Even at a distance of 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) away, activity on the Sun can have adverse effects on technological systems on Earth. Solar flares – intense bursts of energy in the Sun’s atmosphere – and coronal mass ejections – eruptions of plasma from the Sun – can affect the communications, satellite navigation and power grid systems that keep society functioning.
On Sept. 24, 2025, NASA launched two new missions to study the influence of the Sun on the solar system, with further missions scheduled for 2026 and beyond.
I’m an astrophysicist who researches the Sun, which makes me a solar physicist. Solar physics is part of the wider field of heliophysics, which is the study of the Sun and its influence throughout the solar system.
The field investigates the conditions at a wide range of locations on and around the Sun, ranging from its interior, surface and atmosphere, and the constant stream of particles flowing from the Sun – called the the solar wind. It also investigates the interaction between the solar wind and the atmospheres and magnetic fields of planets.
The importance of space weather
Heliophysics intersects heavily with space weather, which is the influence of solar activity on humanity’s technological infrastructure.
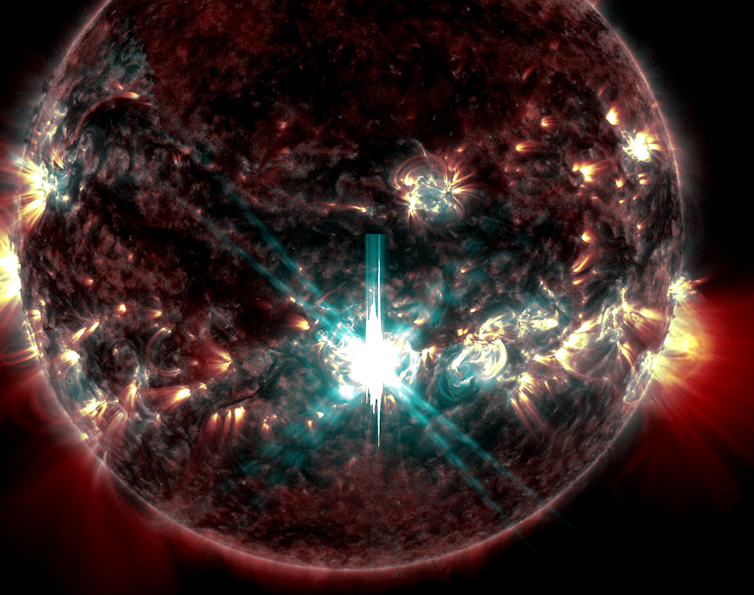
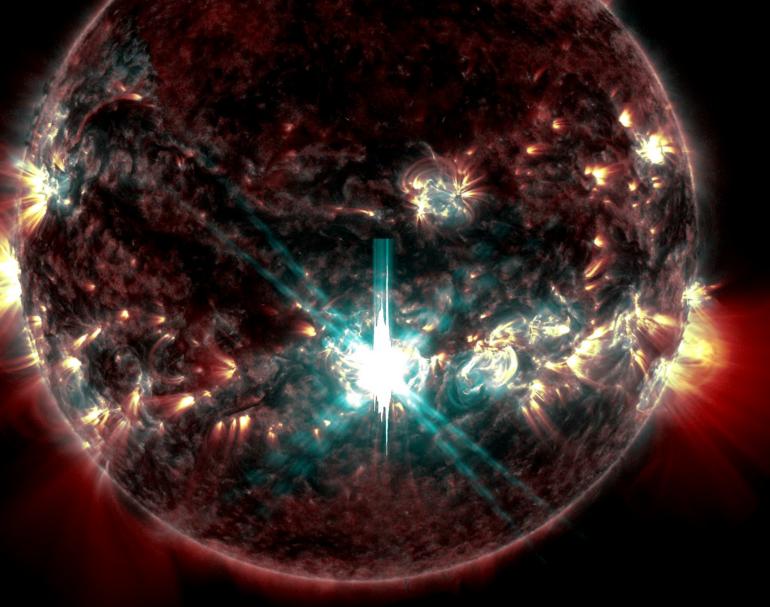
A major solar flare from Sept. 10, 2017, observed by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Ryan French/SDO/NASA
In May 2024, scientists observed the strongest space weather event since 2003. Several Earth-directed coronal mass ejections erupted from the Sun, causing an extreme geomagnetic storm as they interacted with Earth’s magnetic field.
This event produced a beautiful light show of the aurora across the world, providing a view of the northern and southern lights to tens of millions of people at lower latitudes for the first time.
However, geomagnetic storms come with a darker side. The same event triggered overheating alarms in power grids around the world, and triggered a loss in satellite navigation that may have cost the U.S. agricultural industry half a billion dollars.
However, this is far from the worst space weather event on record, with stronger events in 1989 and 2003 knocking out power grids in Canada and Sweden.
But even those events were small compared with the largest space weather event in recorded history, which took place in September 1859. This event, considered the worst-case scenario for extreme space weather, was called the Carrington Event. The Carrington Event produced widespread aurora, visible even close to the equator, and caused disruption to telegraph machines.
If an event like the Carrington event occurred today, it could cause widespread power outages, losses of satellites, days of grounded flights and more. Because space weather can be so destructive to human infrastructure, scientists want to better understand these events.
NASA’s heliophysics missions
NASA has a vast suite of…