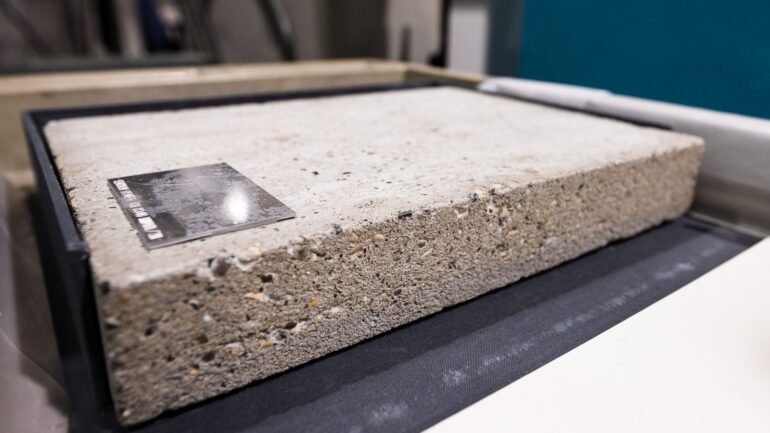
Using Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source, scientists are trying to determine if Wolf Vostell’s piece “Concrete Book” does, in fact, contain a book. The answer may change how this artist’s work is studied and presented.
When is a book not a book?
This seems like a simple question, but in the case of one curious piece of art, researchers have enlisted the resources of one of the world’s leading X-ray facilities at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory to answer it. What they find might end up rewriting a chapter of modern art history, and might shine new light on one of the pioneers of an artistic movement.
The piece in question is called “Betonbuch,” or “Concrete Book,” and is the work of German-born artist Wolf Vostell. He was part of Fluxus, an international community of experimental creators that flourished in the 1960s and 1970s, and was a pioneer of using concrete as a material for art, not just construction. In 1971, Vostell wrote a short book called “Betonierungen,” or “Concretifications,” and as evidence of his commitment to the material, he purportedly encased 100 copies of that book in numbered slabs of concrete.
Six years ago, as part of an exhibit on Vostell and Fluxus organized by art history professor Christine Mehring, the University of Chicago purchased “Concrete Book #83,” and it immediately intrigued Patti Gibbons. As the head of collection management at the UChicago’s Hanna Holborn Gray Special Collections Research Center, Gibbons works at the University’s Joseph Regenstein Library and is involved in curating displays of the institution’s collections.
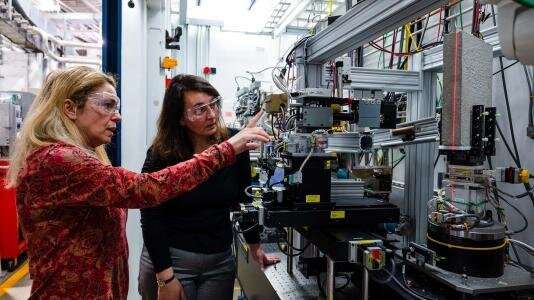
Maria Kokkori, left, of the Art Institute of Chicago and Patti Gibbons of UChicago with the “Concrete Book” at Beamline 6-BM of the Advanced Photon Source. © Jason Creps/Argonne National Laboratory.
“The mystery of what’s supposed to be inside of there intrigued me,” Gibbons said. “I always thought it would be a good idea to look.”
Gibbons teamed up with Maria Kokkori, associate scientist at the Art Institute of Chicago, to finally turn the page on this mystery. Kokkori uses “Concrete Book” in her classroom, teaching materials science as it relates to art. For her, Vostell’s work represents a turning point in the use of concrete to create art, instead of to construct buildings and bridges.
“Concrete is a material you would see in construction, but not in the art world in the ’70s,” Kokkori said. “Construction and art are often considered different fields and disciplines, but Vostell was a pioneer of new technologies to use concrete as an artistic material.”
The pair first tried to peer inside the 20-pound, two-inch thick chunk of concrete using ultrasound and X-ray machines at the UChicago, but were only able to detect metal wires inside, not the book. The wires may hold the book between them, or may be there to provide reinforcement of the concrete.
They knew they’d need a more powerful X-ray beam to truly crack the case, so they turned to the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne. The APS generates some of the brightest X-ray light in the world, at energies that allow it to penetrate thicker objects. At beamline 6-BM, they used a technique called X-ray diffraction to search for signs of paper and vellum inside the concrete.
“First we scanned a different copy of the book itself, the book that is meant to be inside the concrete,” said Argonne beamline scientist John Okasinski. “This gave us a signature to look for in the object itself. Although the sample is different, the techniques we are using are the same we would use for materials science experiments.”
Kokkori said the results of the X-ray scans will be published in a journal. The pair presented details of the experiment as a work in progress at a recent Art Libraries Society of North America conference. Whatever the answers may be, Kokkori said, they would illuminate questions both artistic and scientific.
“How do we define a book?” she asked. “If Argonne scientists do find a booklet there, how do we contextualize this information? If they don’t, then the answer is equally important, because it provides more context and informs history. It will inform how we share this piece with the public.”
“We have the artist’s testimonial, and no reason to doubt there is something there, but we still need scientific proof,” she said. “It’s an important message to students to question the reliability of sources. It’s a great intellectual exercise to question, and then to question the questions.”
Provided by
Argonne National Laboratory
Citation:
Researchers look for concrete answers to decades-old art mystery (2022, September 14)



