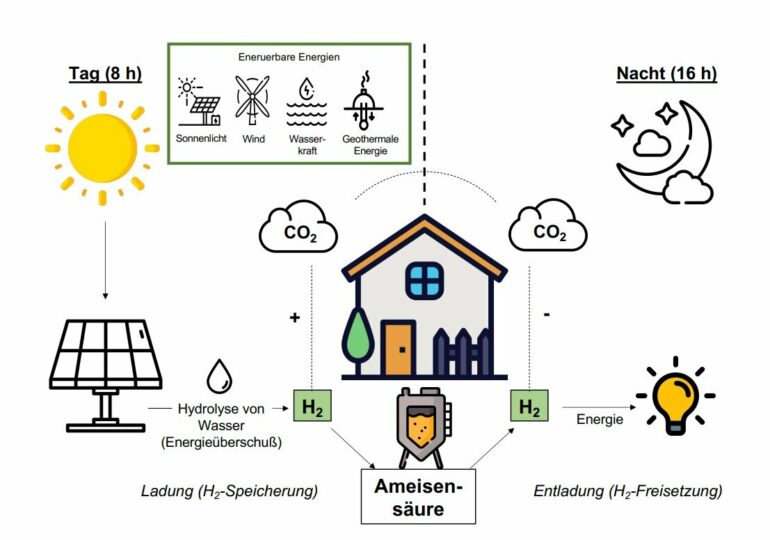
The fight against climate change is making the search for carbon-neutral energy sources increasingly urgent. Green hydrogen, which is produced from water with the help of renewable energies such as wind or solar power, is one of the solutions on which hopes are pinned. However, transporting and storing the highly explosive gas is difficult, and researchers worldwide are looking for chemical and biological solutions.
A team of microbiologists from Goethe University Frankfurt has found an enzyme in bacteria that live in the absence of air and bind hydrogen directly to CO2, producing formic acid. The process is completely reversible—a basic requirement for hydrogen storage. These acetogenic bacteria, which are found, for example, in the deep sea, feed on carbon dioxide, which they metabolize to formic acid with the aid of hydrogen. Normally, however, this formic acid is just an intermediate product of their metabolism and further digested into acetic acid and ethanol. But the team led by Professor Volker Müller, head of the Department of Molecular Microbiology and Bioenergetics, has adapted the bacteria in such a way that makes it possible not only to stop this process at the formic acid stage but also to reverse it. The basic principle has already been patented since 2013.
“The measured rates of CO2 reduction to formic acid and back are the highest ever measured and many times greater than with other biological or chemical catalysts; in addition, and unlike chemical catalysts, the bacteria do not require rare metals or extreme conditions for the reaction, such as high temperatures and high pressures, but instead do the job at 30 °C and normal pressure,” reports Müller. The group now has a new success to report: the development of a biobattery for hydrogen storage with the help of the same bacteria.
For municipal or domestic hydrogen storage, a system is desirable where the bacteria first store hydrogen and then release it again in one and the same bioreactor and as stably as possible over a long period of time. Fabian Schwarz, who wrote his doctoral thesis on this topic at Professor Müller’s laboratory, has succeeded in developing such a bioreactor. He fed the bacteria hydrogen for eight hours and then put them on a hydrogen diet during a 16-hour phase overnight. The bacteria then released all the hydrogen again. It was possible to eliminate the unwanted formation of acetic acid with the help of genetic engineering processes. “The system ran extremely stably for at least two weeks,” explains Fabian Schwarz.
Volker Müller had already studied the properties of these special bacteria in his doctoral thesis—and spent many years conducting fundamental research on them. “I was interested in how these first organisms organized their life processes and how they managed to grow in the absence of air with simple gases such as hydrogen and carbon dioxide,” he explains. As a result of climate change, his research has acquired a new, application-oriented dimension. Surprisingly to many engineers, biology can produce practicable solutions, he says.
“Biological hydrogen storage and release through multiple cycles of bi-directional hydrogenation of CO2 to formic acid in a single process unit” is published in Joule.
More information:
Fabian M. Schwarz et al, Biological hydrogen storage and release through multiple cycles of bi-directional hydrogenation of CO2 to formic acid in a single process unit, Joule (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2022.04.020
Provided by
Goethe University Frankfurt am Main
Citation:
New biobattery for hydrogen storage (2022, May 25)