Measuring blood pressure while patients are standing rather than sitting may improve the accuracy of readings, UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers report. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, could lead to significant improvements in early detection of high blood pressure in healthy adults.
“Blood pressure screening is predominantly performed when patients are sitting down in the doctor’s office,” said lead author Wanpen Vongpatanasin, M.D., Professor of Internal Medicine and Director of the Hypertension Section in the Division of Cardiology at UT Southwestern.
“However, it has limited sensitivity and reliability as it does not reflect blood pressure in real living situations where we often stand or walk. Our study shows that measuring blood pressure in the standing position may offer a more accurate way to determine if someone has hypertension, which requires assessment of a 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitor or home monitoring.”
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, remains the main risk factor for cardiovascular disease and stroke, affecting 48% of adults in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2021 hypertension was a primary or contributing cause for over 690,000 deaths in the U.S.
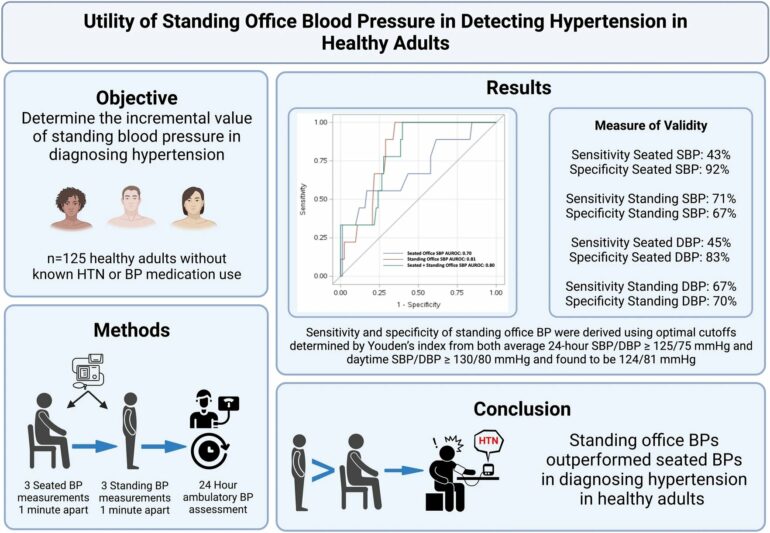
UTSW researchers measured the blood pressure of 125 healthy patients ages 18-80 with no history of hypertension, previous use of blood pressure medication, or other comorbidities.
The statistical analysis used to assess the overall accuracy of each test in diagnosing hypertension revealed that measuring standing blood pressure either on its own or in addition to sitting blood pressure significantly improved diagnostic accuracy. Researchers used several established guidelines for defining hypertension, including those of the American Heart Association.
Blood pressure was measured in three ways: through 24‐hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), seated in the doctor’s office, and standing in the office. The sensitivity (accuracy in detecting a condition, or a “positive” result) and specificity (accuracy in detecting absence of a condition, or a “negative” result) for detecting hypertension in the seated measurements were 43% and 92%, while the sensitivity and specificity in the standing measurements were 71% and 67%.
Based on average 24-hour ABPM measurements, researchers found that 33.6% of participants had hypertension. Of those with hypertension, the average age was 55.7 years old and 57% were female adults, 55% were white adults, 29% were Black adults, 16% were Asian adults, and 16% were of Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Of the participants without hypertension, the only significant difference in demographics observed was younger age (45.3 years old).
Data from the UTSW Dallas Heart Study was used to determine blood pressure levels in the office, home, and 24-hour ABPM that are optimal for cardiovascular health.
Findings from this research create an opportunity for improved diagnosis of hypertension in healthy adults and could lead to better diagnostics for patients who already have the condition.
“This study was performed in healthy adults without diagnosis of hypertension or antihypertensive drug treatment,” Dr. Vongpatanasin said. “We need to determine if standing blood pressure will offer a better diagnostic tool than seated blood pressure in caring for hypertensive patients treated with medications.”
More information:
John M. Giacona et al, Utility of standing office blood pressure in detecting hypertension in healthy adults, Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42297-6
Provided by
UT Southwestern Medical Center
Citation:
Standing blood pressure test found to be more accurate in detecting hypertension (2023, November 6)