In a Maryland operating room one day in November 2025, doctors made medical history by transplanting a genetically modified pig kidney into a living patient. The kidney had been engineered to mimic human tissue and was grown in a pig, as an alternative to waiting around for a human organ donor who might never come. For decades, this idea lived at the edge of science fiction. Now it’s on the table, literally.
The patient is one of six taking part in the first clinical trial of pig-to-human kidney transplants. The goal: to see whether gene-edited pig kidneys can safely replace failing human ones.
A decade ago, scientists were chasing a different solution. Instead of editing the genes of pigs to make their organs human-friendly, they tried to grow human organs – made entirely of human cells – inside pigs. But in 2015 the National Institutes of Health paused funding for that work to consider its ethical risks. The pause remains today.
As a bioethicist and philosopher who has spent years studying the ethics of using organs grown in animals – including serving on an NIH-funded national working group examining oversight for research on human-animal chimeras – I was perplexed by the decision. The ban assumed the danger was making pigs too human. Yet regulators now seem comfortable making humans a little more pig.
Why is it considered ethical to put pig organs in humans but not to grow human organs in pigs?
Urgent need drives xenotransplantation
It’s easy to overlook the desperation driving these experiments. More than 100,000 Americans are waiting for organ transplants. Demand overwhelms supply, and thousands die each year before one becomes available.
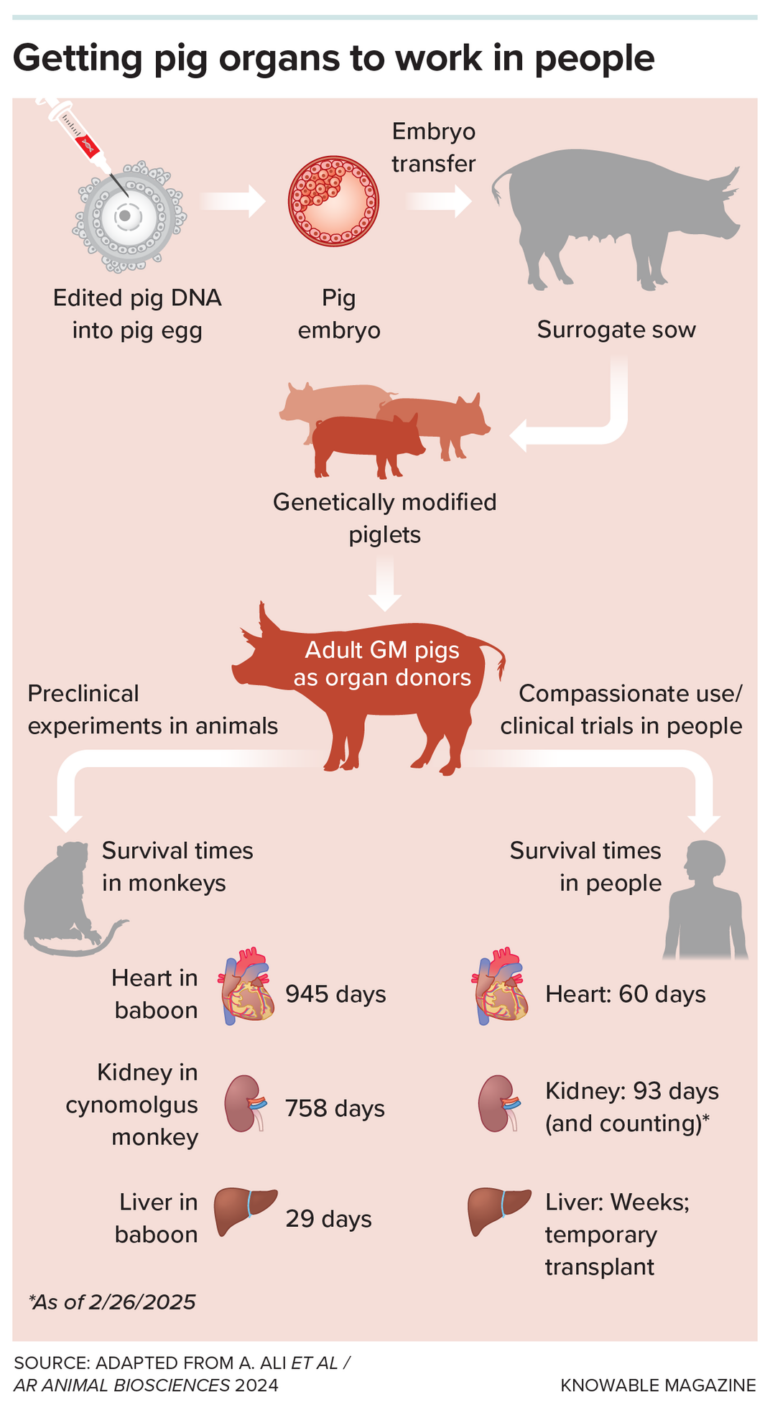
For decades, scientists have looked across species for help – from baboon hearts in the 1960s to genetically altered pigs today. The challenge has always been the immune system. The body treats cells it does not recognize as part of itself as invaders. As a result, it destroys them.
A recent case underscores this fragility. A man in New Hampshire received a gene-edited pig kidney in January 2025. Nine months later, it had to be removed because its function was declining. While this partial success gave scientists hope, it was also a reminder that rejection remains a central problem for transplanting organs across species, also known as xenotransplantation.
Decades of research have led to the first clinical trial of pig kidney transplants.
Researchers are attempting to work around transplant rejection by creating an organ the human body might tolerate, inserting a few human genes and deleting some pig ones. Still, recipients of these gene-edited pig organs need powerful drugs to suppress the immune system both during and long after the transplant procedure, and even this may not prevent rejection. Even human-to-human transplants require lifelong immunosuppressants.
That’s why another approach –