“I’m tracking my macros.”
“I’ll pass on that, it doesn’t fit in my macros.”
“I’m on the Macro Diet.”
Macros seem to come up often in the corners of the internet and social media devoted to people trying to lose weight, improve their health, look better and feel better about themselves. But what the heck is a macro?
With more information than ever available at your fingertips, and more diets out there than you have fingers and toes to count on, it’s no wonder you might be confused. As an exercise science specialist interested in physical health and nutrition, I’ve got you covered.
“Macros” is just a shorthand term for macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates and fats. They’re the nutritional building blocks that all foods are made up of in various ratios.
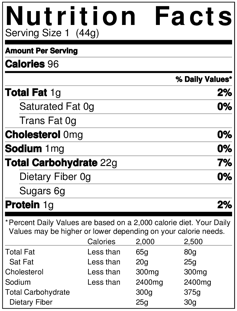
Nutrition labels let consumers know about the macros and other nutrients in packaged foods.
Jaidan899/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
If you look at a nutrition label, you’ll see that macros are measured in grams. But it’s important to understand that the calories per gram for each macro aren’t the same. Protein and carbohydrates each have 4 calories per gram, while fat has 9 calories per gram. In other words, fat provides more than twice the amount of energy per gram compared with protein and carbohydrates.
People rarely eat proteins, carbohydrates or fats in isolation. For example, while chicken is widely considered a source of protein, it also contains fat. Almost every food contains more than one macronutrient.
What macros do and where to find them
Beyond its job building muscle, protein also plays other critical roles in the body: as a component of enzymes, transporting nutrients and producing hormones. Sources of protein include animal meats, eggs, fish and seafood, and dairy. While animal sources have the highest protein content, plant food sources, such as whole grains, legumes such as beans, and nuts and seeds also contain protein. You don’t need to consume animal products to get adequate protein in your diet.
The 2020-2025 federal dietary guidelines for Americans recommend at least 46 grams of protein for adult females and at least 56 grams for adult males, although this may be too low for older adults, pregnant and lactating women, and people with high levels of physical activity.
Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred energy source. They’re found in bread, rice, pasta, fruits, dairy products, legumes and starchy vegetables. Simple sugars also fit into the carbohydrate category, and those are the ones to limit.
As for fats, there are different types: polyunsaturated, monounsaturated, saturated and trans fat. Polyunsaturated and monounsaturated have the greatest health benefits and are found in things such as nuts and seeds and fish. Omega-3s are essential fatty acids that can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and are found in fatty fish such as salmon and nuts such as…



