When someone opens the door and enters a hospital room, wearing a stethoscope is a telltale sign that they’re a clinician. This medical device has been around for over 200 years and remains a staple in the clinic despite significant advances in medical diagnostics and technologies.
The stethoscope is a medical instrument used to listen to and amplify the internal sounds produced by the body. Physicians still use the sounds they hear through stethoscopes as initial indicators of heart or lung diseases. For example, a heart murmur or crackling lungs often signify an issue is present. Although there have been significant advances in imaging and monitoring technologies, the stethoscope remains a quick, accessible and cost-effective tool for assessing a patient’s health.
Though stethoscopes remain useful today, audible symptoms of disease often appear only at later stages of illness. At that point, treatments are less likely to work and outcomes are often poor. This is especially the case for heart disease, where changes in heart sounds are not always clearly defined and may be difficult to hear.
We are scientists and engineers who are exploring ways to use heart sounds to detect disease earlier and more accurately. Our research suggests that combining stethoscopes with artificial intelligence could help doctors be less reliant on the human ear to diagnose heart disease, leading to more timely and effective treatment.
History of the stethoscope
The invention of the stethoscope is widely credited to the 19th-century French physician René Theophile Hyacinthe Laënnec. Before the stethoscope, physicians often placed their ear directly on a patient’s chest to listen for abnormalities in breathing and heart sounds.
In 1816, a young girl showing symptoms of heart disease sought consultation with Laënnec. Placing his ear on her chest, however, was considered socially inappropriate. Inspired by children transmitting sounds through a long wooden stick, he instead rolled a sheet of paper to listen to her heart. He was surprised by the sudden clarity of the heart sounds, and the first stethoscope was born.
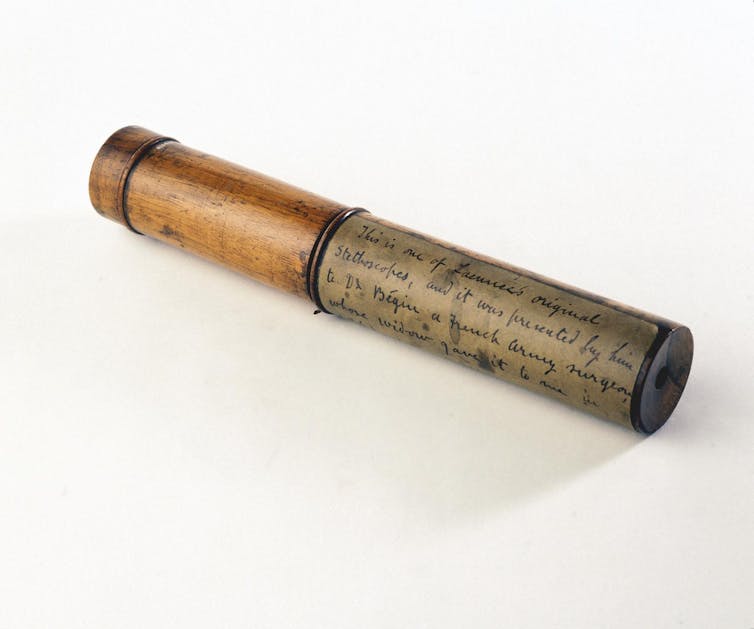

One of René Laënnec’s original wooden stethoscopes.
Science Museum London/Science and Society Picture Library, CC BY-NC-SA
Over the next couple of decades, researchers modified the shape of this early stethoscope to improve its comfort, portability and sound transmission. This includes the addition of a thin, flat membrane called a diaphragm that vibrates and amplifies sound.
The next major breakthrough occurred in the mid-1850s, when Irish physician Arthur Leared and American physician George Philip Cammann developed stethoscopes that could transmit sounds to both ears. These binaural stethoscopes use two flexible tubes connected to separate earpieces, allowing clearer and more balanced sound by reducing outside noise.
These early models are remarkably similar to the stethoscopes medical…