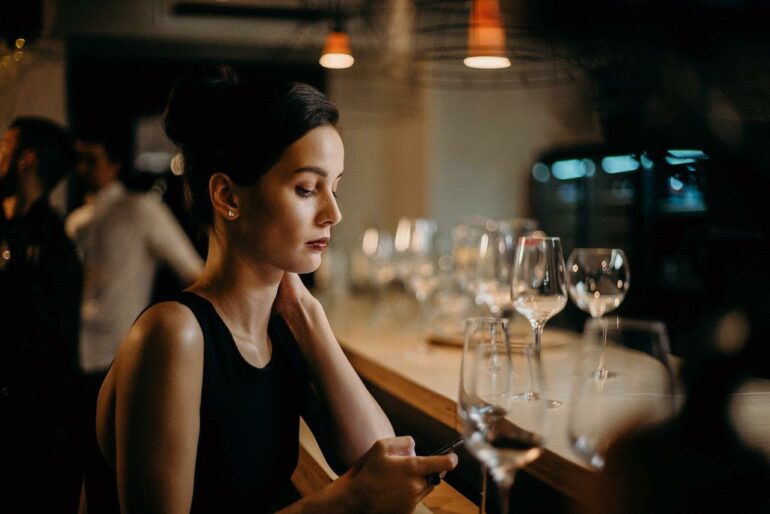
How much do you engage with others when you’re out in public? Lots of people don’t actually engage with others much at all. Think of commuters on public transportation staring down at their phones with earbuds firmly in place.
As a professor of social psychology, I see similar trends on my university campus, where students often put on their headphones and start checking their phones before leaving the lecture hall on the way to their next class.
Curating daily experiences in these ways may appeal to your personal interests, but it also limits opportunities for social connection. Humans are social beings: We desire to feel connected to others, and even connecting with strangers can potentially boost our mood.
Though recent technological advances afford greater means for connection than at any other moment in human history, many people still feel isolated and disconnected. Indeed, loneliness in the American population has reached epidemic levels, and Americans’ trust in each other has reached a historic low.
At the same time, our attention is increasingly being pulled in varied directions within a highly saturated information environment, now commonly known as the “attention economy.”
It is perhaps not surprising, then, that so many Americans are experiencing a crisis of social connection. Research in social psychology helps to explain how the small behaviors and choices we make as individuals affect our experiences with others in public settings.
Where you focus your attention
One factor shaping people’s experiences in public settings concerns where they focus their attention. Since there is more information out in the world than anyone could ever realistically take in, people are driven to conserve their limited mental resources for those things that seem most crucial to navigating the world successfully. What this means is that every person’s attention is finite and selective: By attending to certain bits of information, you necessarily tune out others, whether you’re aware of doing so or not.
More often than not, the information you deem worthy of attention also tends to be self-relevant. That is, people are more likely to engage with information that piques their interest or relates to them in some way, whereas they tend to ignore information that seems unrelated or irrelevant to their existence.
These ingrained tendencies might make logical sense from an evolutionary perspective, but when applied to everyday social interaction, they suggest that people will limit their attention to and regard for other people unless they see others as somehow connected to them or relevant to their lives.
One unfortunate consequence is that a person may end up treating interactions with other people as transactions, with a primary focus on getting one’s own needs met, or one’s own questions answered. A very different approach would involve seeing interactions with others as opportunities for social connection; being…