NASA’s Webb Space Telescope has identified new clues about the surface of Pluto’s largest moon.
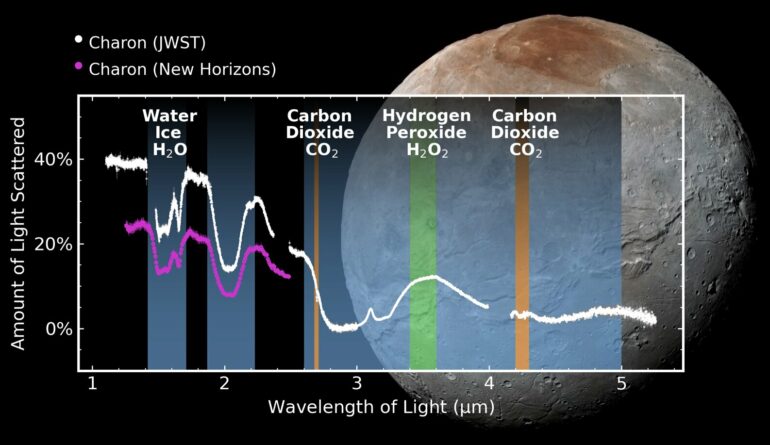
It detected for the first time traces of carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on the surface of Charon, which is about half Pluto’s size.
Previous research, including a flyby from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft in 2015, revealed that the moon’s surface was coated by water ice. But scientists couldn’t sense chemicals lurking at certain infrared wavelengths until the Webb telescope came around to fill in the gaps.
“There’s a lot of fingerprints of chemicals that we otherwise wouldn’t get to see,” said Carly Howett, a New Horizons scientist who was not involved with the new study.
The research published Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications.
Pluto, a dwarf planet, and its moons are in the far fringes of our solar system in a zone known as the Kuiper Belt. Besides water ice, ammonia and organic materials were previously detected on Charon. Both Pluto and Charon are over 3 billion miles (4.83 billion kilometers) from the sun and are likely too chilly to support life.
Scientists think the hydrogen peroxide may have sprung from radiation pinging off water molecules on Charon’s surface. The carbon dioxide might spew to the surface after impacts, said study co-author Silvia Protopapa from the Southwest Research Institute.
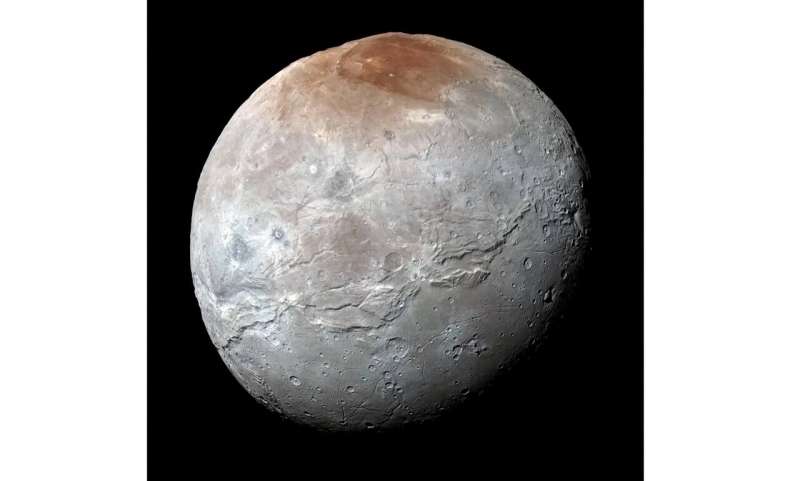

This image provided by NASA shows an enhanced color view of Pluto’s big moon Charon captured by the New Horizons spacecraft, July 14, 2015. © NASA via AP
The latest detection is key to studying how Charon came to be and may help scientists tease out the makeup of other faraway moons and planets.
2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Citation:
Webb telescope detects traces of carbon dioxide on the surface of Pluto’s largest moon (2024, October 1)