Nations around the world are rapidly developing high-energy laser weapons for military missions on land and sea, and in the air and space. Visions of swarms of small, inexpensive drones filling the skies or skimming across the waves are motivating militaries to develop and deploy laser weapons as an alternative to costly and potentially overwhelmed missile-based defenses.
Laser weapons have been a staple of science fiction since long before lasers were even invented. More recently, they have also featured prominently in some conspiracy theories. Both types of fiction highlight the need to understand how laser weapons actually work and what they are used for.
How lasers work
A laser uses electricity to generate photons, or light particles. The photons pass through a gain medium, a material that creates a cascade of additional photons, which rapidly increases the number of photons. All these photons are then focused into a narrow beam by a beam director.
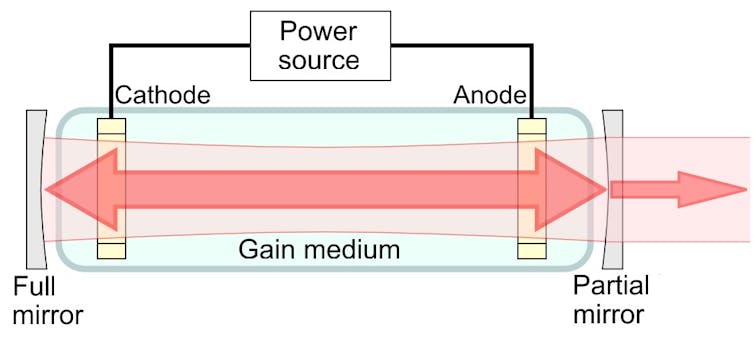
Lasers work by turning electricity into photons and bouncing them back and forth between two mirrors through a special gain material that creates a cascade of many more photons.
Shigeru23/Wikimedia, CC BY-SA
In the decades since the first laser was unveiled in 1960, engineers have developed a variety of lasers that generate photons at different wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, from infrared to ultraviolet. The high-energy laser systems that are finding military applications are based on solid-state lasers that use special crystals to convert the input electrical energy into photons. A key aspect of high-power solid-state lasers is that the photons are created in the infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and so cannot be seen by the human eye.
When it interacts with a surface, a laser beam generates different effects based on its photon wavelength, the power in the beam and the material of the surface. Low-power lasers that generate photons in the visible part of the spectrum are useful as light sources for pointers and light shows at public events. These beams are of such low power that they simply reflect off a surface without damaging it.
Higher-power laser systems are used to cut through biological tissue in medical procedures. The highest-power lasers can heat, vaporize, melt and burn through many different materials and are used in industrial processes for welding and cutting.
In addition to the power level of the laser, the ability to deliver these various effects is determined by the distance between the laser and its target.
Laser weapons
Based in part on the progress made in high-power industrial lasers, militaries are finding an increasing number of uses for high-energy lasers. One key advantage for high-energy laser weapons is that they provide an “infinite magazine.” Unlike traditional weapons such as guns and cannons that have a finite amount of ammunition, a high-energy laser can keep firing as long…



