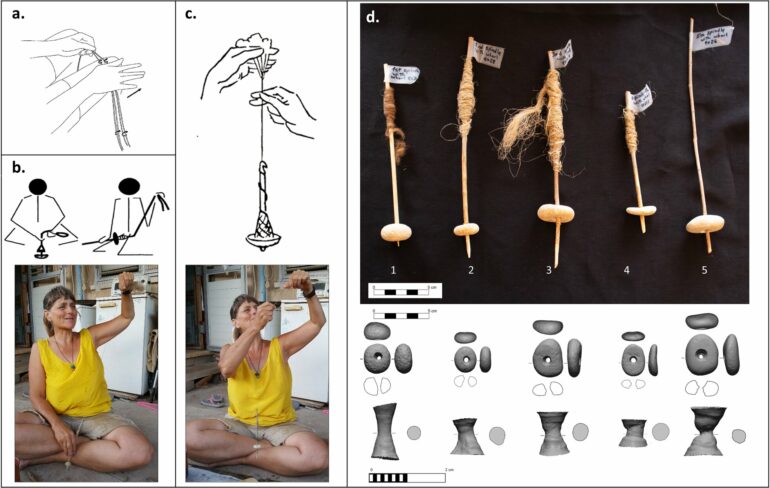
A collection of perforated pebbles from an archaeological site in Israel may be spindle whorls, representing a key milestone in the development of rotational tools including wheels, according to a study published November 13, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Talia Yashuv and Leore Grosman from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel.
Donut-shaped objects connected to a bar, forming a wheel and axle, are a key invention that springboarded technological development and are commonly associated with Bronze Age carts. Spindle whorls, round, weighted objects that are attached to a spindle stick, form a similar wheel-and-axle-like device to help the spindle rotate faster and longer, enabling it to efficiently gather up fibers such as wool or flax and spin them into yarn.
The stones studied in the new paper, recovered from the Nahal-Ein Gev II dig site in northern Israel, date back approximately 12,000 years, during the important transition to an agricultural lifestyle and the Neolithic period, long before the cart wheels of the Bronze Age.
Introducing an innovative method for studying perforated objects, based on digital 3D models of the stones and their negative holes, the authors describe more than a hundred of the mostly-limestone pebbles, which feature a circular shape perforated by a central hole.
Due to this structure and composition, the authors of the new paper deduce that the stones were likely used as spindle whorls—a hypothesis also supported by successfully spinning flax using replicas of the stones.
This collection of spindle whorls would represent a very early example of humans using rotation with a wheel-shaped tool. They might have paved the way for later rotational technologies, such as the potter’s wheel and the cart wheel, which were vital to the development of early human civilizations.
The authors add, “The most important aspect of the study is how modern technology allows us to delve deep into touching the fingerprints of the prehistoric craftsman, then learn something new about them and their innovativeness, and at the same time, about our modern technology and how we’re linked.”
More information:
12,000-year-old spindle whorls and the innovation of wheeled rotational technologies, PLOS ONE (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312007
Provided by
Public Library of Science
Citation:
12,000-year old stones may be very early evidence of wheel-like technology (2024, November 13)