Objects in space reveal different aspects of their composition and behavior at different wavelengths of light. Supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is one of the most well-studied objects in the Milky Way across the wavelength spectrum. However, there are still secrets hidden within the star’s tattered remains.
The latest are being unlocked by one of the newest tools in the researchers’ toolbox, the James Webb Space Telescope—and Webb’s recent look in the near-infrared has blown researchers away.
Like a shiny, round ornament ready to be placed in the perfect spot on a holiday tree, supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A) gleams in a new image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
As part of the 2023 Holidays at the White House, First Lady of the United States Dr. Jill Biden debuted the first-ever White House Advent Calendar. To showcase the “Magic, Wonder, and Joy” of the holiday season, Dr. Biden and NASA are celebrating with this new image from Webb.
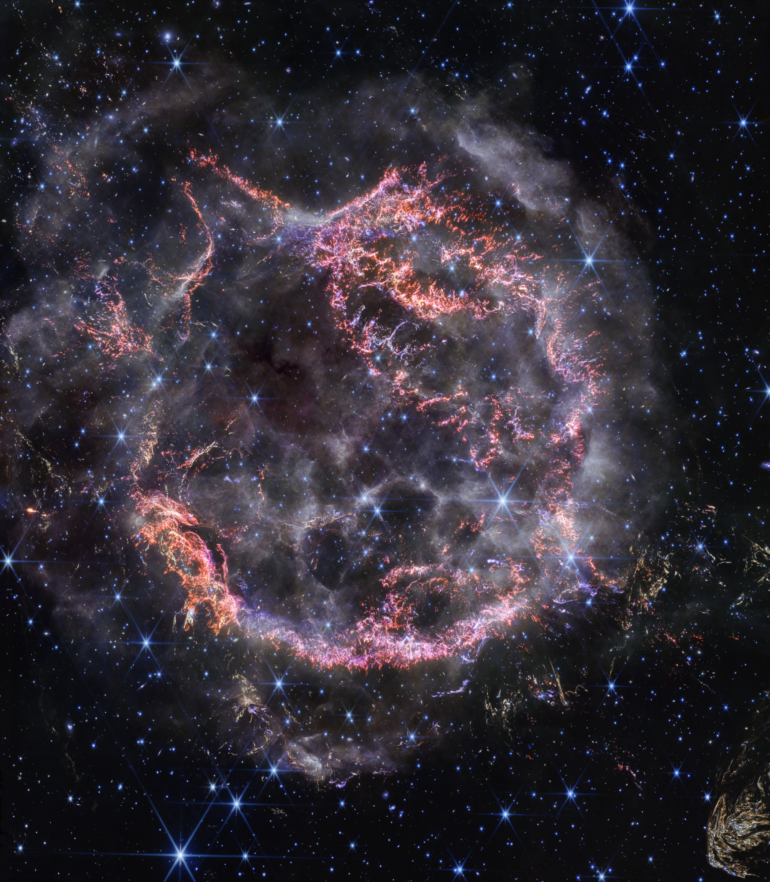
While all is bright, this scene is no proverbial silent night. Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) view of Cas A displays this stellar explosion at a resolution previously unreachable at these wavelengths. This high-resolution look unveils intricate details of the expanding shell of material slamming into the gas shed by the star before it exploded.
Cas A is one of the most well-studied supernova remnants in all of the cosmos. Over the years, ground-based and space-based observatories, including NASA’s Chandra X-Ray Observatory, Hubble Space Telescope, and retired Spitzer Space Telescope have assembled a multiwavelength picture of the object’s remnant.
However, astronomers have now entered a new era in the study of Cas A. In April 2023, Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) started this chapter, revealing new and unexpected features within the inner shell of the supernova remnant. Many of those features are invisible in the new NIRCam image, and astronomers are investigating why.
‘Like shards of glass’
Infrared light is invisible to our eyes, so image processors and scientists translate these wavelengths of light to visible colors. In this newest image of Cas A, colors were assigned to different filters from NIRCam, and each of those colors hints at different activity occurring within the object.
At first glance, the NIRCam image may appear less colorful than the MIRI image. However, this simply comes down to the wavelengths in which the material from the object is emitting its light.
