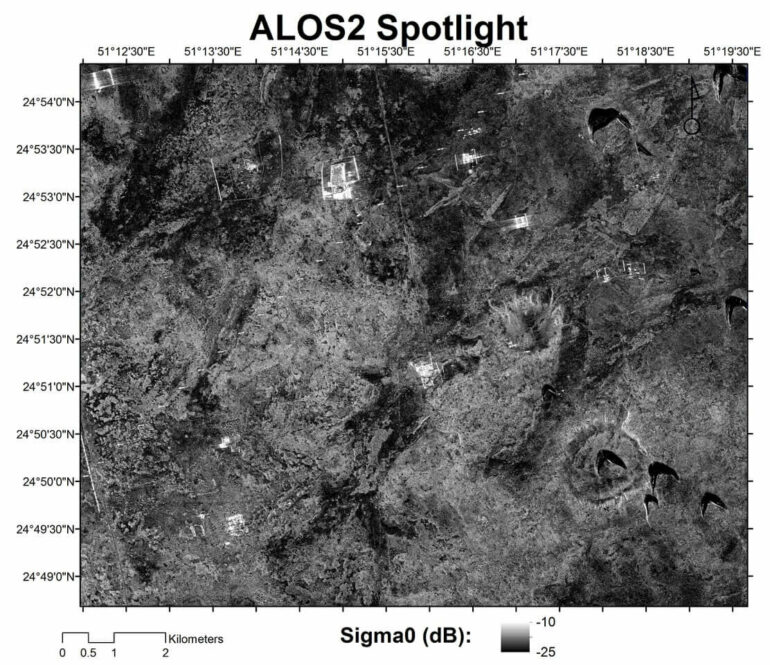
Scholars looking for underground water sources on the Eastern Arabian Peninsula for a project funded by the United State Agency for Aid and International Development, have accidentally uncovered the outlines of a settlement that appears to be more than 3,600 years old. A symmetrical 2 x 3 kilometer, landscaped area—or trace outlines of a settlement (and one of the largest potential settlements uncovered in the area) was identified using advanced radar satellite images in an area of Qatar where there was previously thought to be little evidence of sedentary, ancient civilizations. Their new study, published in the ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, counters the narrative that this peninsula was entirely nomadic and evidence mapped from space indicates that the population appears to have had a sophisticated understanding of how to use groundwater. The research also points to the critical need to study water and safeguard against climate fluctuations in arid areas.
“Makhfia,” the name attributed to the settlement by researchers at University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering and NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (and which refers to an invisible location in the local Arabic language), was discovered using L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar images from the Japanese Satellite ALOS 1 and specially acquired, high-resolution radar images by its successor, ALOS 2. While the settlement was not visible from space using normal satellite imaging tools nor through surface observation on the earth—the large, underground rectangular plot, it was determined, had to be manmade due to its shape, texture and soil composition which were in sharp contrast to surrounding geological features. Independent carbon dating of