Private citizens and companies may one day begin to permanently settle outer space and celestial bodies. But if we don’t enact governing laws in the meantime, space settlers may face legal chaos.
Many wars on Earth start over territorial disputes. In order to avoid such disputes in outer space, nations should consider enacting national laws that specify the extent of each settler’s authority in outer space and provide a process to resolve conflicts.
I have been researching and writing about space law for over 40 years. Through my work, I’ve studied ways to avoid war and resolve disputes in space.
Property in space
Space is an international area, and companies and individuals are free to land their space objects – including satellites, human-crewed and robotic spacecraft and human-inhabited facilities – on celestial bodies and conduct operations anywhere they please. This includes both outer space and celestial bodies such as the Moon.
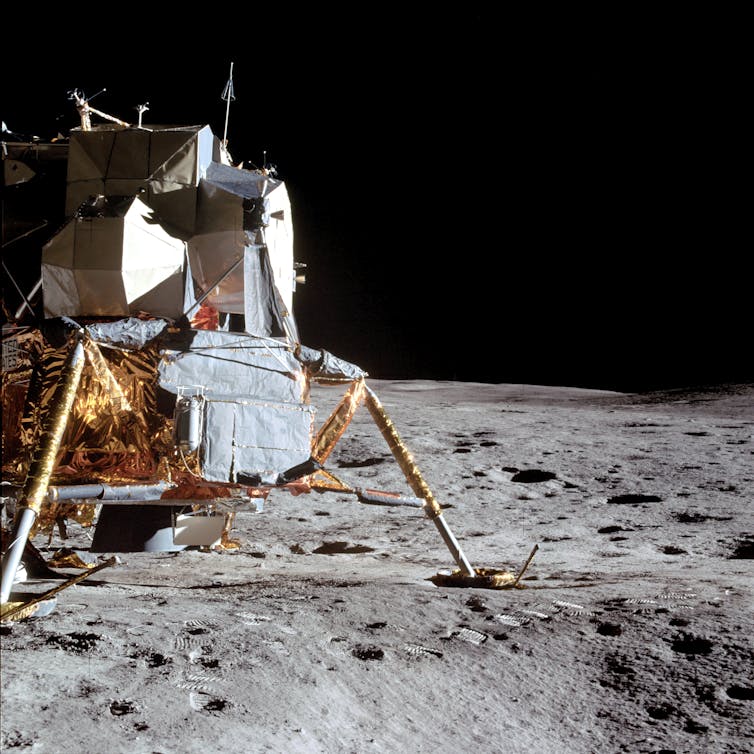

Space objects include landers, rovers, satellites and other objects on the surface of or in orbit around a celestial body.
Stocktrek Images/Stocktrek Images via Getty Images
The 1967 Outer Space Treaty prohibits territorial claims in outer space and on celestial bodies in order to avoid disputes. But without national laws governing space settlers, a nation might attempt to protect its citizens’ and companies’ interests by withdrawing from the treaty. They could then claim the territory where its citizens have placed their space objects.
Nations enforce territorial claims through military force, which would likely cost money and lives. An alternative to territorial claims, which I’ve been investigating and have come to prefer, would be to enact real property rights that are consistent with the Outer Space Treaty.
Territorial claims can be asserted only by national governments, while property rights apply to private citizens, companies and national governments that own property. A property rights law could specify how much authority settlers have and protect their investments in outer space and on celestial bodies.
The Outer Space Treaty
In 1967, the Outer Space Treaty went into effect. As of January 2025, 115 countries are party to this treaty, including the United States and most nations that have a space program.
The Outer Space Treaty is the main international agreement governing outer space. However, it is not self-executing.
The Outer Space Treaty outlines principles for the peaceful exploration and use of outer space and celestial bodies. However, the treaty does not specify how it will apply to the citizens and companies of nations that are parties to the treaty.
For this reason, the Outer Space Treaty is largely not a self-executing treaty. This means U.S. courts cannot apply the terms of the treaty to individual citizens and companies. For that to happen, the…