The most noticeable colors in Webb’s newest image are clumps represented in bright orange and light pink that make up the inner shell of the supernova remnant. Webb’s razor-sharp view can detect the tiniest knots of gas, comprised of sulfur, oxygen, argon, and neon from the star itself.
Embedded in this gas is a mixture of dust and molecules, which will eventually become components of new stars and planetary systems. Some filaments of debris are too tiny to be resolved by even Webb, meaning they are comparable to or less than 10 billion miles across (around 100 astronomical units). In comparison, the entirety of Cas A spans 10 light-years across, or 60 trillion miles.
“With NIRCam’s resolution, we can now see how the dying star absolutely shattered when it exploded, leaving filaments akin to tiny shards of glass behind,” said Danny Milisavljevic of Purdue University, who leads the research team. “It’s really unbelievable after all these years studying Cas A to now resolve those details, which are providing us with transformational insight into how this star exploded.”
Hidden green monster
When comparing Webb’s new near-infrared view of Cas A with the mid-infrared view, its inner cavity and outermost shell are curiously devoid of color.
The outskirts of the main inner shell, which appeared as a deep orange and red in the MIRI image, now look like smoke from a campfire. This marks where the supernova blast wave is ramming into surrounding circumstellar material. The dust in the circumstellar material is too cool to be detected directly at near-infrared wavelengths, but lights up in the mid-infrared.
Researchers say the white color is light from synchrotron radiation, which is emitted across the electromagnetic spectrum, including the near-infrared. It’s generated by charged particles traveling at extremely high speeds spiraling around magnetic field lines. Synchrotron radiation is also visible in the bubble-like shells in the lower half of the inner cavity.
Also not seen in the near-infrared view is the loop of green light in the central cavity of Cas A that glowed in mid-infrared, nicknamed the Green Monster by the research team. This feature was described as “challenging to understand” by researchers at the time of their first look.
While the “green” of the Green Monster is not visible in NIRCam, what’s left over in the near-infrared in that region can provide insight into the mysterious feature. The circular holes visible in the MIRI image are faintly outlined in white and purple emission in the NIRCam image—this represents ionized gas. Researchers believe this is due to the supernova debris pushing through and sculpting gas left behind by the star before it exploded.
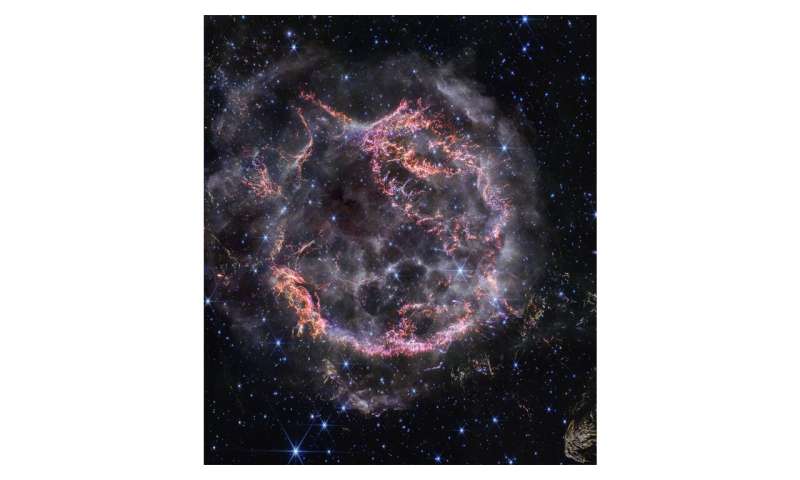
Cassiopeia A (NIRCam Image). © Webb Space Telescope
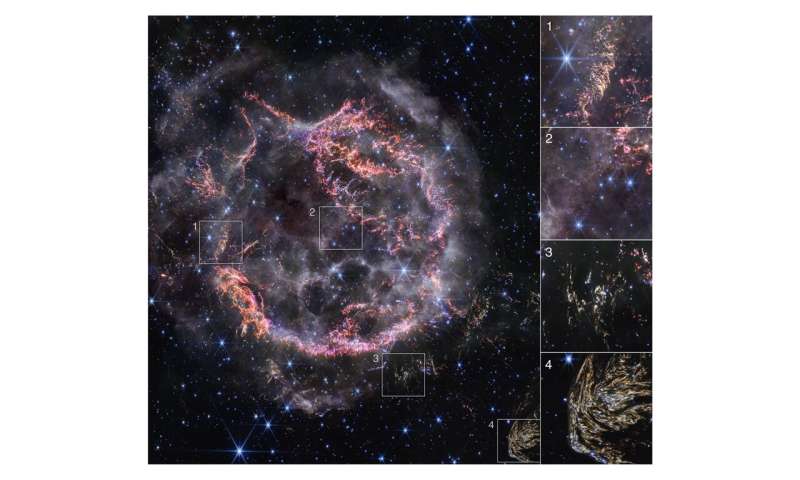
