Astronomers have discovered more than 5,000 planets outside of the solar system to date. The grand question is whether any of these planets are home to life. To find the answer, astronomers will likely need more powerful telescopes than exist today.
I am an astronomer who studies astrobiology and planets around distant stars. For the last seven years, I have been co-leading a team that is developing a new kind of space telescope that could collect a hundred times more light than the James Webb Space Telescope, the biggest space telescope ever built.
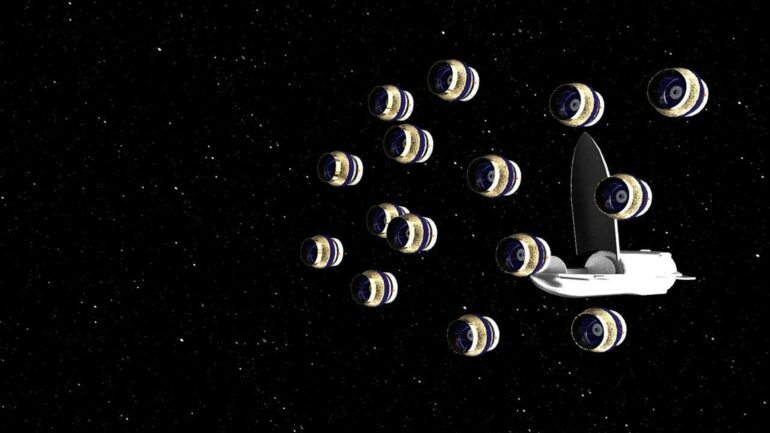
Almost all space telescopes, including Hubble and Webb, collect light using mirrors. Our proposed telescope, the Nautilus Space Observatory, would replace large, heavy mirrors with a novel, thin lens that is much lighter, cheaper and easier to produce than mirrored telescopes. Because of these differences, it would be possible to launch many individual units into orbit and create a powerful network of telescopes.

Exoplanets, like TOI-700d shown in this artist’s conception, are planets beyond our solar system and are prime candidates in the search for life.
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
The need for larger telescopes
Exoplanets – planets that orbit stars other than the Sun – are prime targets in the search for life. Astronomers need to use giant space telescopes that collect huge amounts of light to study these faint and faraway objects.

The James Webb Space Telescope is just barely able to search exoplanets for signs of life.
NASA
Existing telescopes can detect exoplanets as small as Earth. However, it takes a lot more sensitivity to begin to learn about the chemical composition of these planets. Even Webb is just barely powerful enough to search certain exoplanets for clues of life – namely gases in the atmosphere.
The James Webb Space Telescope cost more than US$8 billion and took over 20 years to build. The next flagship telescope is not expected to fly before 2045 and is estimated to cost $11 billion. These ambitious telescope projects are always expensive, laborious and produce a single powerful – but very specialized – observatory.
A new kind of telescope
In 2016, aerospace giant Northrop Grumman invited me and 14 other professors and NASA scientists – all experts on exoplanets and the search for extraterrestrial life – to Los Angeles to answer one question: What will exoplanet space telescopes look like in 50 years?
In our discussions, we realized that a major bottleneck preventing the construction of more powerful telescopes is the challenge of making larger mirrors and getting them into orbit. To bypass this bottleneck, a few of us came up with the idea of revisiting an old technology called diffractive lenses.