A new study led by Dr. Assaf Hochman from the Institute of Earth Sciences at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem sheds light on the complex dynamics of sub-seasonal precipitation anomalies in the Middle East, revealing significant correlations with key climate indices. The research offers valuable insights into the predictability of rainfall patterns crucial for both society and the environment.
The work is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The research shows promise in two areas significantly affected in the Middle East.
The study’s insights into evolving climate patterns can offer crucial information for policymakers and stakeholders involved in managing water resources, information that could be vital for planning and implementing effective water conservation and distribution strategies as well as addressing the region’s water scarcity concerns.
Agriculture in the Middle East heavily depends on precipitation for irrigation. The study’s findings on sub-seasonal precipitation anomalies and their correlation with climate indices can assist farmers and agricultural policymakers in anticipating and adapting to changing rainfall patterns. This knowledge is particularly important for crop planning and mitigating the potential impacts of extreme weather events on agriculture, enhancing the resilience of the region’s agricultural practices.
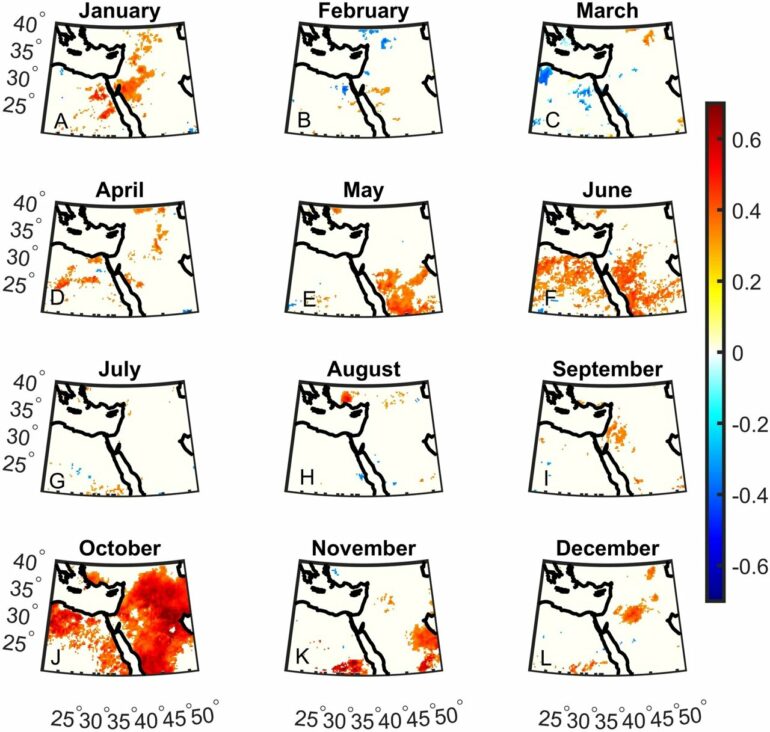
The work delves into the intricate relationships between climate indices such as the Indian Ocean Dipole Mode Index, West Tropical Indian Ocean Index, and precipitation variability in the Middle East. Through careful analysis of data from the month of October, researchers found strong correlations, with coefficients around 0.7, persisting up to a two-month lag period.
Furthermore, the research highlights a significant upward trend of approximately 0.4° C in both Indian Ocean Dipole Mode Index and West Tropical Indian Ocean Index over the past four decades. This trend underscores the evolving climate patterns in the Indian Ocean, intensifying their impact on precipitation dynamics in the Middle East. The findings suggest a continued trend into the twenty-first century, with potential regional consequences.
Notably, the study identifies substantial correlations between Indian Ocean Dipole Mode Index, West Tropical Indian Ocean Index, and maximum daily precipitation, emphasizing their role in extreme rainfall events. By attributing much of October’s precipitation variability to Indian Ocean sea surface temperature anomalies, the research elucidates how these temperature fluctuations influence the Indian Ocean’s Walker circulation, thereby shaping regional precipitation patterns.
Dr. Assaf Hochman, lead researcher, commented, “Our findings underscore the importance of understanding the intricate ocean-atmosphere interactions and their implications for Middle Eastern climate variability. By elucidating the connections between climate indices and sub-seasonal precipitation anomalies, we pave the way for improved prediction and adaptation strategies.”
The implications of this study extend beyond academic circles, offering valuable insights for policymakers, meteorologists, and stakeholders concerned with water resource management, agriculture, and disaster preparedness in the Middle East.
More information:
Assaf Hochman et al, Unraveling sub-seasonal precipitation variability in the Middle East via Indian Ocean sea surface temperature, Scientific Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-53677-x
Provided by
Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Citation:
Climate indices and precipitation anomalies reveal stark implications for the Middle East (2024, February 14)