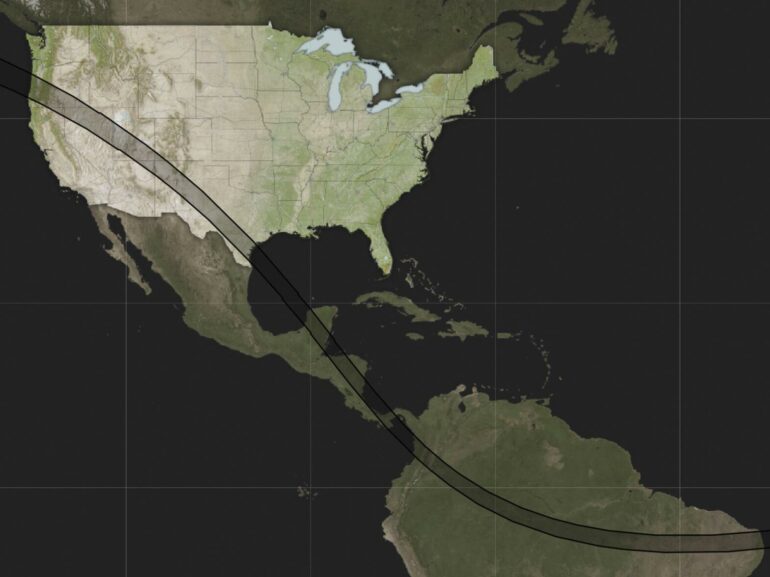
A rare “ring of fire” eclipse of the sun cuts across the Americas on Saturday, stretching from Oregon to Brazil, and huge crowds were on the move before dawn in cities, rural areas and national parks to try to catch a glimpse of it.
For the small towns and cities along its narrow path, there was a mix of excitement, worries about the weather and concerns they’d be overwhelmed by visitors flocking to see the celestial event, also called an annular solar eclipse. Clouds and fog threatened to obscure the view of the eclipse in some western states, including California and Oregon.
Unlike a total solar eclipse, the moon doesn’t completely cover the sun during a ring of fire eclipse. When the moon lines up between Earth and the sun, it leaves a bright, blazing border.
Saturday’s path: Oregon, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico and Texas in the U.S., with a sliver of California, Arizona and Colorado. Next: Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula, Belize, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia and Brazil. Much of the rest of the Western Hemisphere gets a partial eclipse.
The celestial event brought eclipse watchers from around the U.S. to remote corners of the country to try to get the best view possible. At Bryce Canyon national park in southern Utah tiny lights could be seen along a well known trail that snakes through a valley of red rock hoodoos as eclipse enthusiasts hit the trail before sunrise to stake out their preferred spot
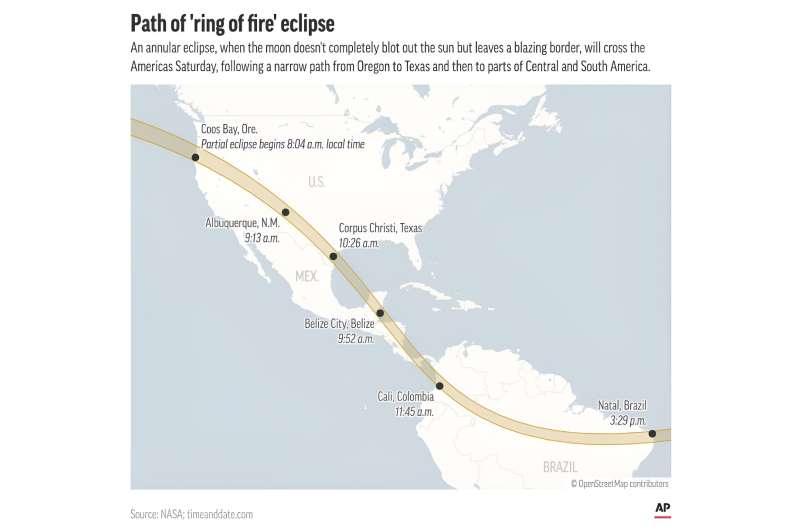
An annular eclipse will be viewable along a narrow swath of the Americas Saturday. © AP Digital Embed
“I just think it’s one of those things that unites us all,” said John Edwards, a cancer drug developer who traveled alone across the country to try to watch the eclipse from Bryce Canyon. “I just think it’s seeing these unique experiences that come rarely is what got me here. This is about as rare as it gets.”
Viewing all depends on clear skies—part of the U.S. path could see clouds. NASA and other groups planned to livestream it.
With a chance of rain in its forecast, the small town of Reedsport near Oregon’s Pacific Coast moved its eclipse festival inside so that a bounce house and games wouldn’t get soaked in the mud.
“But we’re still hoping that we might get a glimpse of it,” said city official Rosa Solano.
Weather was less of a concern in tiny Baker, Nevada, where the population hovers around 100. Inn and general store owner Liz Woolsey made T-shirts and planned a slate of activities including a drum circle and a dance party. Her seven rooms have been booked for over a year.
