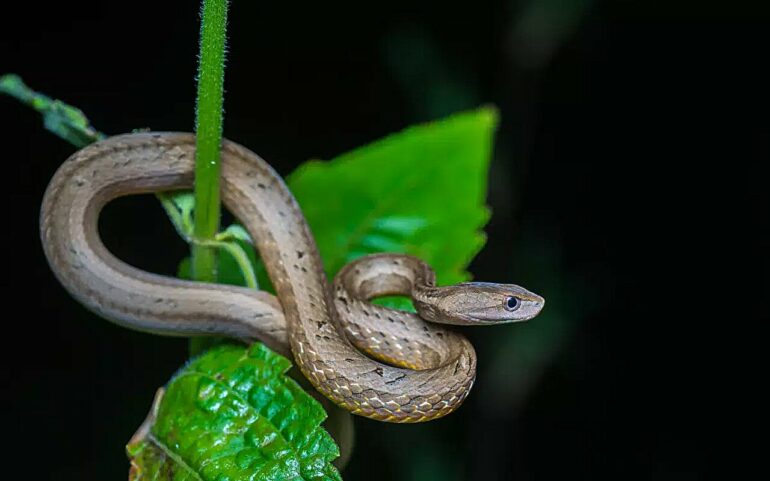
The evolutionary history of the mock viper, a mildly venomous, widely distributed Asian snake that mimics highly venomous vipers for self-defense, has been solved. The mock viper represents a completely unique branch in the tree of life of snakes, and hence, it has been allocated into its own new family named Psammodynastidae. The study is published in Scientific Reports.
This small, feisty snake has long presented a puzzle to evolutionary scientists due to its unresolved evolutionary history. To solve the puzzle, the researchers analyzed DNA sequences of more than 4,500 genes and several dozen high-resolution micro-computed tomographic scans.
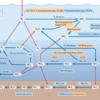
“Mock vipers are part of the superfamily Elapoidea, a major group of snakes to which one-fifth of global serpent diversity belongs. Evolutionary diversification within this superfamily happened very rapidly approximately 50 million years ago. Rapid evolutionary diversifications are probably the most challenging evolutionary scenario for a geneticist or evolutionary biologist to resolve,” says the lead researcher Sunandan Das from the University of Helsinki.
Mock vipers not only look like tree-dwelling vipers but also act like them. Intriguingly, they have a fake “fang” in the front of their mouth, which fools a predator into thinking that they possess venom fangs during an open-mouthed threat display. However, there is also an actual fang in the back of the jaw, which carries a weak venom effective only on their lizard prey. The Elapoidea superfamily has multiple snake families with various types of venom and fangs, for example cobras and mambas.
Another completely new family-level lineage, Micrelapidae, within Elapoidea was discovered in 2023 by Das and Professor Juha Merilä.
“The discovery of a new family of any vertebrate animals is surprisingly rare, an almost once-in-a-century phenomenon. This is a lifetime achievement for an evolutionary biologist. You rarely, if ever, see descriptions of whole new families of well-studied vertebrate animals anymore,” says Das.
The inference of the phylogenetic position of mock vipers, along with that of other elapoid snakes, will pave the way for a much better understanding of snake venom fang origin and evolution. Long, unique branches in the phylogeny, like that of mock vipers, contain a high degree of evolutionary distinctiveness, an index used by biologists for prioritizing conservation. Hence, reinstating the mock viper or Psammodynastes into its own “dynasty” also serves an important conservation goal.
More information:
Sunandan Das et al, Phylogenomics of Psammodynastes and Buhoma (Elapoidea: Serpentes), with the description of a new Asian snake family, Scientific Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-60215-2
Provided by
University of Helsinki
Citation:
Viper-mimicking snake from Asia is a unique branch in the reptile evolutionary tree (2024, May 27)