In the past century, there have been three waves of opposition to transgender health care.
In 1933, when the Nazis rose to power, they cracked down on transgender medical research and clinical practice in Europe. In 1979, a research report critical of transgender medicine led to the closure of the most well-respected clinics in the United States. And since 2021, when Arkansas became the first U.S. state among now at least 21 other states banning gender-affirming care for minors, we have been living in a third wave.
In my work as a scholar of transgender history, I study the long history of gender-affirming care in the U.S., which has been practiced since at least the 1940s. Puberty blockers, hormone therapies and anatomical surgeries are neither experimental nor untested and have been safely administered to cisgender, transgender and intersex adults and children for decades.
On the other hand, the archives of transgender medicine demonstrate that backlash against these practices has historically been rooted in pseudoscience. And today, an anti-science movement that aims to discredit science altogether is fueling the fire of the current wave of anti-trans panic.
The 1930s − eugenics and sexology collide
In the 1920s, the new science of hormones was just reaching maturation and entering mainstream consciousness. In the field of sexology – the study of human sexuality, founded in 19th century Europe – scientists were excited about research on animals demonstrating that removing or transplanting gonads could effectively change an organism’s sex.
In 1919, the German sexologist Magnus Hirschfeld founded the Institut für Sexualwissenschaft in Berlin, which became the world’s leading center for queer and transgender research and clinical practice. Hirschfeld worked closely with trans women as co-researchers throughout the 1920s. Several trans women also received care at the institute, including orchiectomies that halted the production of testosterone in their bodies.
Within months of Hitler’s rise to power in early 1933, a mob of far-right students broke into and shuttered the institute for being “un-German.” Some of the most famous images of Nazi book burning show the institute’s library set ablaze in an outdoor plaza.
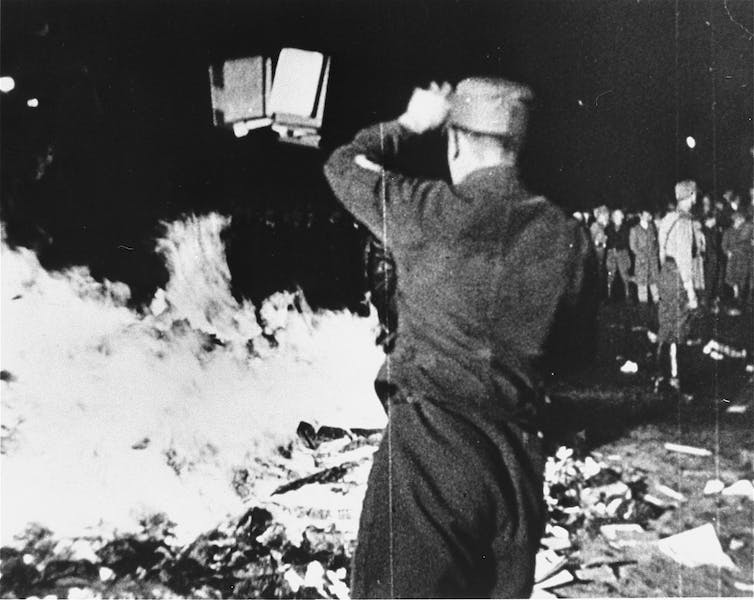

Members of the Nazi party confiscated and burned ‘un-German’ books, including those from the Institut für Sexualwissenschaft.
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, courtesy of National Archives and Records Administration, College Park
Nazi ideology was based on another prominent field of science of that time: eugenics, the belief that certain superior populations should survive while inferior populations must be exterminated. In fact, Hirschfeld’s sexology and Nazi race science had common roots in the Enlightenment-era effort to classify and categorize the world’s life forms.
But in the late 19th century, many scientists went a step further and