The ingredients for life are spread throughout the universe. While Earth is the only known place in the universe with life, detecting life beyond Earth is a major goal of modern astronomy and planetary science.
We are two scientists who study exoplanets and astrobiology. Thanks in large part to next-generation telescopes like James Webb, researchers like us will soon be able to measure the chemical makeup of atmospheres of planets around other stars. The hope is that one or more of these planets will have a chemical signature of life.
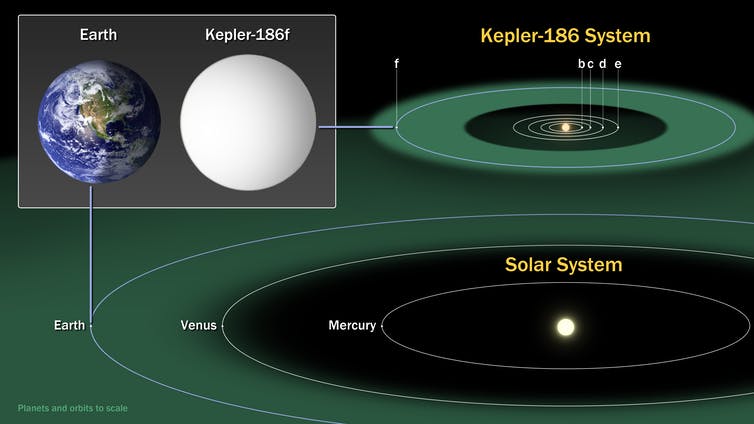
There are many known exoplanets in habitable zones – orbits not too close to a star that the water boils off but not so far that the planet is frozen solid – as marked in green for both the solar system and Kepler-186 star system with its planets labeled b, c, d, e and f.
NASA Ames/SETI Institute/JPL-Caltech/Wikimedia Commons
Habitable exoplanets
Life might exist in the solar system where there is liquid water – like the subsurface aquifers on Mars or in the oceans of Jupiter’s moon Europa. However, searching for life in these places is incredibly difficult, as they are hard to reach and detecting life would require sending a probe to return physical samples.
Many astronomers believe there’s a good chance that life exists on planets orbiting other stars, and it’s possible that’s where life will first be found.
Theoretical calculations suggest that there are around 300 million potentially habitable planets in the Milky Way galaxy alone and several habitable Earth-sized planets within only 30 light-years of Earth – essentially humanity’s galactic neighbors. So far, astronomers have discovered over 5,000 exoplanets, including hundreds of potentially habitable ones, using indirect methods that measure how a planet affects its nearby star. These measurements can give astronomers information on the mass and size of an exoplanet, but not much else.
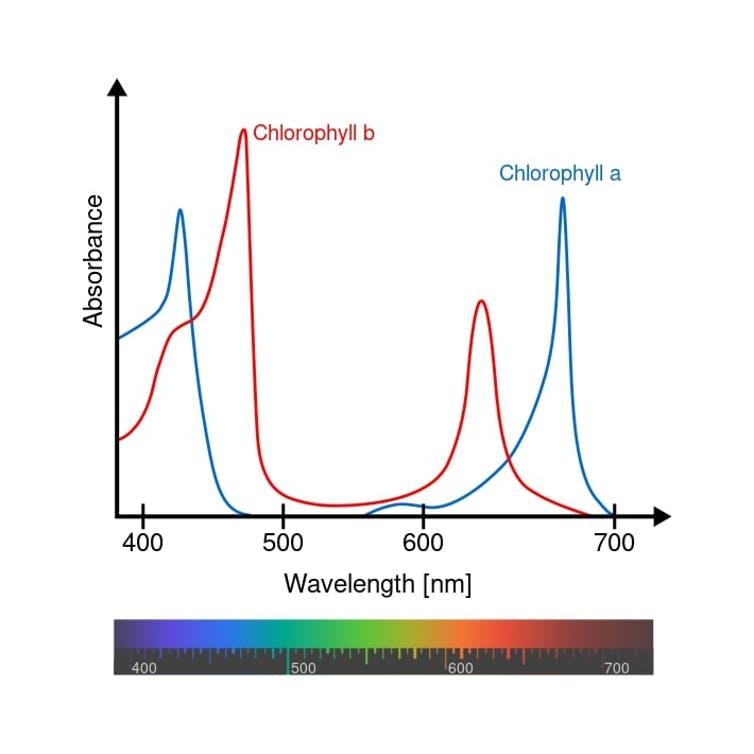
Every material absorbs certain wavelengths of light, as shown in this diagram depicting the wavelengths of light absorbed most easily by different types of chlorophyll.
Daniele Pugliesi/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Looking for biosignatures
To detect life on a distant planet, astrobiologists will study starlight that has interacted with a planet’s surface or atmosphere. If the atmosphere or surface was transformed by life, the light may carry a clue, called a “biosignature.”
For the first half of its existence, Earth sported an atmosphere without oxygen, even though it hosted simple, single-celled life. Earth’s biosignature was very faint during this early era. That changed abruptly 2.4 billion years ago when a new family of algae evolved. The algae used a process of photosynthesis that produces free oxygen – oxygen that isn’t chemically bonded to any other element. From that time on, Earth’s oxygen-filled atmosphere has left a strong and easily…


