In a new study published in PLOS Computational Biology, an international research team from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology, Cardiff University, and Google has reexamined Robert Axelrod’s groundbreaking work.
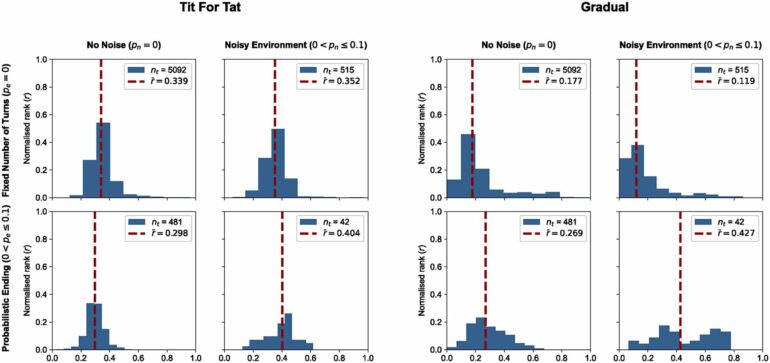
By simulating more than 195 strategies in thousands of tournaments, the study revealed that success in the Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma depends heavily on adaptation to diverse environments. Strategies that excelled in Axelrod’s controlled scenarios often failed when faced with a wider variety of opponents. Winning strategies are not only nice and reciprocal but also clever, slightly envious, and adaptable to the surrounding conditions.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma, a classic game in game theory, presents players with the choice to cooperate or defect. Mutual cooperation results in moderate rewards for both players, while unilateral defection yields a high reward for the defector and a significant loss for the cooperator. If both players defect, they receive less than they would through mutual cooperation. This tension between individual and collective benefit has made the game a model for decision-making in economics, politics, and biology.
In 1980, Robert Axelrod organized one of the most influential Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma tournaments. He invited scientists worldwide to submit strategies in computer code. The winning strategy, “Tit for Tat,” followed four key principles: avoid envy, be nice, reciprocate, and keep it simple.
While these principles explained the success of “Tit for Tat” in Axelrod’s tournament, the study had notable limitations. Only 14 strategies were tested, and preliminary results were shared with participants, potentially influencing submissions. Moreover, the controlled nature of the tournaments, with limited variety and rigid rules, did not reflect the complexity of real-world scenarios.
The recent study tested 195 strategies from published works in thousands of tournaments under diverse conditions. The results showed that strategies considered dominant in controlled environments often struggled against more varied opponents. Instead of identifying a single winning strategy, the team uncovered shared traits of successful approaches: They are slightly envious, smart, reciprocal, adaptable, and willing to align cooperation levels with their environment.
The analyses relied on “Axelrod-Python,” an open-source tool that catalogs strategies and facilitates large-scale simulations. This tool promotes open science, enabling researchers worldwide to explore game theory in more realistic scenarios. The study underscores the need to revisit Axelrod’s principles to better account for the dynamics of more complex environments.
More information:
Nikoleta E. Glynatsi et al, Properties of winning Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma strategies, PLOS Computational Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012644
Provided by
Max Planck Society
Citation:
Reexamining the Prisoner’s Dilemma: Study finds diversity and context play a larger role than thought (2025, January 7)