Microsoft and OpenAI have collaborated to build an AI pair-programming system called GitHub Copilot. Copilot, now available in preview as a Visual Studio Code extension, is meant to help programmers write code faster and with less work, Microsoft officials said on June 29.
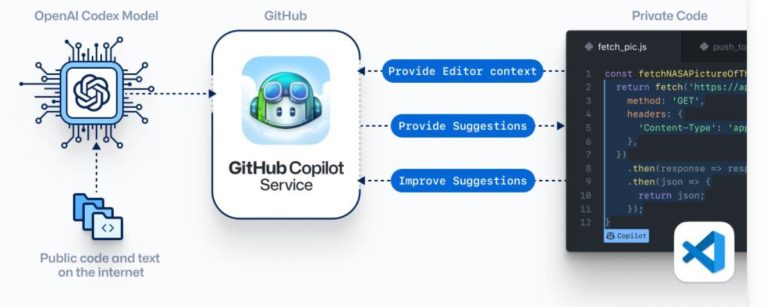
Copilot is powered by OpenAI Codex, a new AI system. Microsoft and OpenAI have been working together for the past few years on various projects; Copilot is their latest collaboration.
“If the technical preview is successful, our plan is to build a commercial version of GitHub Copilot in the future. We want to use the preview to learn how people use GitHub Copilot and what it takes to operate it at scale,” GitHub officials said in a frequently asked questions (FAQ) document published today.
Copilot will work with a variety of frameworks and languages. Microsoft officials said the technical preview works especially well with Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Ruby and Go, but works with many other languages, as well.
Codex was trained on billions of lines of publicly available source code — including code in public repositories on GitHub — and also on natural language, which means it can understand both programming and human languages. The Copilot editor extension sends comments and code to the Copilot service. The service uses OpenAI Codex to synthesize and then suggest both individual lines of code and whole functions, Microsoft officials explained in the FAQ.
Copilot is meant to try to discern intent and generate the best code it can. It doesn’t test the code it suggests, however, and Microsoft cuations that it may suggest old or deprecated uses of libraries and languages.
Copilot is meant to improve with time and use. Microsoft advises developers to divide their code into small functions, use meaningful names for functions parameters and write good docstrings and comments as they go. They also said Copilot “seems to do best when it’s helping you navigate unfamiliar libraries or frameworks.”
Developers are always in charge when using Copilot, officials emphasized, as Copilot is meant to be an adjunct to, not a replacement for, human programmers. Using Copilot, developers can cycle through alternative suggestions, choosing which to accept or reject and manually edit suggested code. Microsoft officials said it will match users’ coding style over time.
Two years ago, Microsoft invested $1 billion in OpenAI, which, in return committed to using Azure and codeveloping with MIcrosoft new Azure AI supercomputing technologies. Earlier this year, Microsoft announced plans to make coding “in plain English” easier by integrating OpenAI’s GPT-3 AI model with Microsoft’s PowerFx low code language.