You might think it’s a simple, straightforward task to find out whether your current PC will run Windows 11. Think again. Even Microsoft can’t quite get its story straight.
For starters, two pieces of core documentation disagree with one another. The official Windows 11 System Requirements page has one set of specs, while the Compatibility for Windows 11 documentation that the Windows engineering team prepared for Microsoft partners as part of the Compatibility Cookbook for Windows tells a different story. And in both cases the details are incomplete.
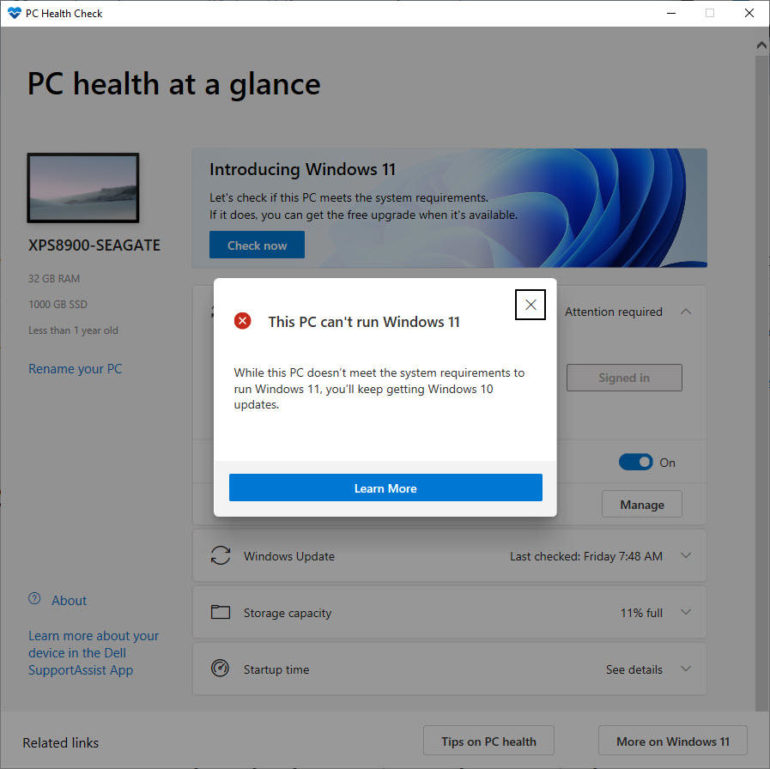
To cap things off, the official compatibility checker (included in the new PC Health Check app) delivers results without details. If the compatibility checker says your PC will run Windows 11, you’re good to go. But if you run the compatibility check and get results like this on a system that appears to meet every specification with ease, read on to learn how to track down the problem.
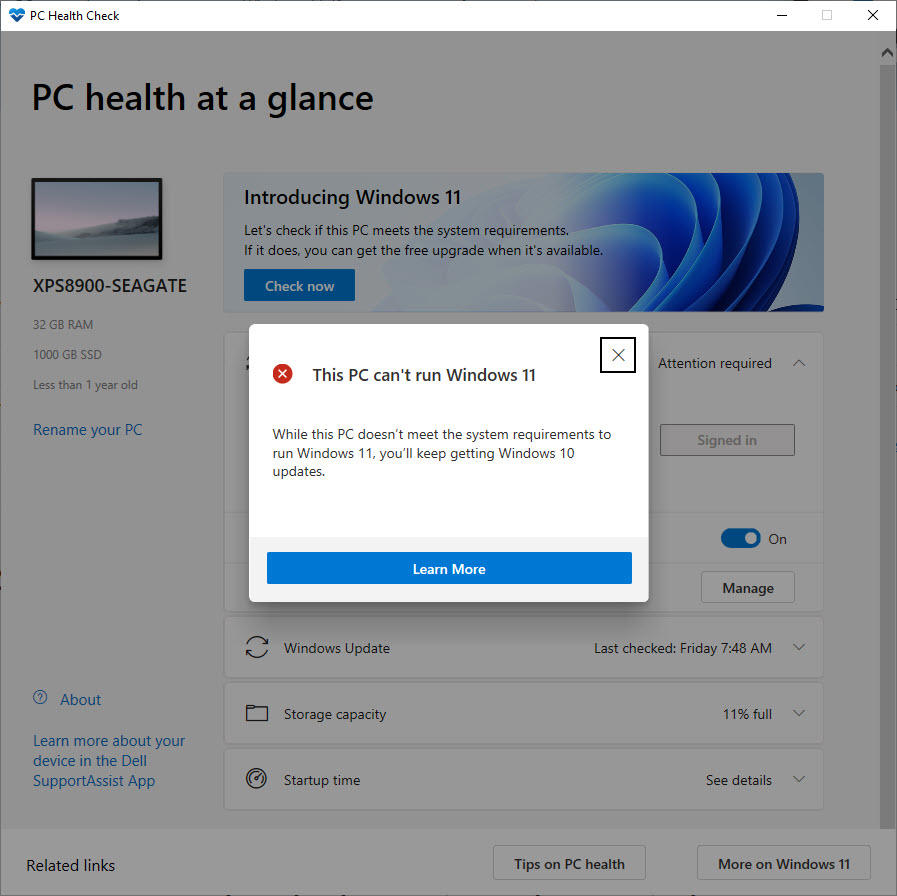
Frustratingly, this tool doesn’t appear to create a log file
The basic hurdles are easy enough to clear. You need a 64-bit Intel or AMD processor running at a speed of at least 1 GHz with 2 or more cores, or, on Arm-based PCs, a compatible System on a Chip (SoC). The biggest change from Windows 10 specs is that 32-bit (x86) CPUs are no longer supported. You also need at least 4 GB of RAM and 64 GB of storage. Most PCs built in the last 10 years will meet those specs.
