A bright fireball streaked across the sky above mountains, glaciers and spruce forest near the town of Revelstoke in British Columbia, Canada, on the evening of March 31, 1965. Fragments of this meteorite, discovered by beaver trappers, fell over a lake. A layer of ice saved them from the depths and allowed scientists a peek into the birth of the solar system.
Nearly 60 years later, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission returned from space with a sample of an asteroid named Bennu, similar to the one that rained rocks over Revelstoke. Our research team has published a chemical analysis of those samples, providing insight into how some of the ingredients for life may have first arrived on Earth.
Born in the years bracketing the Revelstoke meteorite’s fall, the two of us have spent our careers in the meteorite collections of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C., and the Natural History Museum in London. We’ve dreamed of studying samples from a Revelstoke-like asteroid collected by a spacecraft.
Then, nearly two decades ago, we began turning those dreams into reality. We joined NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission team, which aimed to send a spacecraft to collect and return an asteroid sample to Earth. After those samples arrived on Sept. 24, 2023, we got to dive into a tale of rock, ice and water that hints at how life could have formed on Earth.
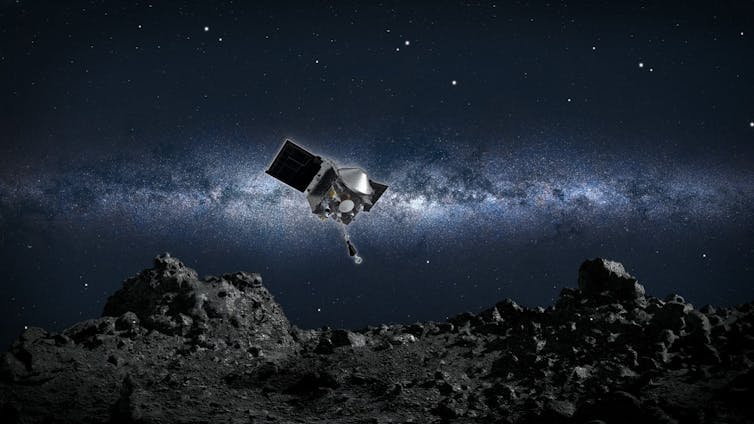

In this illustration, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft collects a sample from the asteroid Bennu.
NASA/Goddard/University of Arizona
The CI chondrites and asteroid Bennu
To learn about an asteroid – a rocky or metallic object in orbit around the Sun – we started with a study of meteorites.
Asteroids like Bennu are rocky or metallic objects in orbit around the Sun. Meteorites are the pieces of asteroids and other natural extraterrestrial objects that survive the fiery plunge to the Earth’s surface.
We really wanted to study an asteroid similar to a set of meteorites called chondrites, whose components formed in a cloud of gas and dust at the dawn of the solar system billions of years ago.
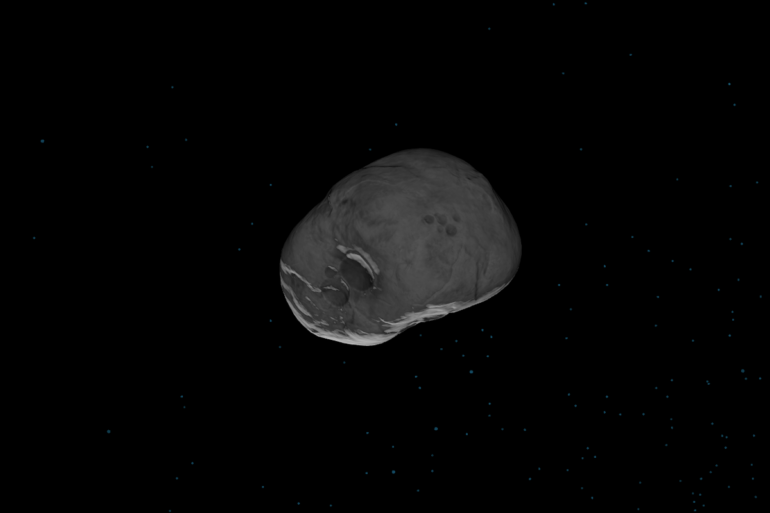
The Revelstoke meteorite is in a group called CI chondrites. Laboratory-measured compositions of CI chondrites are essentially identical, minus hydrogen and helium, to the composition of elements carried by convection from the interior of the Sun and measured in the outermost layer of the Sun. Since their components formed billions of years ago, they’re like chemically unchanged time capsules for the early solar system.
So, geologists use the chemical compositions of CI chondrites as the ultimate reference standard for geochemistry. They can compare the compositions of everything from other chondrites to Earth rocks. Any differences from the CI chondrite composition would have happened through the same processes that formed asteroids and planets.
CI chondrites are rich in clay and formed when ice melted in an ancient asteroid, altering the rock. They are also…