This image highlights several interesting features of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A as seen with Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera): 1) NIRCam’s exquisite resolution is able to detect tiny knots of gas, comprised of sulfur, oxygen, argon, and neon from the star itself. Some filaments of debris are too tiny to be resolved even by Webb, meaning they are comparable to or less than 10 billion miles across (around 100 astronomical units). Researchers say this represents how the star shattered like glass when it exploded. 2) Circular holes visible in the MIRI image within the Green Monster, a loop of green light in Cas A’s inner cavity, are faintly outlined in white and purple emission in the NIRCam image—this represents ionized gas. Researchers believe this is due to the supernova debris pushing through and sculpting gas left behind by the star before it exploded. 3) This is one of a few light echoes visible in NIRCam’s image of Cas A. A light echo occurs when light from the star’s long-ago explosion has reached, and is warming, distant dust, which is glowing as it cools down. 4) NIRCam captured a particularly intricate and large light echo, nicknamed Baby Cas A by researchers. It is actually located about 170 light-years behind the supernova remnant. © NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Danny Milisavljevic (Purdue University), Ilse De Looze (UGent), Tea Temim (Princeton University)
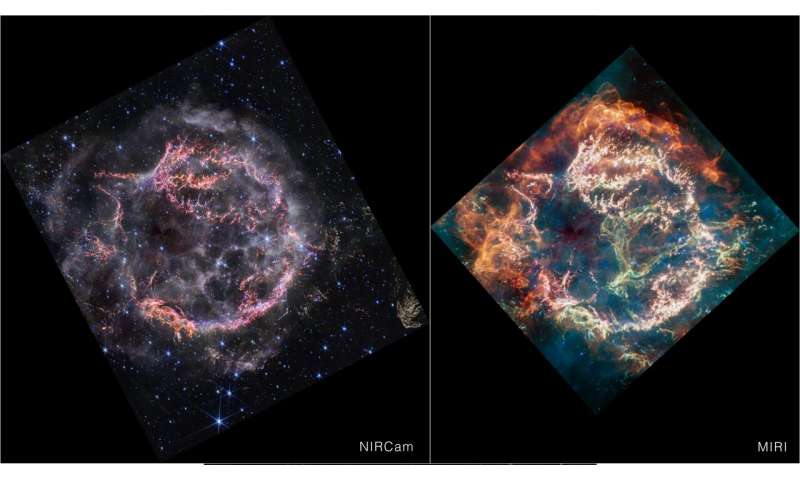

This image provides a side-by-side comparison of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A) as captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). © NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Danny Milisavljevic (Purdue University), Ilse De Looze (UGent), Tea Temim (Princeton University)
Baby Cas A
Researchers were also absolutely stunned by one fascinating feature at the bottom right corner of NIRCam’s field of view. They’re calling that large, striated blob Baby Cas A—because it appears like an offspring of the main supernova.
This is a light echo, where light from the star’s long-ago explosion has reached and is warming distant dust, which is glowing as it cools down. The intricacy of the dust pattern, and Baby Cas A’s apparent proximity to Cas A itself, are particularly intriguing to researchers. In actuality, Baby Cas A is located about 170 light-years behind the supernova remnant.
There are also several other, smaller light echoes scattered throughout Webb’s new portrait.
The Cas A supernova remnant is located 11,000 light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia. It’s estimated to have exploded about 340 years ago from our point of view.
Provided by
Space Telescope Science Institute
Citation:
Webb stuns with new high-definition look at exploded star (2023, December 11)



