A new study has unveiled surprising findings about mercury pollution: where it comes from and how it moves through the environment vary significantly depending on the ecosystem. In drier regions, most mercury is deposited through rain and snow. In wetter, forested areas, gaseous mercury from the air sticks to leaves, which then fall and carry the toxin into the ground.
Scientists from the U.S. Geological Survey, National Park Service, the Appalachian Mountain Club and public participants made this discovery by examining an unexpected indicator: dragonflies. Their findings were published today in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Mercury contamination is a global concern, coming from both natural sources and human activities. Mercury accumulates in living organisms, becoming more concentrated as it moves up the food chain from smaller to larger animals. The toxin can harm both humans and animals, damaging brain development in the young, affecting adult health and interfering with reproduction.
The study used the Dragonfly Mercury Project, a nationwide program that works with public participants to collect dragonfly larvae for mercury analysis. Citizen scientists and community volunteers in 150 National Parks helped collect and measure dragonfly larvae from more than 750 sites, turning a fun outdoor activity into valuable scientific data.
Samples were analyzed using a state-of-the-art instrument capable of detecting different types of mercury in dragonfly larvae. The chemical signature of mercury from different sources is as unique as a fingerprint and can be used to reveal how mercury reached the area. This collaborative effort can help to inform resource management decisions while improving public awareness of environmental issues.
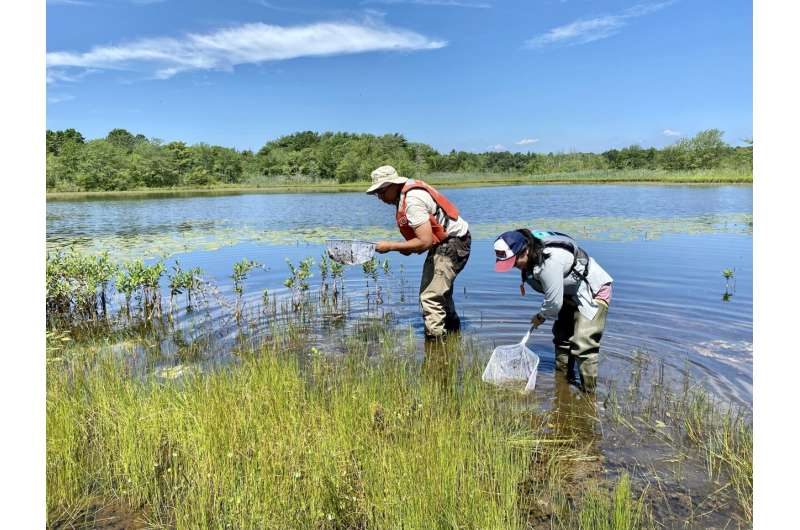

Public participants help collect dragonfly larvae and record field data. Park staff work to engage students, conservation corps, interns, and others in this hands-on research experience. © NPS
Sarah Janssen, USGS scientist and lead author of the study, said, “These groundbreaking findings have reshaped our understanding of mercury delivery within protected lands, particularly in dry ecosystems. By using cutting-edge technology and working with public participants, we were able to uncover surprising results that have the potential to change how mercury is monitored and managed at a global scale.”
While previous studies have focused on measuring mercury levels in fish and birds, recent research demonstrates that dragonfly larvae are a more cost-effective, accessible and widespread accurate indicator of mercury contamination.
As larvae, dragonflies are found in nearly every aquatic habitat, including areas where fish are rare, such as deserts. Understanding how the mercury moves through different ecosystems is critical in predicting how concentrations in organisms will respond to declining mercury emissions.

High school students from Eagle Rock School participate in Dragonfly Mercury Project sampling at Rocky Mountain National Park in 2017. © J. Peters, NPS
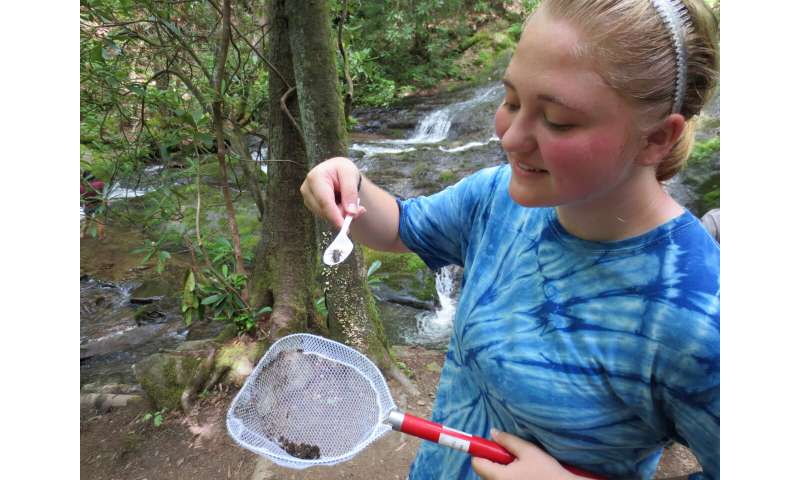

