At the 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society’s Division of Fluid Dynamics, researchers shared new insights into melting icebergs and lake ice formation.
Eric Hester has spent the last three years chasing icebergs. A mathematics graduate student at the University of Sydney in Australia, Hester and researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in Massachusetts are studying how the shape of an iceberg shapes the way it melts.
“Ice deforms as it melts,” said physical oceanographer Claudia Cenedese, who has worked with Hester on the project. “It makes these very weird shapes, especially on the bottom, like the way the wind shapes a mountain on a longer time scale.”
At the 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society’s Division of Fluid Dynamics, Hester presented results from his group’s experiments aimed at understanding how melting alters the face-changing boundary of a shrinking iceberg—and how those alterations in turn affect the melting.
The dynamics of iceberg melt is missing from most climate models, Cendese said. Including them could help with prediction: icebergs pump fresh water from ice sheets into oceans, boosting communities of living organisms. Icebergs are the dominant source of freshwater in the fjords of Greenland—and a significant contributor to freshwater loss in Antarctica. Icebergs play a critical role in the climate, Cenedese said, and shouldn’t be neglected in models. The physics of melting ice is well understood, and some models simulate it accurately, she said. Others don’t. “But what you can’t do in those simulations is change the shape of the ice.”
Icebergs form with a wide range of shapes and sizes, Hester said, and distinct thermodynamic processes affect different surfaces. The base, submerged in water, doesn’t melt in the same way as the side. “And each face doesn’t melt uniformly,” added Cenedese.
Hester conducted his experiments by submerging a dyed block of ice in a flume with a controlled flow of water passing by, and watching it melt. He and his colleagues found that the side facing a current melts faster than sides that run parallel to flow. By combining experimental and numerical approaches, Hester and his collaborators charted the relative influences of factors like relative water velocity and aspect ratio, or the proportion of height to width on a side. Not surprisingly, they found that the bottom had the slowest melt rate.
Cenedese said Hester’s project brings together collaborators from a range of disciplines and countries, and that a diverse collaboration was needed for such an interdisciplinary project. “Working in isolation isn’t as productive in this case.”
Other studies discussed at the conference focused on ice formation, rather than melting. During a session on particle-laden flows, engineer Jiarong Hong from the St. Anthony Falls Laboratory at the University of Minnesota, in Minneapolis, discussed results from experiments showing how turbulence influences both the speed and distribution of snow as it falls and settles. The findings could also help scientists better understand precipitation, Hong said.
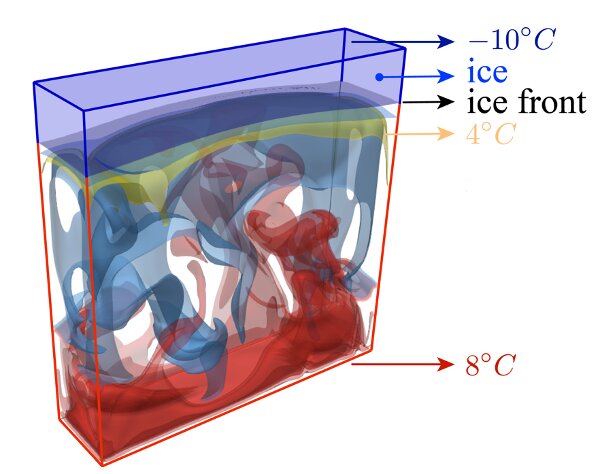
Another project, presented by physicist Chao Sun from Tsinghua University in China and his group during a session on convection and buoyancy-driven flows, focused on ice formation in lakes.
Working on a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China with Ziqi Wang from Tsinghua University, Enrico Calzavarini from the University of Lille in France, and Federico Toschi from Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands, Sun showed how the formation of ice on a lake is closely tied to the fluid dynamics of the water beneath.
A lake may possess layers of water of differing densities and temperatures. “The water density anomalies can induce elaborate fluid dynamics beneath a moving ice front and can drastically change system behaviors,” said Sun. “This has often been ignored in previous studies.”
Sun’s group combined physical experiments, numerical simulations, and theoretical models to investigate the connection between the ice and (turbulent) convective flows. They identified four distinct regimes of different flow dynamics, each of which interacts with other layers and the ice in its own ways. Even with that complexity, though, the group developed an accurate theoretical model that could be used in future studies.
“It made a fair prediction of ice layer thickness and of icing time,” said Sun.
Since the formation and melting of ice plays such a critical role in the climate, he said, a better understanding of the fluid dynamics behind the process could help researchers identify and study accurately the markers of a warming world. “The time for ice to form and melt, for example, could potentially provide an indicator of climate change.”
Antarctic ice loss expected to affect future climate change
More information:
How Does Iceberg Shape Affect Melting? meetings.aps.org/Meeting/DFD20/Session/U07.3
Snow Settling Dynamics in Atmospheric Turbulence meetings.aps.org/Meeting/DFD20/Session/R13.4
How the Growth of Lake Ice Depends on the Fluid Dynamics Underneath meetings.aps.org/Meeting/DFD20/Session/F15.1
Provided by
American Physical Society
Citation:
Breaking the ice on melting and freezing (2020, November 22)
retrieved 22 November 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-11-ice.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.