Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to [email protected].
What is the universe expanding into if it’s already infinite? – Mael, age 10, Missoula, Montana
When you bake a loaf of bread or a batch of muffins, you put the dough into a pan. As the dough bakes in the oven, it expands into the baking pan. Any chocolate chips or blueberries in the muffin batter become farther away from each other as the muffin batter expands.
The expansion of the universe is, in some ways, similar. But this analogy gets one thing wrong – while the dough expands into the baking pan, the universe doesn’t have anything to expand into. It just expands into itself.
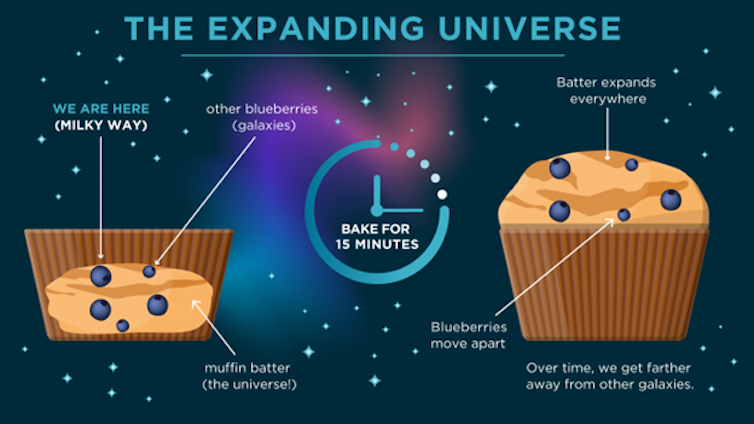
The universe expands like a baking muffin. The objects in space move farther apart, with more space between them.
UChicago Creative
It can feel like a brain teaser, but the universe is considered everything within the universe. In the expanding universe, there is no pan. Just dough. Even if there were a pan, it would be part of the universe and therefore it would expand with the pan.
Even for me, a teaching professor in physics and astronomy who has studied the universe for years, these ideas are hard to grasp. You don’t experience anything like this in your daily life. It’s like asking what direction is farther north of the North Pole.
Another way to think about the universe’s expansion is by thinking about how other galaxies are moving away from our galaxy, the Milky Way. Scientists know the universe is expanding because they can track other galaxies as they move away from ours. They define expansion using the rate that other galaxies move away from us. This definition allows them to imagine expansion without needing something to expand into.
The expanding universe
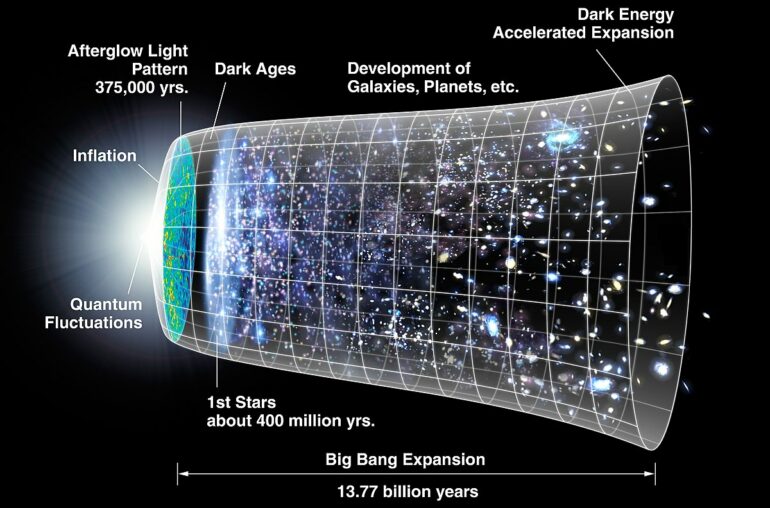
The universe started with the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago. The Big Bang describes the origin of the universe as an extremely dense, hot singularity. This tiny point suddenly went through a rapid expansion called inflation, where every place in the universe expanded outward. But the name Big Bang is misleading. It wasn’t a giant explosion, as the name suggests, but a time where the universe expanded rapidly.
The universe then quickly condensed and cooled down, and it started making matter and light. Eventually, it evolved to what we know today as our universe.
The idea that our universe was not static and could be expanding or contracting was first published by the physicist Alexander Friedman in 1922. He confirmed mathematically that the universe is expanding.
While Friedman proved that the universe was expanding, at least in some spots, it was Edwin Hubble who looked deeper into the expansion rate. Many other scientists confirmed that other galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way, but in 1929, Hubble published his famous paper…