wildlife. Even President Calvin Coolidge, who famously received a raccoon intended for the dinner table from a supporter in Mississippi, ended up keeping it as a beloved White House pet.
And the role confusion continues today with glimpses of humanlike behaviors in raccoons as they enter our living spaces. One report described raccoons interacting with playground equipment at a child care center on Canada’s west coast in ways similar to human children, and even breaking into classrooms as if they were auditing the morning lesson.

Raccoons know how to get around.
RLO’Leary/Moment Open
Inspired by Montessori education…