The legacy of the medieval Swahili civilization is a source of extraordinary pride in East Africa, as reflected in its language being the official tongue of Kenya, Tanzania and even inland countries like Uganda and Rwanda, far from the Indian Ocean shore where the culture developed nearly two millennia ago.
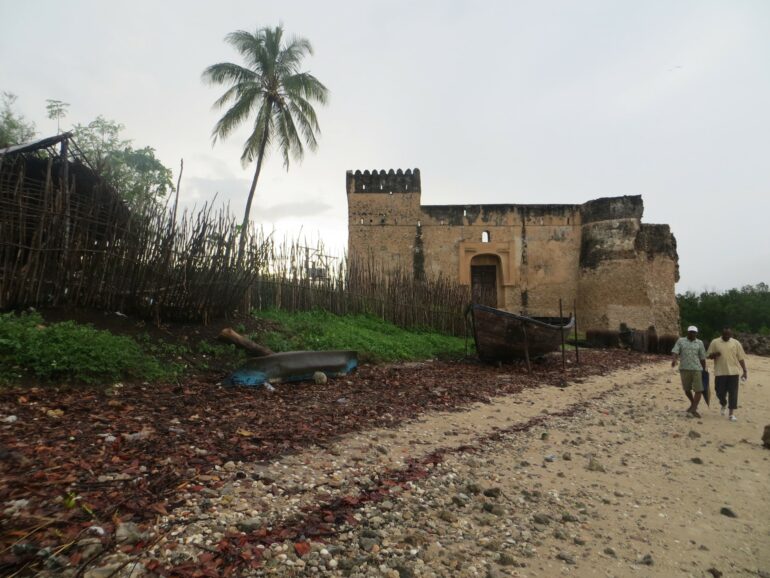
Its ornate stone and coral towns hugged 2,000 miles (3,200 kilometers) of the coast, and its merchants played a linchpin role in the lucrative trade between Africa and lands across the ocean: Arabia, Persia, India, Southeast Asia and China.
By the turn of the second millennium, Swahili people embraced Islam, and some of their grand mosques still stand at the UNESCO World Heritage sites of Lamu in Kenya and Kilwa in Tanzania.
Self-governance ended following Portuguese colonization in the 1500s, with control later shifting to the Omanis (1730-1964), Germans in Tanganyika (1884-1918) and British in Kenya and Uganda (1884-1963). Following independence, coastal peoples were absorbed into the modern nation-states of Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique and Madagascar.
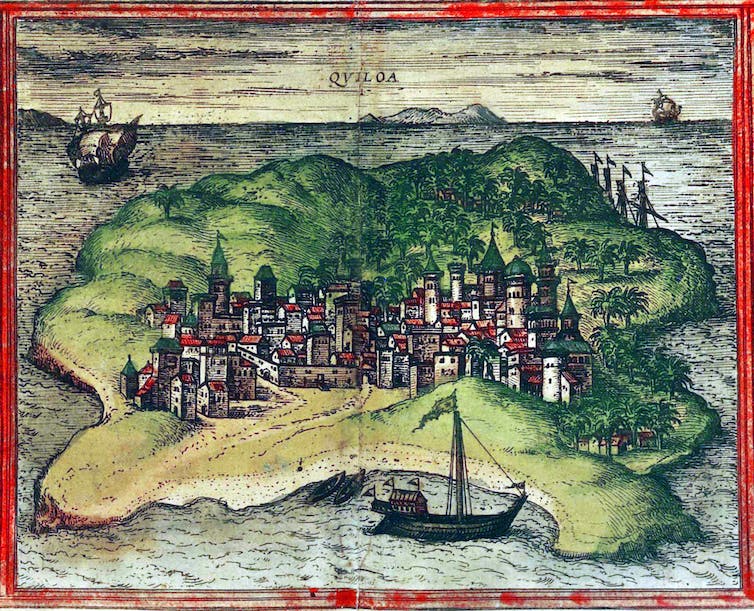
The Swahili island settlement of Kilwa, in present-day Tanzania, grew over centuries to be a major coastal city and trading center.
Pictures From History/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
So who were the Swahili people, and where did their ancestors originally come from?
Ironically, the story of Swahili origins has been molded almost entirely by non-Swahili people, a challenge shared with many other marginalized and colonized peoples who are the modern descendants of cultures of the past with extraordinary achievements.
Working with a team of 42 colleagues, including 17 African scholars and multiple members of the Swahili community, we’ve now published the first ancient DNA sequences from peoples of the Swahili civilization. Our results do not provide simple validation for the narratives previously advanced in archaeological, historical or political circles. Instead, they contradict and complicate all of them.
Colonization affected how the story was told
Western archaeologists in the mid-20th century emphasized the connections of the medieval Swahili to Persia and Arabia, sometimes suggesting that their impressive achievements could not have been attained by Africans.
Post-colonial scholars, including one of us (Kusimba), pushed back against that view. Earlier researchers had inflated the importance of non-African influences by focusing on imported objects at Swahili sites. They minimized the vast majority of locally made materials and what they revealed about African industry and innovation.
But viewing Swahili heritage as primarily African or non-African is too simplistic; In fact, both perspectives are byproducts of colonialist biases.
The truth is that colonization of the East African coast did not end with the departure of the British in the middle of the 20th century. Many colonial institutions were inherited and…



