The size and spin of black holes can reveal important information about how and where they formed, according to new research.
The study, led by scientists at Cardiff University, tests the idea that many of the black holes observed by astronomers have merged multiple times within densely populated environments containing millions of stars.
The work is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The team examined the public catalogue of 69 gravitational wave events involving binary black holes detected by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) and Virgo Observatory for clues about these successive mergers, which they believe create black holes with distinctive spin patterns.
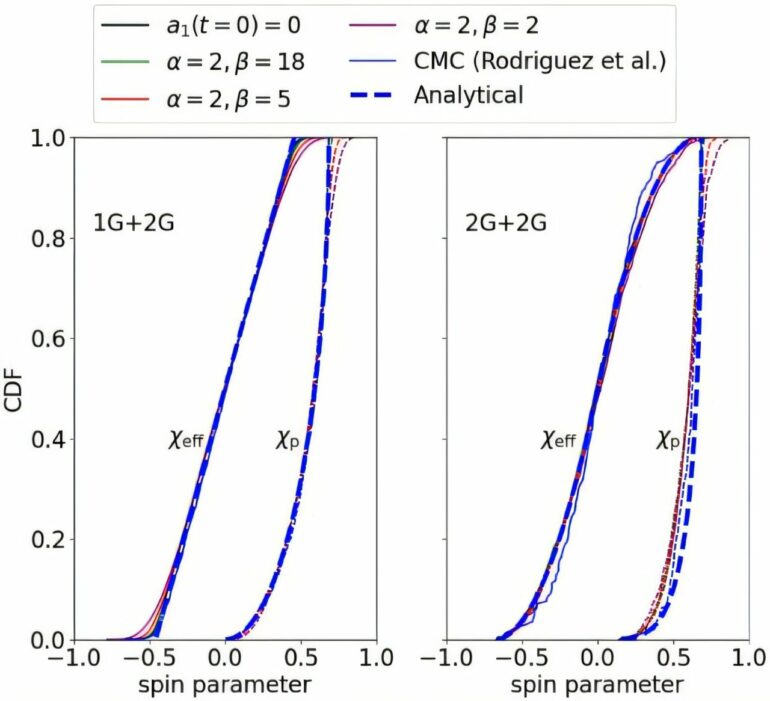
They discovered that a black hole’s spin changes when it reaches a certain mass, suggesting it may have been produced through a series of multiple previous mergers. Their study shows how spin measurements can reveal the formation history of a black hole and offers a step forward in understanding the diverse origins of these astrophysical phenomena.
Lead author Dr. Fabio Antonini from Cardiff University’s School of Physics and Astronomy said, “As we observe more black hole mergers with gravitational wave detectors like LIGO and Virgo, it becomes ever clearer that black holes exhibit diverse masses and spins, suggesting they may have formed in different ways. However, identifying which of these formation scenarios is most common has been challenging.”
The team pinpointed a clear mass threshold in the gravitational waves data where black hole spins consistently change. They say this pattern aligns with existing models that assume black holes are produced through repeated collisions in clusters, rather than in other environments where spin distributions are different.
This result supports a robust and relatively model-independent signature for identifying these kinds of black holes, something that has been challenging to confirm until now, according to the team.
Dr. Isobel Romero-Shaw, a co-author and a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Cambridge, added, “Our study gives us a powerful, data-driven way to identify the origins of a black hole’s formation history, showing that the way it spins is a strong indicator of it belonging to a group of high-mass black holes, which form in densely populated star clusters where small black holes repeatedly collide and merge with one another.”
This study will now help astrophysicists further refine computer models which simulate the formation of black holes, helping to shape how future gravitational wave detections are interpreted.
Thomas Callister, one of the study’s co-authors and a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Chicago, added, “Collaborating with other researchers and using advanced statistical methods will help to confirm and expand our findings, especially as we move toward next-generation detectors. The Einstein Telescope, for example, could detect even more massive black holes and provide unprecedented insights into their origins.”
More information:
Fabio Antonini et al, Star Cluster Population of High Mass Black Hole Mergers in Gravitational Wave Data, Physical Review Letters (2025). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.011401
Provided by
Cardiff University
Citation:
Origins of black holes are revealed in their spin, gravitational wave data analysis finds (2025, January 7)