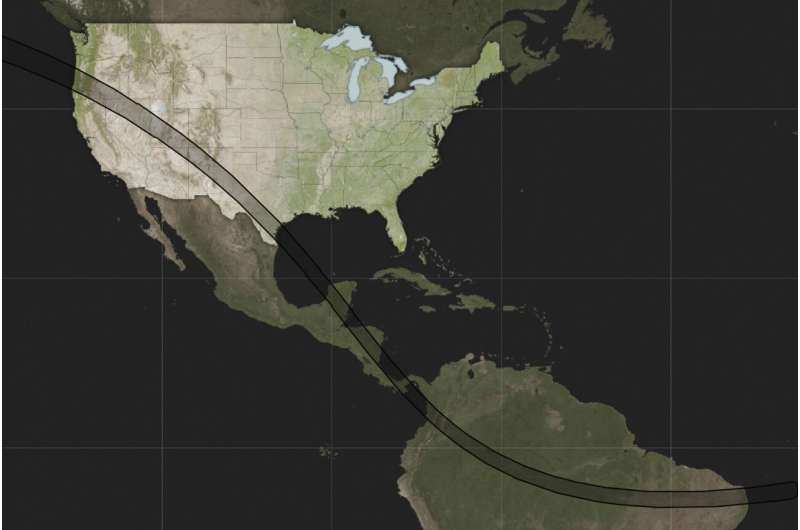
Este mapa, proporcionado por la NASA, muestra la ruta que seguirá el eclipse anular solar del sábado 14 de octubre de 2023 a través de Norteamérica, Centroamérica y Sudamérica. © NASA vía AP
“For a little place, we’re putting on a good show,” said Woolsey, who became an eclipse enthusiast after seeing the 2017 total solar eclipse that swept the U.S. from coast to coast.
Viewers on the East Coast were prepared to see less of the event—close to a quarter eclipse around midday in some areas, such as New York City—but were nonetheless geared up to watch the skies. In Maine, viewers expected to see only about 12% of the sun covered, but the Clark Telescope on the grounds of the Versant Power Astronomy Center at the University of Maine was open to the public.
The planetarium was selling safety glasses for $2 Saturday to encourage safe viewing, said Shawn Laatsch, director of the Versant Power Astronomy and the Maynard Jordan Planetarium
“As the Moon passes between the Earth and the sun, it casts its shadow on our planet,” said Laatsch. “In a very real sense, solar eclipses are ‘made in the shade’ of the moon.”
Tens of thousands could get a double treat in Albuquerque, New Mexico. For the city’s annual air balloon fiesta, which ends this weekend, hundreds of colorful hot air balloons lift off around dawn, hours before the eclipse briefly dims the skies.
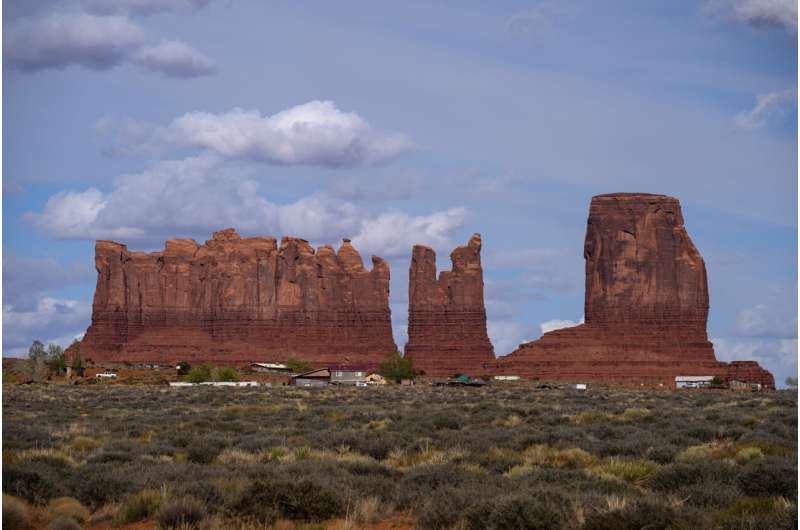

Homes and other structures are seen in Monument Valley, Ariz., on the Navajo reservation, April 19, 2020. Monument Valley and various other parks on the Navajo Nation will be closed Saturday, Oct. 14, 2023, due to the “Ring of Fire” solar eclipse. © AP Photo/Carolyn Kaster, File
Colombia’s Tatacoa desert was playing host to astronomers helping a group of visually impaired people experience the eclipse through raised maps and temperature changes as the moon blots out the sun.
At the Cancun Planetarium, young visitors built box projectors to indirectly and safely view the ring of fire. The ancient Maya—who called eclipses “broken sun”—may have used dark volcanic glass to protect their eyes, said archeologist Arturo Montero of Tepeyac University in Mexico City.
Towns and national parks in the path braced for a huge throngs. Officials in Oregon’s Klamath County urged residents to stock up on groceries and fill their gas tanks in case traffic backs up on its two-lane highways. Utah’s Bryce Canyon expected Saturday to be the park’s busiest day of the year, spokesperson Peter Densmore said. Brazil’s Pedra da Boca state park, known for its rocky outcrops for climbing and rappelling was also expecting crowds.
The entire eclipse—from the moment the moon starts to obscure the sun until it’s back to normal—is 2 1/2 to three hours at any given spot. The ring of fire portion lasts from three to five minutes, depending on location.
Next April, a total solar eclipse will crisscross the U.S. in the opposite direction. That one will begin in Mexico and go from Texas to New England before ending in eastern Canada.
The next ring of fire eclipse is in October next year at the southernmost tip of South America. Antarctica gets one in 2026. It will be 2039 before another ring of fire is visible in the U.S., and Alaska will be the only state in its direct path.
2023 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Citation:
‘Ring of fire’ solar eclipse will cut across the Americas, stretching from Oregon to Brazil (2023, October 14)