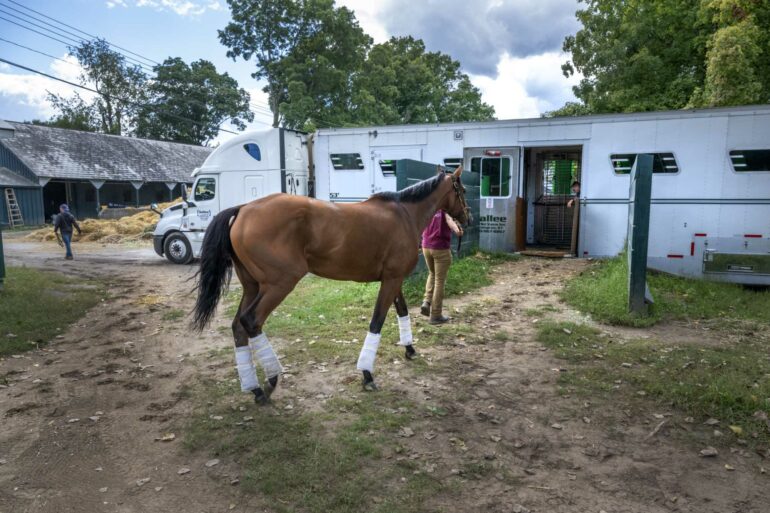
Across human history, no single animal has had a deeper impact on human societies than the horse. But when and how people domesticated horses has been an ongoing scientific mystery.
Half a million years ago or more, early human ancestors hunted horses with wooden spears, the very first weapons, and used their bones for early tools. During the late Paleolithic era, as far back as 30,000 years ago or more, ancient artists chose wild horses as their muse: Horses are the most commonly depicted animal in Eurasian cave art.
Following their first domestication, horses became the foundation of herding life in the grasslands of Inner Asia, and key leaps forward in technology such as the chariot, saddle and stirrup helped make horses the primary means of locomotion for travel, communication, agriculture and warfare across much of the ancient world. With the aid of ocean voyages, these animals eventually reached the shores of every major landmass – even Antarctica, briefly.
As they spread, horses reshaped ecology, social structures and economies at a never-before-seen scale. Ultimately, only industrial mechanization supplanted their near-universal role in society.
Because of their tremendous impact in shaping our collective human story, figuring out when, why and how horses became domesticated is a key step toward understanding the world we live in now.
Doing so has proven to be surprisingly challenging. In my new book, “Hoof Beats: How Horses Shaped Human History,” I draw together new archaeological evidence that is revising what scientists like me thought we knew about this story.
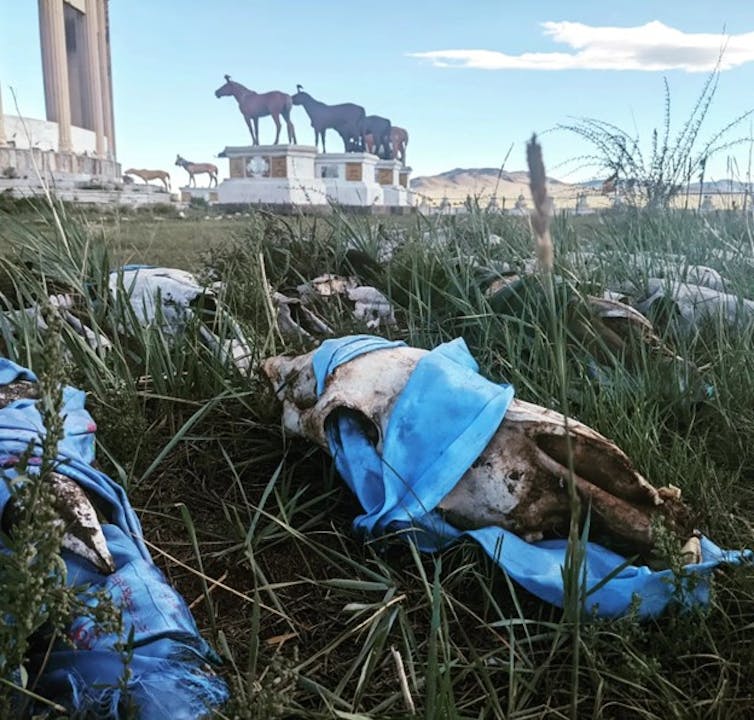

Horses have long been revered in the steppes of Inner Asia, as seen by the horse skulls and prayer flags at this monument to racehorses in central Mongolia.
William Taylor
A horse domestication hypothesis
Over the years, almost every time and place on Earth has been suggested as a possible origin point for horse domestication, from Europe tens of thousands of years ago to places such as Saudi Arabia, Anatolia, China or even the Americas.
By far the most dominant model for horse domestication, though, has been the Indo-European hypothesis, also known as the “Kurgan hypothesis.” It argues that, sometime in the fourth millennium BCE or before, residents of the steppes of western Asia and the Black Sea known as the Yamnaya, who built large burial mounds called kurgans, hopped astride horses. The newfound mobility of these early riders, the story goes, helped catalyze huge migrations across the continent, distributing ancestral Indo-European languages and cultures across Eurasia.
But what’s the actual evidence supporting the Kurgan hypothesis for the first horse domestication? Many of the most important clues come from the bones and teeth of ancient animals, via a discipline known as archaeozoology. Over the past 20 years, archaeozoological data seemed to converge on the idea that horses were first domesticated in…