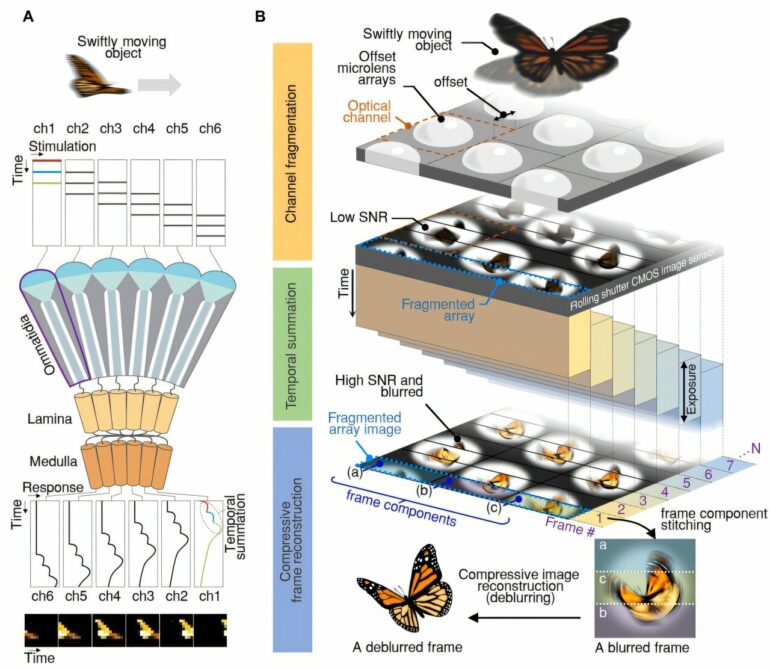
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras. Their work is published in Science Advances.
A research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
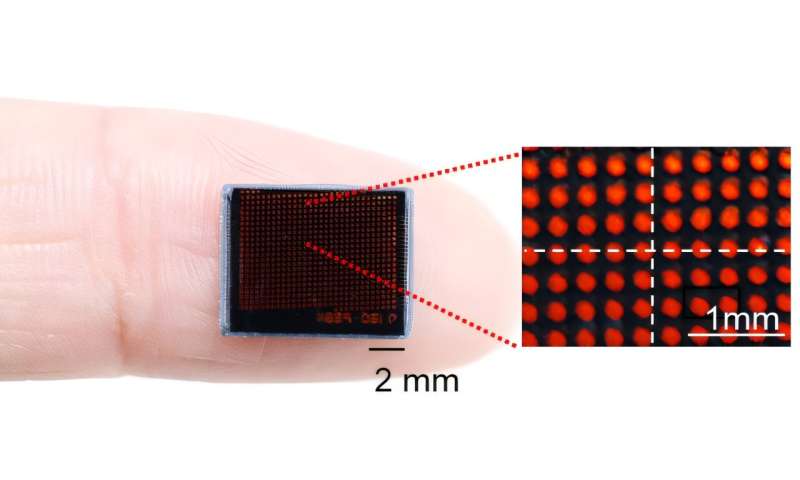
A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. © Science Advances (2025). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
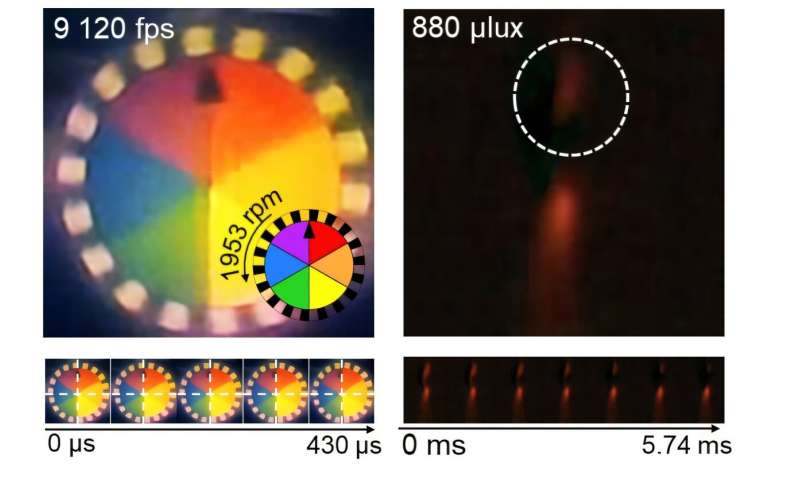
Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. © Science Advances (2025). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
The team also introduced a “channel-splitting” technique to significantly enhance the camera’s speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a “compressed image restoration” algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than 1 millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study’s first author, said, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
More information:
Hyun-Kyung Kim et al, Biologically inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging, Science Advances (2025). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
Provided by
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Citation:
Insect-eye-inspired camera captures 9,120 frames per second (2025, January 16)