The device also can’t be running in S Mode.
The two biggest stumbling blocks for PCs involve support for an essential security feature called a Trusted Platform Module, or TPM, and support for a minimum CPU generation.
TPM support
The system requirements page says you’ll need a TPM version 2.0 to run Windows 11. The Compatibility Cookbook says you’ll need a TPM version of 1.2 or greater. Specifically, the TPM 1.2 requirement (with a Secure Boot capable PC) is part of a so-called Hard Floor, while the TPM 2.0 spec is part of the Soft Floor.
According to the docs, “Devices that do not meet the hard floor cannot be upgraded to Windows 11, and devices that meet the soft floor will receive a notification that upgrade is not advised.”
That’s not a trivial detail, because millions of older PCs are equipped with TPM 1.2 in hardware and can’t be upgraded.
To make things even more confusing, the compatibility checker might tell you your PC can’t be upgraded to Windows 11 if the device has a TPM but that feature is disabled in firmware.
You can check for the presence of a TPM by looking in Device Manager (Devmgmt.msc) under the Security Devices heading, as shown here.
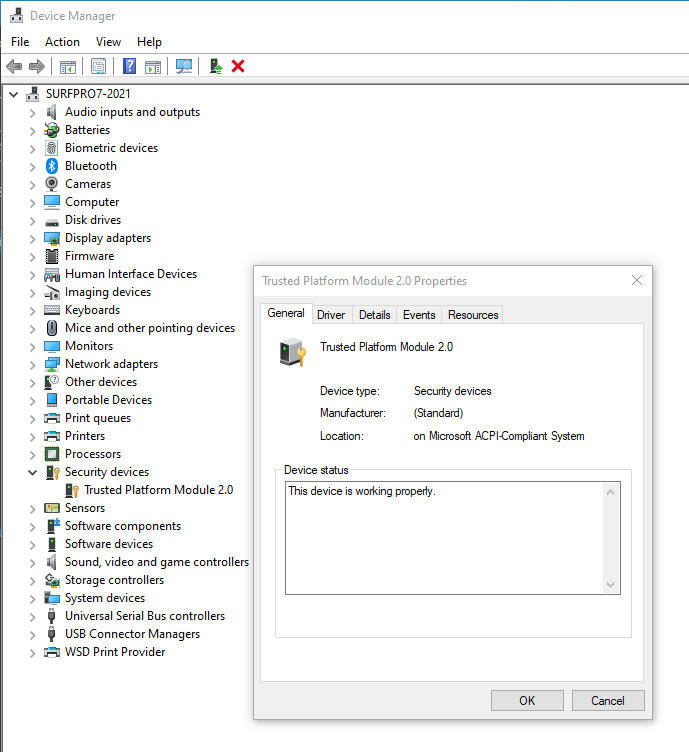

Use Device Manager to check the TPM version
You can also run the TPM Management snap-in (Tpm.msc). That tool will tell you the name of the TPM manufacturer as well as the version information. Be sure to close the snap-in without making any changes.
If you’re certain your PC has a TPM but you don’t see it listed in Device Manager, you’ll need to go into firmware settings and enable it. On a UEFI-based Windows 10 PC, the easiest way to do that is to follow these steps:
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.Under the Advanced Startup heading, click Restart Now.After restarting, click Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.
Look for a setting labeled TPM or PTT (short for Intel Platform Trust Technology) or, on AMD systems, fTPM (short for Firmware Trusted Platform Module). You might need the PC’s manual to find the exact setting. And while you’re in the firmware setting, make sure Secure Boot is enabled.
That should resolve any TPM issues.
CPU Generation
If the compatibility checker still insists that you can’t run Windows 11, and you’ve confirmed that the TPM isn’t the sticking point, the problem might be an older CPU.
Yes, there’s also a Soft Floor requirement for CPU. Frustratingly, the documentation simply says this is defined by “CPU Generation,” without going into any additional details.
It appears that any device running on an Intel 7th Generation (Skylake) CPU or earlier will also trigger that compatibility check. That was the case on a Dell desktop PC I checked. Frustratingly, the PC Health Check app doesn’t appear to generate any log files that would make the sleuthing easier.
Instead, I turned to an open source tool called Win11SysCheck, which is available on GitHub as source code and a precompiled binary. (The executable download is here. You might get a SmartScreen error if you try to download this tool and run it, because Windows flags it, for now at least, as “not commonly downloaded.”)
That tool confirmed that the i7-6700 CPU on my desktop PC was the culprit.


This open source tool provides more details than the official compatibility checker
That’s a 2015-era CPU, which makes it about six years old. The good news is that Windows 11 should run on it, although it’s not recommended.
Another Microsoft engineering document, prepared for hardware manufacturers, includes a full list of supported Windows 11 CPUs from AMD, Intel, and Qualcomm. Of course, those specs should only apply to PC makers, but apparently that’s the “soft floor” that Windows 11 will use for upgraders as well.
Hopefully, this will all be sorted out by the time Windows 11 is ready for its first general release, but don’t count on it.