When NASA scientists opened the sample return canister from the OSIRIS-REx asteroid sample mission in late 2023, they found something astonishing.
Dust and rock collected from the asteroid Bennu contained many of life’s building blocks, including all five nucleobases used in DNA and RNA, 14 of the 20 amino acids found in proteins, and a rich collection of other organic molecules. These are built primarily from carbon and hydrogen, and they often form the backbone of life’s chemistry.
For decades, scientists have predicted that early asteroids may have delivered the ingredients of life to Earth, and these findings seemed like promising evidence.
Even more surprising, these amino acids from Bennu were split almost evenly between “left-handed” and “right-handed” forms. Amino acids come in two mirror-image configurations, just like our left and right hands, called chiral forms.
On Earth, almost all biology requires the left-handed versions. If scientists had found a strong left-handed excess in Bennu, it would have suggested that life’s molecular asymmetry might have been inherited directly from space. Instead, the near-equal mixture points to a different story: Life’s left-handed preference likely emerged later, through processes on Earth, rather than being pre-imprinted in the material delivered by asteroids.
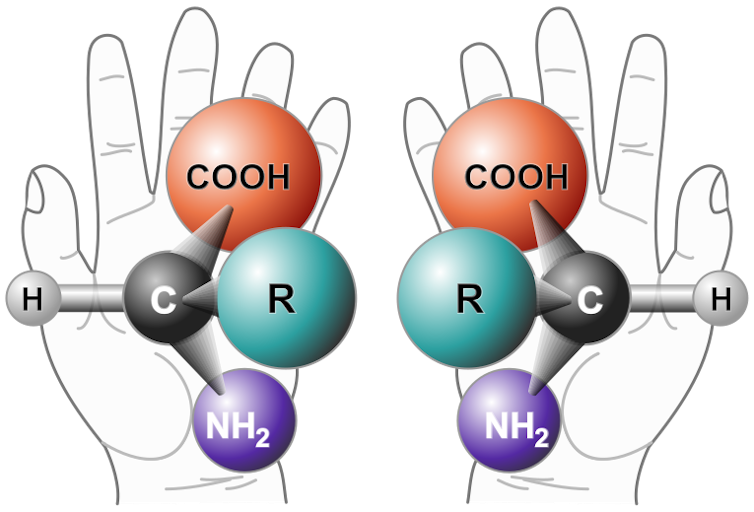
A ‘chiral’ molecule is one that is not superposable with another that is its mirror image, even if you rotate it.
NASA
If space rocks can carry familiar ingredients but not the chemical “signature” that life leaves behind, then identifying the true signs of biology becomes extremely complicated.
These discoveries raise a deeper question – one that becomes more urgent as new missions target Mars, the Martian moons and the ocean worlds of our solar system: How do researchers detect life when the chemistry alone begins to look “lifelike”? If nonliving materials can produce rich, organized mixtures of organic molecules, then the traditional signs we use to recognize biology may no longer be enough.
As a computational scientist studying biological signatures, I face this challenge directly. In my astrobiology work, I ask how to determine whether a collection of molecules was formed by complex geochemistry or by extraterrestrial biology, when exploring other planets.
In a new study in the journal PNAS Nexus, my colleagues and I developed a framework called LifeTracer to help answer this question. Instead of searching for a single molecule or structure that proves the presence of biology, we attempted to classify how likely mixtures of compounds preserved in rocks and meteorites were to contain traces of life by examining the full chemical patterns they contain.
Identifying potential biosignatures
The key idea behind our framework is that life produces molecules with purpose, while nonliving chemistry does not. Cells must store energy, build membranes and…