A public participant helps collect dragonfly larvae for mercury analysis at Great Smoky Mountains National Park in 2015. © NPS. © NPS
Richard Haeuber, a scientist at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s clean air and power division, said, “This study significantly enhances our understanding of how various ecosystems receive atmospheric mercury. It provides resource management agencies with new insights to better align and optimize their monitoring methods based on the primary sources and pathways of mercury in specific locations.”
The implications of this study extend beyond the borders of the United States, as findings can inform global efforts to address mercury pollution under the Minamata Convention. This international treaty aims to protect human health and the environment from mercury’s harmful effects and could benefit from insights on ecosystem-specific mercury deposition and using dragonflies as global monitoring tools.
Complementing these findings, scientists recently discovered surprisingly high mercury levels in desert dragonflies, challenging previous assumptions that arid regions were low-risk for mercury contamination. This highlights the importance of further studying arid regions for mercury and contaminant cycling.
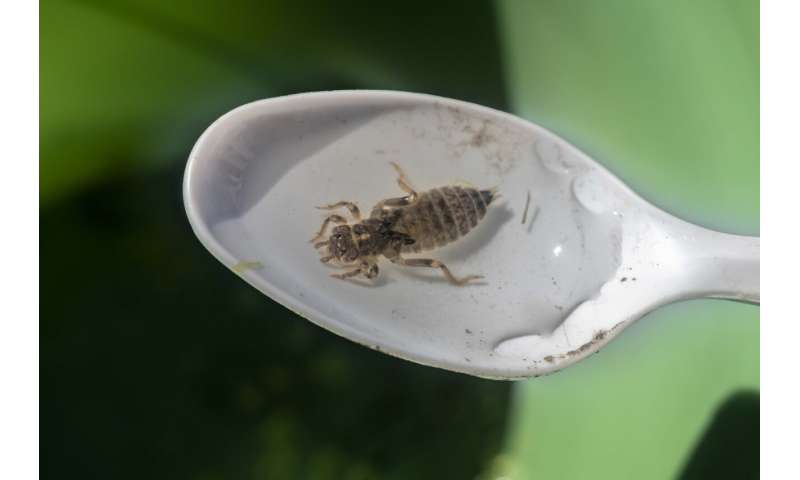

Dragonfly larvae samples were collected as part of the Dragonfly Mercury Project. Many national parks and other protected places, including national forests, wildlife refuges, and tribal lands, have participated in DMP sampling. © USGS
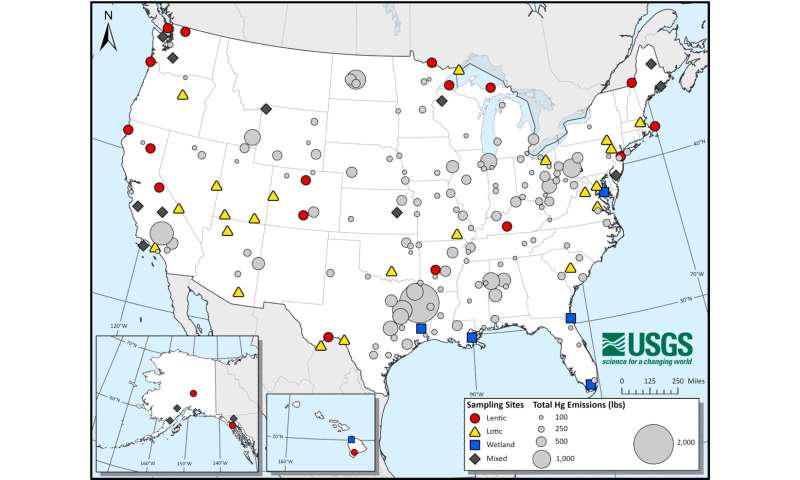
The map above shows sites where dragonfly larvae were collected for the Janssen et al. 2024 paper. Dragonfly larvae were collected at three types of sites including wetlands, lotic systems (flowing water like streams or rivers), and lentic systems (still waters like lakes or ponds). These sampling sites covered different regions of the United States, which can have different amounts of mercury emissions to the atmosphere. These sites are only a small subset of the larger Dragonfly Mercury Project. © USGS
Colleen Flanagan Pritz, NPS ecologist and co-author of the study, emphasized the broader implications of these findings for park lands, “National parks are not only iconic symbols of our natural heritage but also critical refuges for biodiversity.
“By engaging the public in data collection for this novel study in parks, we have gained invaluable insights into the impacts of mercury pollution on these ecosystems and the tools to protect them. This is a shining example of how citizen science can drive meaningful conservation outcomes and inform park management.”
As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of mercury pollution in our environment, the unexpected insights provided by dragonflies highlight the importance of collaborative research and the power of public participation in protecting our planet’s ecosystems.
If you are interested participating in an upcoming Dragonfly Mercury Project study, learn more by connecting to your local National Park.
More information:
Sarah E. Janssen et al, Geographic Drivers of Mercury Entry into Aquatic Food Webs Revealed by Mercury Stable Isotopes in Dragonfly Larvae, Environmental Science & Technology (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.4c02436
Provided by
United States Geological Survey
Citation:
Local dragonflies expose mercury pollution patterns (2024, July 16)



