Many human activities release pollutants into the air, water and soil. These harmful chemicals threaten the health of both people and the ecosystem. According to the World Health Organization, air pollution causes an estimated 4.2 million deaths annually.
Scientists are looking into solutions, and one potential avenue is a class of materials called photocatalysts. When triggered by light, these materials undergo chemical reactions that initial studies have shown can break down common toxic pollutants.
I am a materials science and engineering researcher at the University of Tennessee. With the help of robots and artificial intelligence, my colleagues and I are making and testing new photocatalysts with the goal of mitigating air pollution.
Breaking down pollutants
The photocatalysts work by generating charged carriers in the presence of light. These charged carriers are tiny particles that can move around and cause chemical reactions. When they come into contact with water and oxygen in the environment, they produce substances called reactive oxygen species. These highly active reactive oxygen species can bond to parts of the pollutants and then either decompose the pollutants or turn them into harmless – or even useful – products.
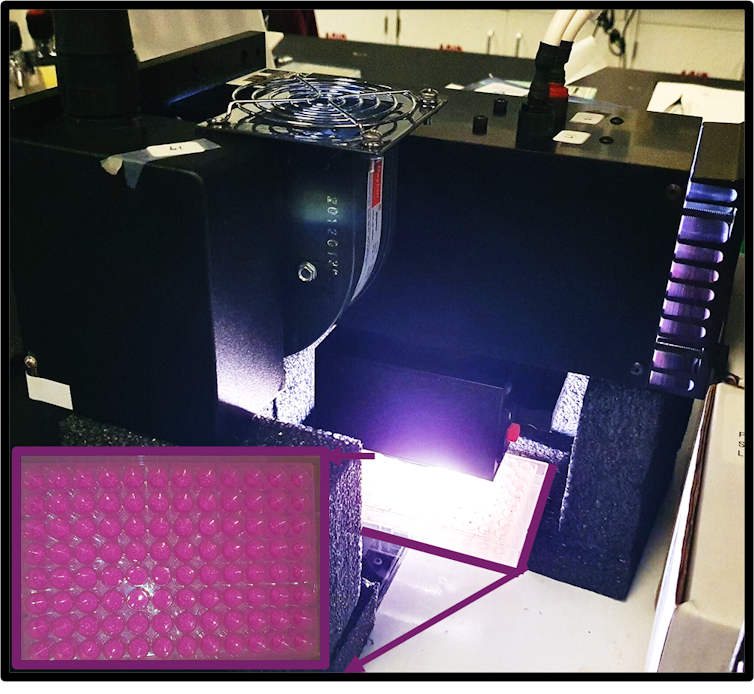
To facilitate the photocatalytic reaction, researchers in the Ahmadi lab put plates of perovskite nanocrystals and pollutants under bright light to see whether the reaction breaks down the pollutants.
Astita Dubey
But some materials used in the photocatalytic process have limitations. For example, they can’t start the reaction unless the light has enough energy – infrared rays with lower energy light, or visible light, won’t trigger the reaction.
Another problem is that the charged particles involved in the reaction can recombine too quickly, which means they join back together before finishing the job. In these cases, the pollutants either do not decompose completely or the process takes a long time to accomplish.
Additionally, the surface of these photocatalysts can sometimes change during or after the photocatalytic reaction, which affects how they work and how efficient they are.
To overcome these limitations, scientists on my team are trying to develop new photocatalytic materials that work efficiently to break down pollutants. We also focus on making sure these materials are nontoxic so that our pollution-cleaning materials aren’t causing further pollution.
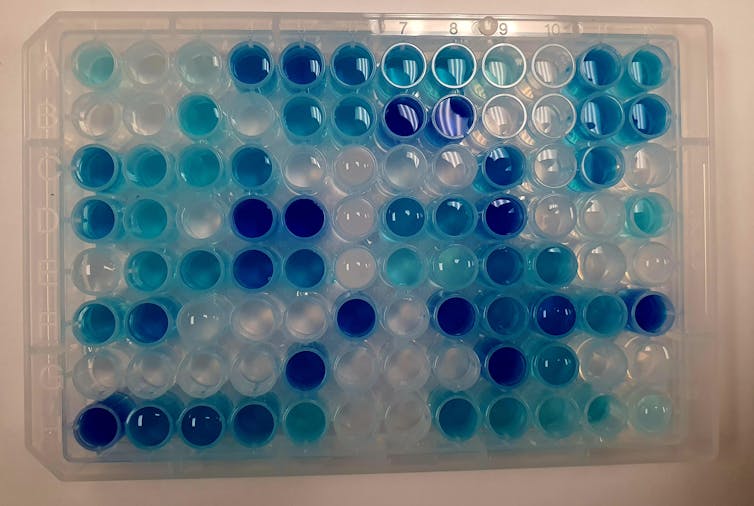
This plate from the Ahmadi lab is used while testing how perovskite nanocrystals and light break down pollutants, like the blue dye shown. The light blue color indicates partial degradation, while transparent water signifies complete degradation.
Astita Dubey
Teeny tiny crystals
Scientists on my team use automated experimentation and artificial intelligence to figure out which photocatalytic materials could be the best candidates to quickly break…