Diversifying the science, technology, engineering and math fields has long been a top priority of many universities and tech companies. It’s also a goal of the National Science Foundation, the biggest funder of university-led research and development in the U.S.
But in the field of engineering, at least, there hasn’t been a lot of progress in diversifying the academic pipeline beyond white men.
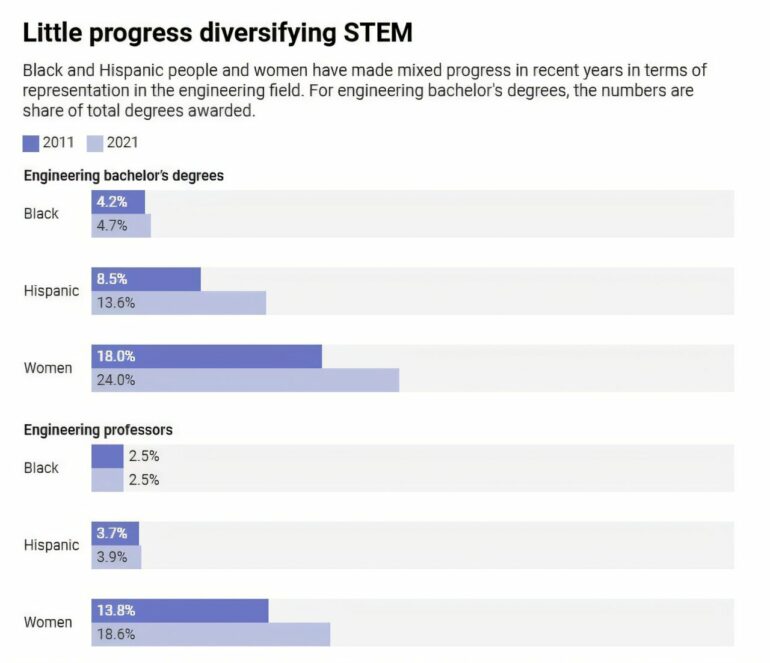
The share of engineering bachelor’s degrees awarded to Black students has barely budged over the past decade. Women and Hispanic students fared better, but their respective percentages are still well below their shares of the population as a whole. The shares of engineering professors who are Black or Hispanic are also little changed and remain in the low single digits.
Many reasons have been cited for this lack of progress, including stereotypes, lack of exposure, limited role models and the recent backlash against so-called woke policies that emphasize diverse hiring policies. But, as a scholar of STEM education accessibility, I believe there’s another culprit: poorly prepared professors. Unlike the other challenges, it happens to be a much easier problem for universities themselves to remedy.
Some progress – but not a lot
A quick look at the numbers shows there hasn’t been much to show for all the efforts to improve diversity of the engineering field.
For example, in 2011, 4.2% of engineering bachelor’s degrees were awarded to African American students. A decade later, 4.7% of degrees went to African American students.
Progress was better for women and Hispanic students, but the numbers are still far from proportional to demographics. In 2011, Hispanic students earned 8.5% of engineering degrees. That rose to 13.6% in 2021 – versus the group’s 20% share of the U.S. population.
Women similarly saw gains over the years, going from 18% to 24%. But 6 percentage points in 10 years doesn’t look as good when you consider that women make up over half of the population.
The situation is worse when you look at the share who become professors. In 2020, 2.5% of engineering professors were African American, the same share as 10 years earlier. The share of Hispanic engineering professors edged up to 3.9% from 3.7%.
Women fared slightly better, rising to 18.6% from 13.8%, but as noted, that’s still a pretty poor result from all those efforts to diversity the academy.
More broadly, there’s a deeper problem in engineering schools. Just 56% of engineering students complete their bachelor’s degree in six years, according to a 2021 report by the American Society for Engineering Education. That compares with 64% for all fields. A National Science Foundation survey from the same year found that only 65% of science and engineering college graduates were working in a field related to their degree.
In other words, roughly a third of engineering students aren’t getting their degrees, and among those who do, around a…