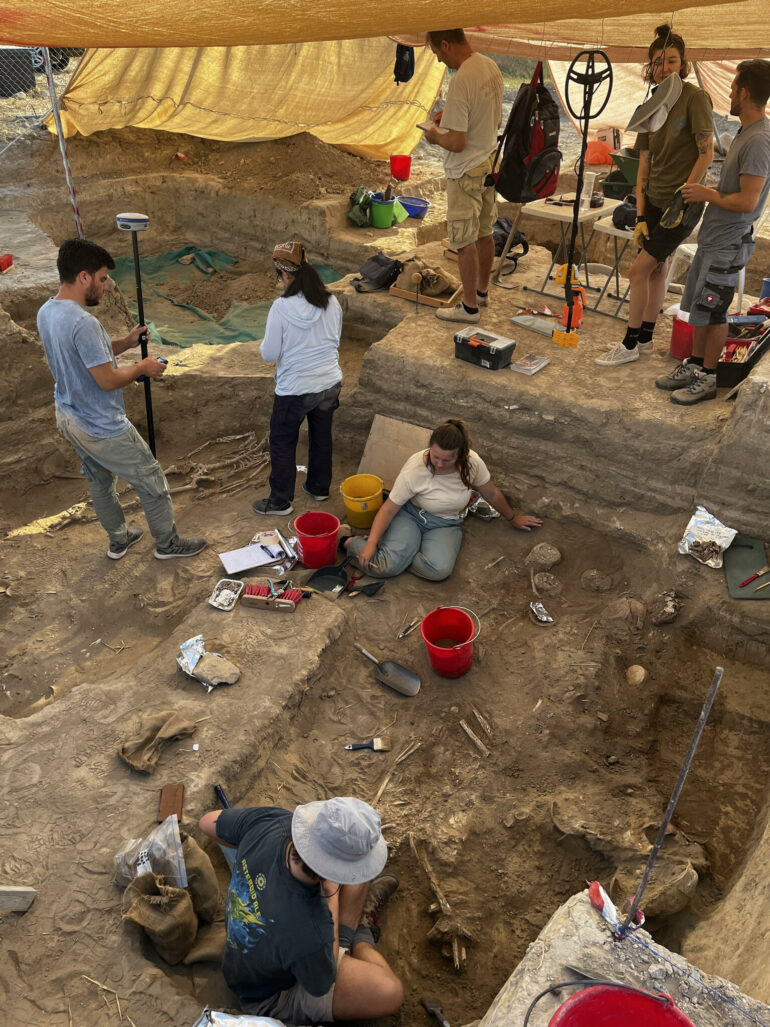
A Swedish-led excavation on Cyprus has unearthed a wealth of artifacts suggesting an ancient port city in Larnaca on the south coast was the region’s key Bronze Age trading post, an official said Wednesday.
“The city’s wealth seems to have been based on the production of copper and trade with near and distant cultures,” said Giorgos Georgiou, acting director of Cyprus’ Antiquities Department.
“Judging by the rich burial gifts, the tombs belonged to families of the city’s ruling class, which must have been involved in the export of copper and intercultural trade,” he added in a written response to AFP.
He said the excavation site at Dromolaxia-Vyzakia was a Late Bronze Age harbor settlement, estimated by some authorities to be at least 25 hectares (60 acres) in size.
The settlement, which flourished from 1600 to 1100 BC, lies along the shores of the Larnaca salt lake at Hala Sultan Tekke.
Last month, the University of Gothenburg said it recently discovered tombs outside the Bronze Age trading metropolis.
It said they rank among the richest ever found in the Mediterranean region, and the precious tomb artifacts indicate their occupants ruled the city, which was a center for the copper trade in 1500–1300 BC.
“Considering the richness of the grave goods, it is a reasonable assumption that these were royal tombs,”said Peter Fischer, an archaeology professor and leader of the expedition.
The tombs consist of underground chambers accessed via a narrow passage from the surface. The chambers vary in size, measuring up to 4 x 5 meters (yards).
The Swedish expedition, excavating around Hala Sultan Tekke since 2010, has previously found chamber tombs.
“We found more than 500 complete artifacts distributed among two tombs,” it said.
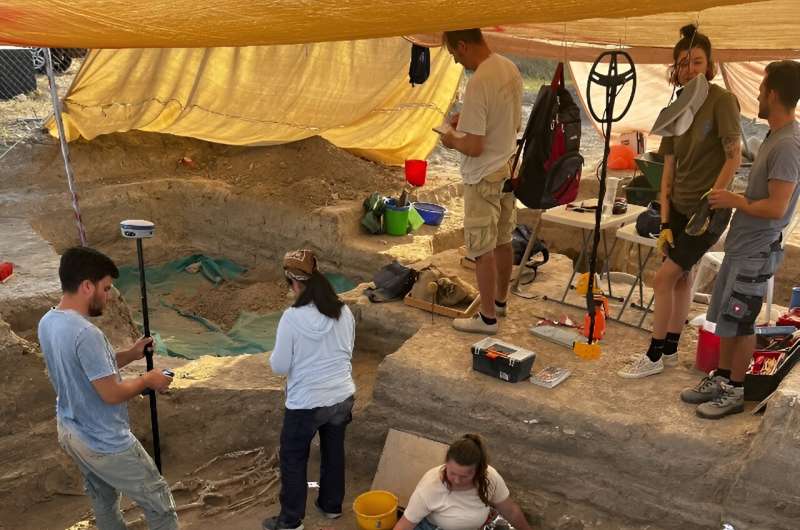

A handout picture shows an archaeological expedition team from the University of Gothenburg working at a site in Cyprus, on the shore of the Larnaca salt lake at Hala Sultan Tekke.
“Many of the artifacts consist of precious metals, gems, ivory and high-quality ceramics,” said Fischer on the university’s website.
He said about half of the artifacts were imported from neighboring cultures.
Gold and ivory came from Egypt.
Precious stones, such as blue lapis lazuli, dark red carnelian and blue-green turquoise, were imported from Afghanistan, India, and the Sinai, respectively.
The tombs also contain amber objects from the Baltic region.
‘From cultures east and north’
The tombs were discovered using magnetometers, an instrument that can detect objects and structures up to two meters beneath the surface.
Georgiou said three chamber tombs, preliminarily dated to the 14th century BC, were exposed during the most recent excavation season.
“One had been looted, most likely in the 19th century AD. “Two nearby tombs were found undisturbed.”
The tombs contained locally produced pottery and ornaments, “as well as numerous items of jewelry and other imported objects from the Aegean, Anatolia, Egypt, the Levant and cultures further east and north”.
He said other metal objects included jewelry of precious metals, diadems, daggers, knives, spearheads, and a mirror of bronze.
2023 AFP
Citation:
Cyprus dig reveals key trading hub in antiquity (2023, August 16)