James Diaz, MD, MHA, MPH & TM, Dr. PH, Professor and Head of Environmental Health Sciences at LSU Health New Orleans School of Public Health, has proposed a possible explanation for the severe lung complications being seen in some people diagnosed with COVID-19. The manuscript was published by Oxford University Press online in the Journal of Travel Medicine, available here.
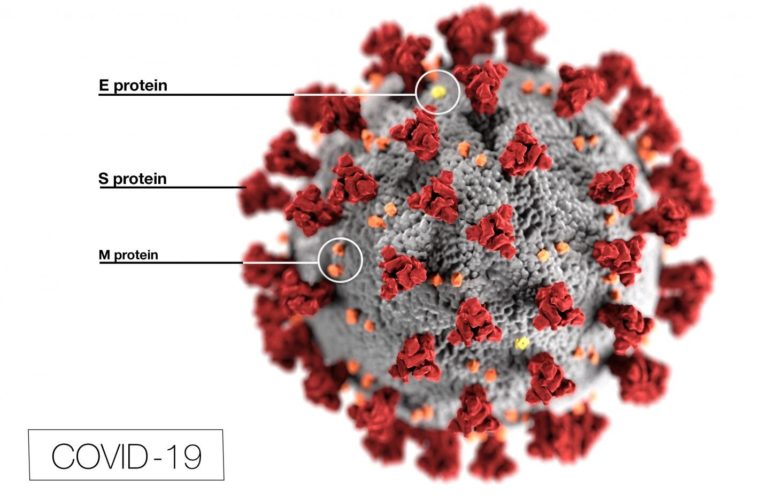
The SARS beta coronaviruses, SARS-CoV, which caused the SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) outbreak in 2003 and the new SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, bind to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors in the lower respiratory tracts of infected patients to gain entry into the lungs. Viral pneumonia and potentially fatal respiratory failure may result in susceptible persons after 10-14 days.
“Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are highly recommended medications for patients with cardiovascular diseases including heart attacks, high blood pressure, diabetes and chronic kidney disease to name a few,” notes Dr. Diaz. “Many of those who develop these diseases are older adults. They are prescribed these medications and take them every day.”
Research in experimental models has shown an increase in the number of ACE2 receptors in the cardiopulmonary circulation after intravenous infusions of ACE inhibitors.
“Since patients treated with ACEIs and ARBS will have increased numbers of ACE2 receptors in their lungs for coronavirus S proteins to bind to, they may be at increased risk of…